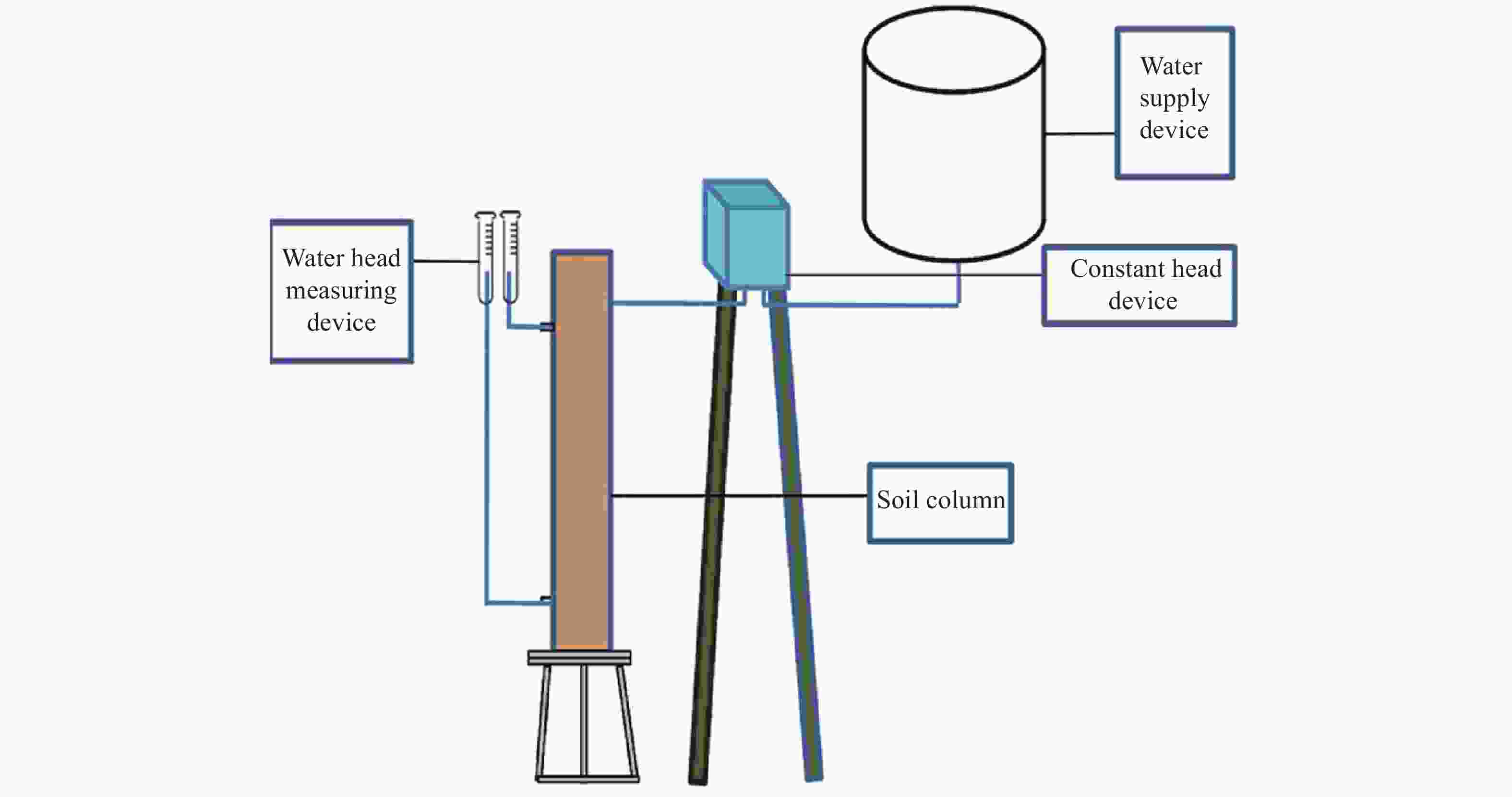
Using pore-solid fractal dimension to estimate residual LNAPLs saturation in sandy aquifers: A column experiment
-
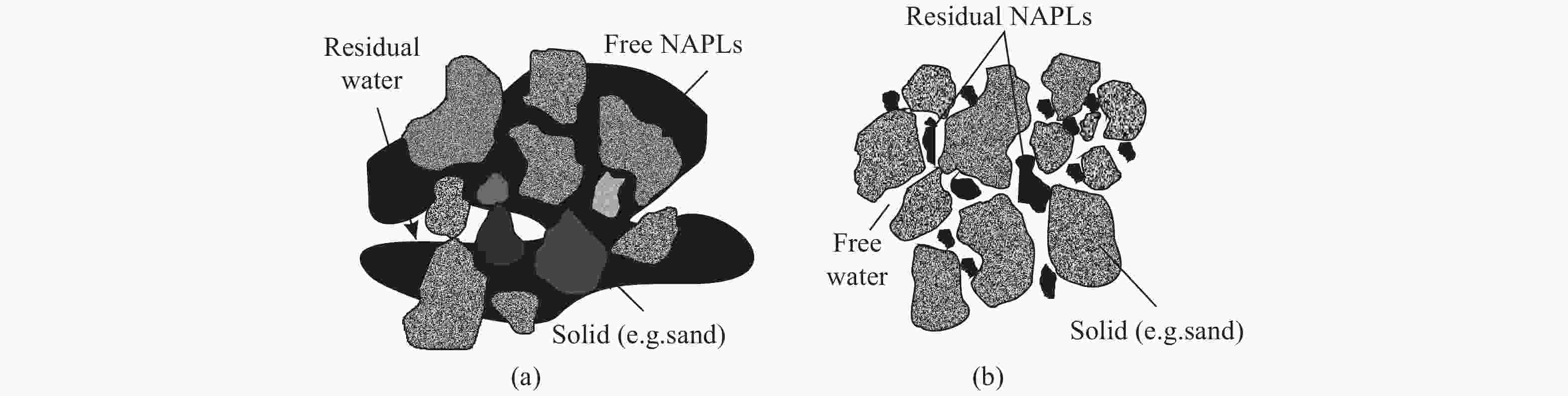
Abstract: : The“tailing” effect caused by residual non-aqueous phase liquids (NAPLs) in porous aquifers is one of the frontiers in pollution hydrogeology research. Based on the current knowledge that the residual NAPLs is mainly controlled by the pore structure of soil, this study established a method for evaluating the residual saturation of NAPLs by investigating the fractal dimension of porous