Research on the characteristics and influencing factors of terrestrial heat flow in Guizhou Province
-
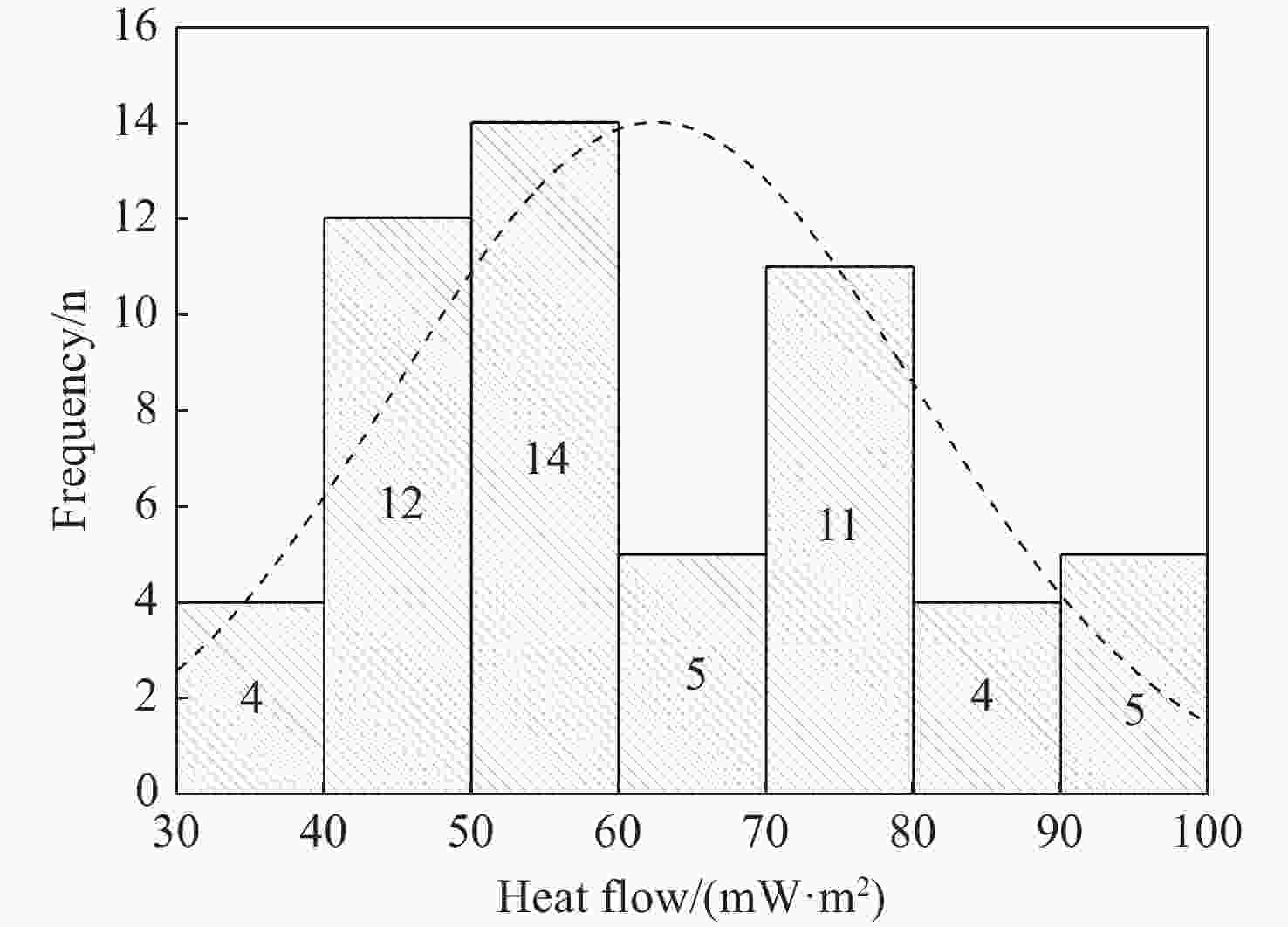
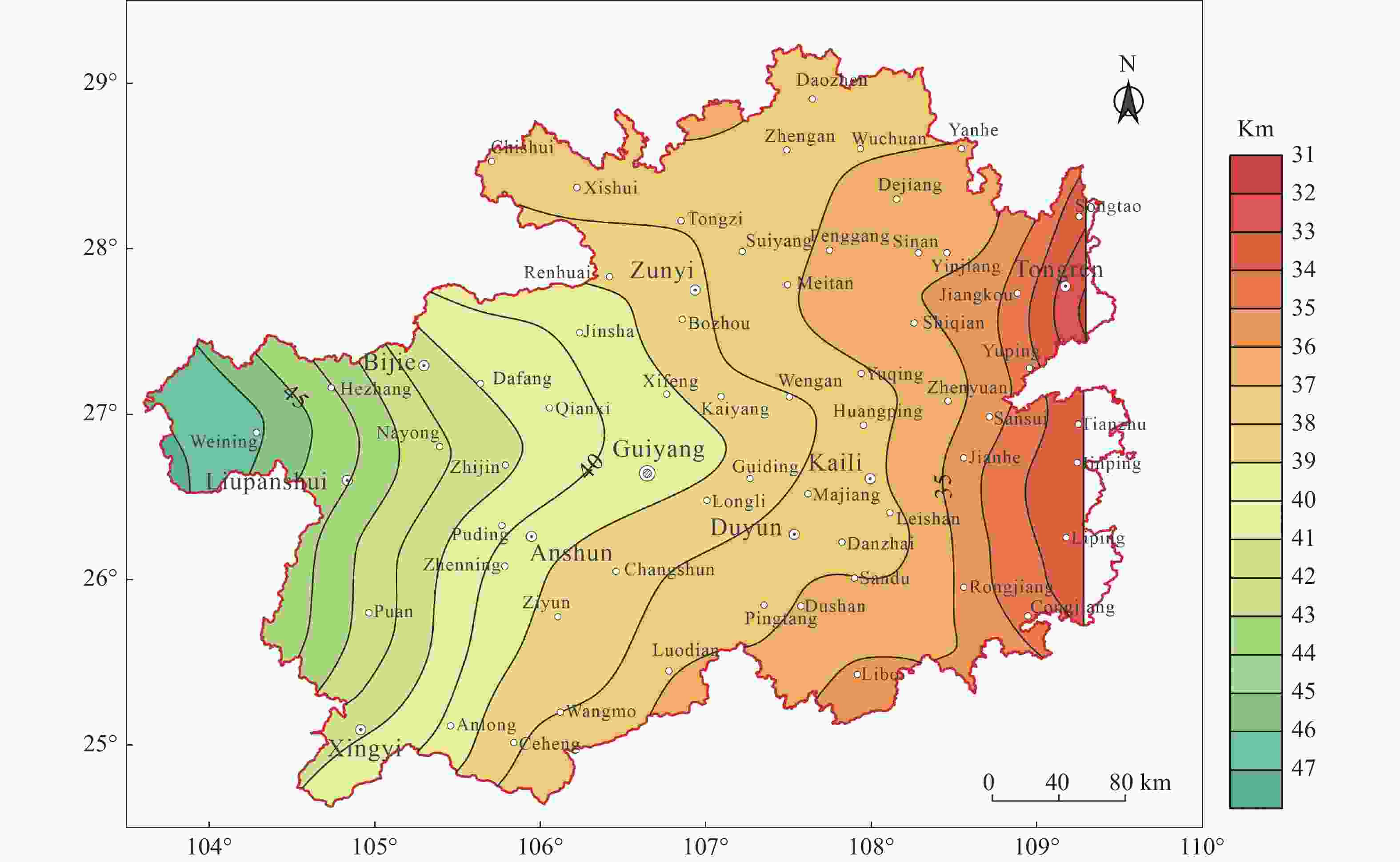
Abstract: Terrestrial heat flow is an important physical parameter in the study of heat transfer and thermal structure of the earth and it has great significance in the genesis and development and utilization potential of regional geothermal resources. Although several breakthroughs in geothermal exploration have been made in Guizhou Province. The terrestrial heat flow in this area has not been properly measured, restricting the development of geothermal resources in the province. For this reason, the terrestrial heat flow in Guizhou was measured in this study, during which the characteristics of heat flow were determined using borehole thermometry, geothermal monitoring and thermal property testing. Moreover, the influencing factors of the terrestrial heat flow were analyzed. The results show that the thermal conductivity of rocks ranges from 2.0 W/(m·K) to 5.0 W/(m·K), with an average of 3.399 W/(m·K); the heat flow varies from 30.27 mW/m2 to 157.55 mW/m2, with an average of 65.26 ± 20.93 mW/m2, which is slightly higher than that of the average heat flow in entire land area in China. The heat flow in Guizhou generally follows a dumbbell-shaped distribution, with high values present in the east and west and low values occurring in the north and south. The terrestrial heat flow is related to the burial depths of the Moho and Curie surface. The basaltic eruptions in the Emeishan led to a thinner lithosphere, thicker crust and lateral emplacement, which dominated the basic pattern of heat flow distribution in Guizhou. In addition, the dichotomous structure of regional active faults and concealed deep faults jointly control the heat transfer channels and thus influence the terrestrial heat flow.
-
Key words:
- Thermal conductivity /
- Terrestrial heat flow /
- Moho /
- Curie surface /
- Emeishan basaltic
-