media. In this study, the soil column experiments of residual light NAPLs (LNAPLs) in sandy aquifer with different ratios of sands and soil were carried out, and the correlation between the fractal dimension of the medium, the residual of LNAPLs and the soil structure parameters are statistically analyzed, and its formation mechanism and main control factors are discussed. The results show that: Under our experimental condition: (1) the fractal dimension of the medium has a positive correlation with the residual saturation of NAPLs generally, and the optimal fitting function can be described by a quadratic model:
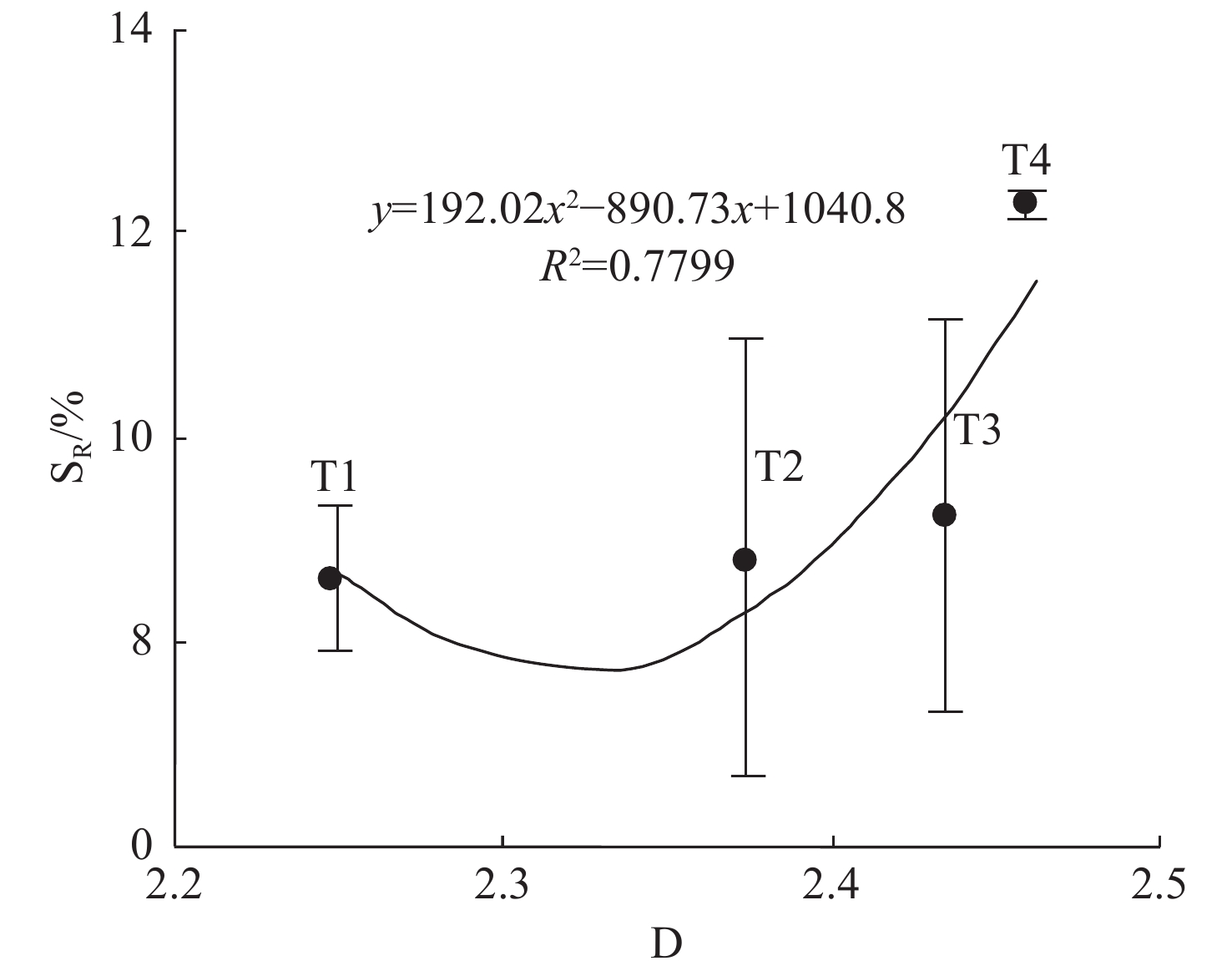
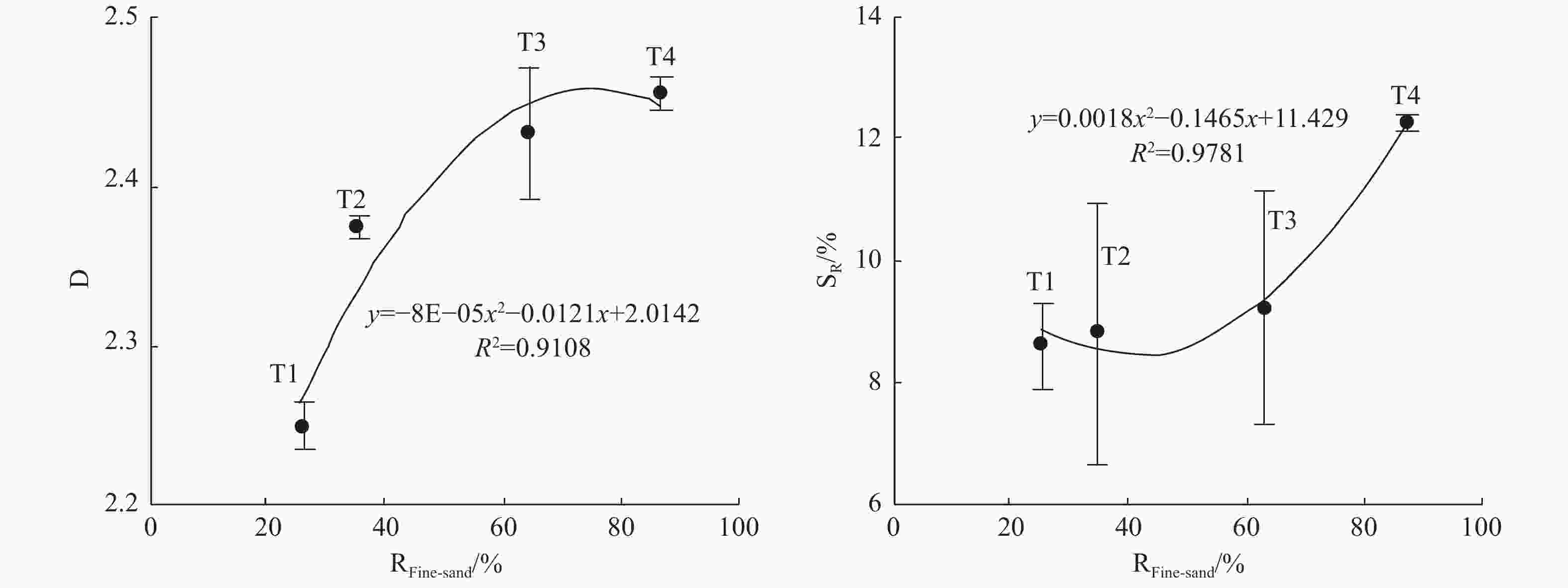
${S_R} = {\text{192}}{\text{.02}}{D^2} - 890.73D + {\text{1 040}}{\text{.8}}$ ; (2) the dominant formation mechanism is: Smaller pores in the medium is related to larger fractal dimension, which leads to higher residual saturation of NAPLs; stronger heterogeneity of the medium is related to larger fractal dimension, which also leads to higher residual saturation of NAPLs; (3) the micro capillary pores characterized by fine sand are the main controlling factors of the formation mechanism. It is concluded that both the theory and the method of using fractal dimension of the medium to evaluate the residual saturation of NAPLs are feasible. This study provides a new perspective for the research of “tailing” effect of NAPLs in porous media aquifer.-
Key words:
- Residual saturation /
- NAPLs /
- Pore structure /
- Fractal /
- Tailing effect
-
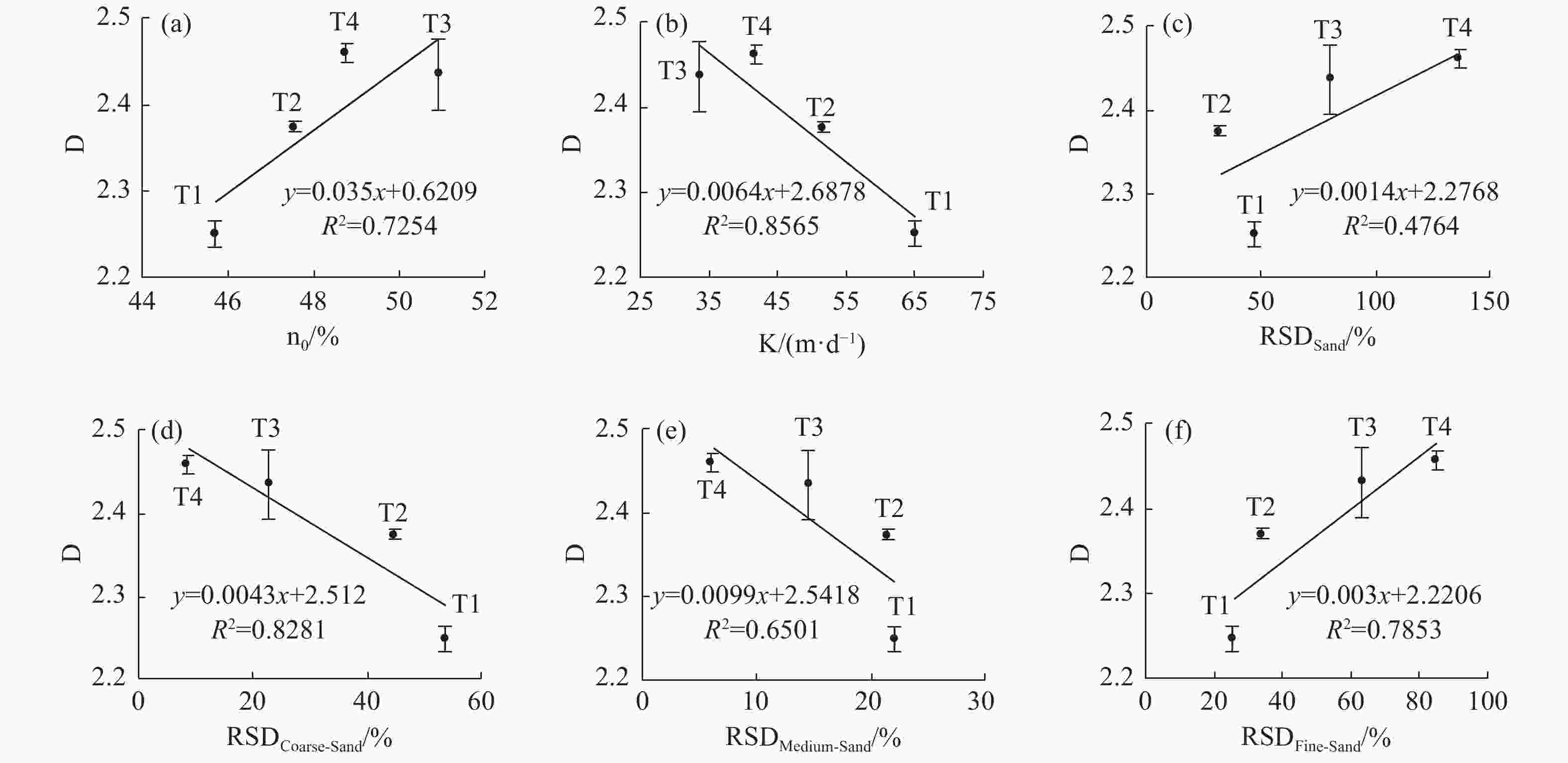
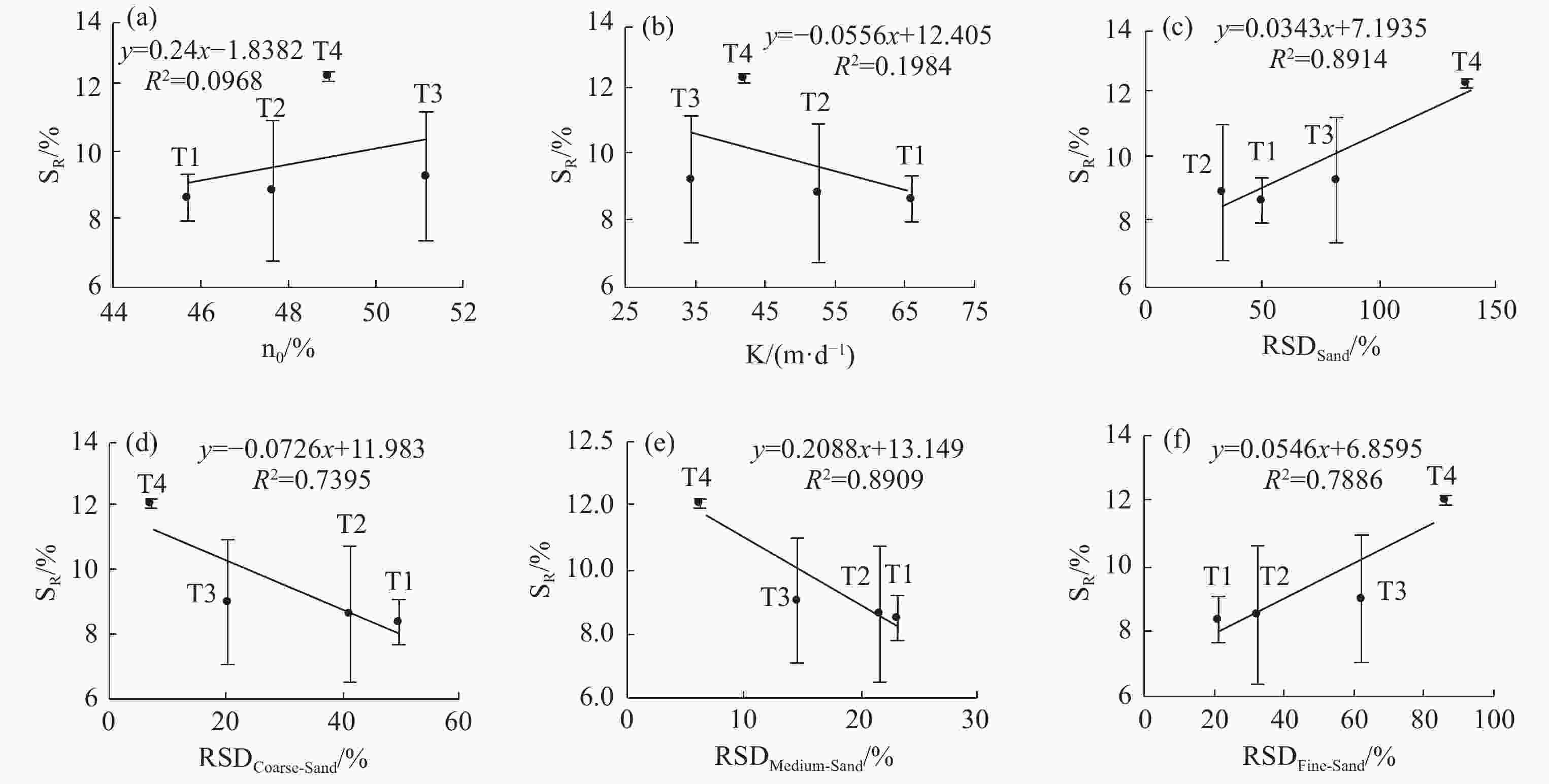
Figure 6. Relationship between pore structure parameters and fractal dimension
NOTES:(a) porosity - fractal dimension, (b) permeability coefficient - fractal dimension, (c) particle size variation coefficient - fractal dimension, (d) coarse grain content - fractal dimension, (e) medium sand content - Fractal dimension, (f) fine sand content - fractal dimension
Figure 7. Relationship between medium structure parameters and residual saturation of LNAPLs
NOTES: (a) porosity - residual saturation, (b) permeability coefficient - residual saturation, (c) particle size variation coefficient - residual saturation, (d) coarse grain content - residual saturation, (e) medium sand content - residual saturation, (f) fine sand content - residual saturation.
Table 4. Key results
Treatment 1-1 1-2 2-1 2-2 3-1 3-2 4-1 4-2 $ D $ Line 1 2.44 2.41 2.59 2.55 2.73 2.69 2.71 2.73 Line 2 2.08 2.07 2.17 2.19 2.19 2.12 2.18 2.20 Mean 2.26 2.24 2.38 2.37 2.46 2.41 2.45 2.47 $ {S_R} $ (%)
Residual saturation8.14 9.12 10.33 7.34 10.58 7.90 12.34 12.14 $ {n_0} $ (%)
Porosity46.45 44.91 47.90 47.18 51.09 50.70 49.06 48.46 K(m/d)
Permeability coefficient79.16 50.85 41.91 61.36 27.35 39.82 37.04 46.51 $ {R_{Coarse - sand}} $
Coarse sand (%)51.52 43.05 21.44 7.73 $ {R_{Medium - sand}} $
Medium sand (%)22.52 21.91 14.76 6.19 $ {R_{Fine - sand}} $
Fine sand (%)25.96 35.04 63.8 86.09 $ RS{D_{sand}} $
RSD of sand content (%)47.53 32.02 79.79 137.06 NOTE:$ RS{D}_{sand}=\dfrac{SD({R}_{Coarse-sand},{R}_{Medium-sand},{R}_{Fine-sand})}{Average({R}_{Coarse-sand},{R}_{Medium-sand},{R}_{Fine-sand})}\times 100 $. Table 1. Particle ratio scheme of soil column medium
Treatment T1 T2 T3 T4 NO. 1-1 1-2 2-1 2-2 3-1 3-2 4-1 4-2 Table 2. the observed results of the three permeability coefficients before the end of the residual LNAPLs formation experiment
1-1 1-2 2-1 2-2 3-1 3-2 4-1 4-2 Third from last 80.08 54.05 39.8 53.72 27.75 51.68 37.88 40.58 Second from last 79.83 41.84 40.37 66.06 27.3 31.2 36.23 45.89 Last 77.58 56.65 45.55 64.3 26.99 36.57 37.01 53.05 RSD% 6 16 8 11 1 27 2 13 Table 3. Volume of samples and particle size
NO. Volume (cm3) Accumulated in particle size $ \dfrac{W}{{{W_0}}} $(%) $ {V_{soil}} $ $ {V_{sand}} $ $ {V_{oil}} $ 0.03-0.3 mm 0.3-0.4 mm 0.4-0.5 mm 0.5-0.65 mm 0.65-0.8 mm 0.8-1 mm 1-2 mm 1-1 3377.20 1808.39 127.71 8.58 7.23 6.38 6.53 4.81 3.27 63.25 1-2 3354.15 1847.72 137.35 7.97 6.88 6.09 6.40 4.74 3.46 64.46 2-1 3384.92 1763.58 167.47 12.71 9.48 7.74 7.38 4.75 2.81 55.15 2-2 3338.76 1763.58 115.66 13.05 9.41 7.76 7.56 5.09 3.27 53.87 3-1 3365.69 1646.01 181.93 22.63 15.98 12.57 11.39 6.76 3.33 27.35 3-2 3338.76 1646.01 133.73 19.82 15.68 12.81 12.01 7.40 3.90 28.39 4-1 3323.38 1692.96 201.20 24.24 19.97 16.46 15.37 9.22 4.40 10.35 4-2 3338.76 1720.87 196.39 24.86 19.93 16.39 15.24 9.00 4.02 10.56 Table 5. Parameter relationship statistics and physical significance
Structural parameters Fractal dimension Residual saturation Significance Coarse sand content Negative correlation Negative correlation The smaller the pores, the larger the fractal dimension and the larger the residual saturation Medium sand content Negative correlation Negative correlation The smaller the pores, the larger the fractal dimension and the larger the residual saturation Fine sand content Positive correlation Positive correlation The smaller the pores, the larger the fractal dimension and the larger the residual saturation Coefficient of particle size variation Positive correlation Positive correlation The stronger the heterogeneity, the larger the fractal dimension and the larger the residual saturation. Porosity Positive correlation / The more pores, the larger the fractal dimension, but the change of residual saturation is not obvious Permeability
coefficientNegative correlation / The worse the pore connectivity is, the larger the fractal dimension is, but the residual saturation does not change significantly NOTE: / means no relationship -
Celia MA, Reeves PC, Ferrand LA. 1995. Recent advances in pore scale models for multiphase flow in porous media. Reviews of Geophysics, 33(S2): 1049-1057. doi: 10.1029/95RG00248 Cheng Y, Zhu J. 2021. Significance of mass–concentration relation on the contaminant source depletion in the nonaqueous phase liquid (NAPL) contaminated zone. Transport in Porous Media, 137(2): 399-416. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1007/s11242-021-01567-5 Cheng Z, Wu JC, Xu HX, et al. 2014. Migration of DNAPL under the action of lens and surfactant. China Environmental Science, 34(11): 2888-2896. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2014.11.028 Costa A. 2006. Permeability‐porosity relationship: A reexamination of the Kozeny‐Carman equation based on a fractal pore‐space geometry assumption. Geophysical research letters, 33(2): L02318. doi: 10.1029/2005GL025134 Ezeh CG. 2019. Novel ideas for enhanced oil recovery and oil spill remediation in porous media. Tulane University School of Science and Engineering. Feng XD, Zhang Y, Ma YF, et al. 2019. Research status of NAPLs seepage characteristics and models in porous media. Journal of Shandong University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 33(04): 15-18+23. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13367/j.cnki.sdgc.2019.04.003 Forsyth PA, Shao BY. 1991. Numerical simulation of gas venting for NAPL site remediation. Advances in Water Resources, 14(6): 354-367. doi: 10.1016/0309-1708(91)90022-G Fetter CW, Boving TB, Kreamer DK. 1999. Contaminant hydrogeology. Upper Saddle River: Prentice hall: 178-218. Gao F, Liu F, Chen H H. 2008. Research progress on remediation of trichloroethylene-contaminated soil and groundwater pollution source areas. Advances in Earth Science, 23(08): 39-47. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2008.08.005 Guo WM, Li ZP, Jia GL, et al. 2014. Quantitative interpretation of residual oil microdistribution and study on pore microstructure changes. Science Technology and Engineering(31): 32-36. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2014.31.006 Han H, Ding Z, Dong C, et al. 2018. Fractal characteristics of bulk-mudrock, washed, and kerogen samples of Chang 7 member mudrocks from the Ordos Basin, China. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 170: 592-606. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.07.004 Hayden N, Diebold J, Farrell C, et al. 2006. Characterization and removal of DNAPL from sand and clay layered media. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 86(1/2): 53-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2006.02.008 Hou ZY, Wang Y, Lu WX. 2019. An alternative model for multiphase flow simulation for groundwater DNAPLs pollution remediation. China Environmental Science, 39(7): 2913-2920. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.07.027 Hunt JR, Sitar N, Udell KS. 1988. Nonaqueous phase liquid transport and cleanup: 1. Analysis of mechanisms. Water Resources Research, 24(8): 1247-1258. doi: 10.1029/WR024i008p01247 Jia FS, Shen PP, Li KW. Fractal characteristics and application of sandstone pore structure. Fault Block Oil and Gas Field, 1995, 02(1): 16-21. (in Chinese). Kacem M, Esrael D, Boeije CS, et al. 2019. Multiphase flow model for NAPL infiltration in both the unsaturated and saturated zones. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 145(11): 04019072. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0001586 Karaoglu AG, Copty NK, Akyol NH, et al. 2019. Experiments and sensitivity coefficients analysis for multiphase flow model calibration of enhanced DNAPL dissolution. Journal of contaminant hydrology, 225: 103515. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2019.103515 Kemblowski MW, Wen JC. 1993. Contaminant spreading in stratified soils with fractal permeability distribution. Water resources research, 29(2): 419-425. doi: 10.1029/92WR01861 Khasi S, Ramezanzadeh M, Ghazanfari MH. 2020. Experimentally based pore network modeling of NAPL dissolution process in heterogeneous porous media. Journal of contaminant hydrology, 228: 103565. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2019.103565 Le YX, Wang CJ. 2004. Using fractal conditional simulation and streamline model to predict the distribution of remaining oil and gas saturation. Natural Gas Geoscience, 15(1): 42-46. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2004.01.008 Lei G, Mo S, Dong Z, et al. 2018. Theoretical and experimental study on stress-dependency of oil–water relative permeability in fractal porous media. Fractals, 26(02): 1840010. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1142/S0218348X18400108 Li HY, Du XM, Yang B, et al. 2013. Capillary fingering morphology and fractal characterization of NAPLs fluids in porous media. Environmental Science (10): 334-341. (in Chinese) Li ZF, He SL, Yang WX, et al. 2006. Microphysical simulation of water flooding experiment and research on fractal characteristics of residual oil distribution. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Natural Science Edition), (03): 75-79, 84. (in Chinese). Liu HY, Tian ZY, Xu ZY. 2017. Quantitative evaluation of pore structure of carbonate reservoirs based on fractal characteristics. Lithologic Reservoirs, (5): 97-105. (in Chinese). Mackay D, Shiu WY, Maijanen A, et al. 1991. Dissolution of non-aqueous phase liquids in groundwater. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 8(1): 23-42. doi: 10.1016/0169-7722(91)90007-N Mackay DM, Cherry JA. 1989. Groundwater contamination: pump-and-treat remediation. Environmental Science & Technology, 23(6): 630-636. doi: 10.1021/es00064a001 Mateas DJ, Tick GR, Carroll KC. 2017. In situ stabilization of NAPL contaminant source-zones as a remediation technique to reduce mass discharge and flux to groundwater. Journal of contaminant hydrology, 204: 40-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2017.07.007 Mukhopadhyay S, Cushman JH. 1998. Diffusive transport of volatile pollutants in nonaqueous-phase liquid contaminated soil: A fractal model. Transport in porous media, 30(2): 125-154. doi: 10.1023/A:1006554303400 Neuman SP. 1995. On advective transport in fractal permeability and velocity fields. Water Resources Research, 31(6): 1455-1460. doi: 10.1029/95WR00426 Patmonoaji A, Muharrik M, Hu Y, et al. 2020. Three-dimensional fingering structures in immiscible flow at the crossover from viscous to capillary fingering. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 122: 103147. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2019.103147 Ramezanzadeh M, Khasi S, Fatemi M, et al. 2020. Remediation of trapped DNAPL enhanced by SDS surfactant and silica nanoparticles in heterogeneous porous media: Experimental data and empirical models. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(3): 2658-2669. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-07194-4 Rane K S, Goual L, Zhang B. 2020. Graphene wuantum dots for the mobilization and solubilization of nonaqueous phase liquids in natural porous media. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 3(11): 10691-10701. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.0c01937 Saripalli KP, Rao PSC, Annable MD. 1998. Determination of specific NAPL-water interfacial areas of residual NAPLs in porous media using the interfacial tracers technique. Journal of contaminant hydrology, 30(3-4): 375-391. doi: 10.1016/S0169-7722(97)00052-1 Soto MAA, Lenhard R, Chang HK, et al. 2019. Determination of specific LNAPL volumes in soils having a multimodal pore-size distribution. Journal of environmental management, 237: 576-584. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.02.077 Wang X, Lanning LM, Ford RM. 2016. Enhanced retention of chemotactic bacteria in a pore network with residual NAPL contamination. Environmental science & technology, 50(1): 165-172. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b03872 White MD, Oostrom M, Lenhard RJ. 2004. A practical model for mobile, residual, and entrapped NAPL in water‐wet porous media. Groundwater, 42(5): 734-746. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2004.tb02727.x Wiedemeier, Todd H. 1999. Natural attenuation of fuels and chlorinated solvents in the subsurface. New York: John Wiley. Yang K, Xu SY. 2009. Research on microscopic residual oil experimental method. Fault block oil and gas fields, 16(4). (in Chinese) Doi: CNKI: SUN: DKYT.0.2009-04-026. Yu BM. 2003. Research progress on fractal analysis of transport properties in porous media. Advances in Mechanics, 33(3): 333-346. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0992.2003.03.005 Zhang GH, Ren XJ. 2011. Fractal characteristics of pore structure in low-permeability reservoirs and its influence on water flooding efficiency. Petroleum Geology and Oilfield Development in Daqing, 30(2): 94-99. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1000-3754.2011.02.019 Zhang FC, Kang SZ. 2007. Research progress on the migration of non-aqueous fluids in porous media. Journal of Soil Sciences(04): 170-177. (in Chinese) Zhang XG, Zhang T, Lin CY. 2013. Pore structure evaluation of low permeability reservoirs based on pore fractal characteristics. Lithologic Reservoirs, 25(6): 40-45. (in Chinese) Zhao YS, Han HH, Chi ZF, et al. 2018. Study on the effect of permeability difference on the migration of pollutants in low-permeability lenses. China Environmental Science, 38(12): 4559-4565. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.12.021 -

 E-mail alert
E-mail alert Rss
Rss



 下载:
下载: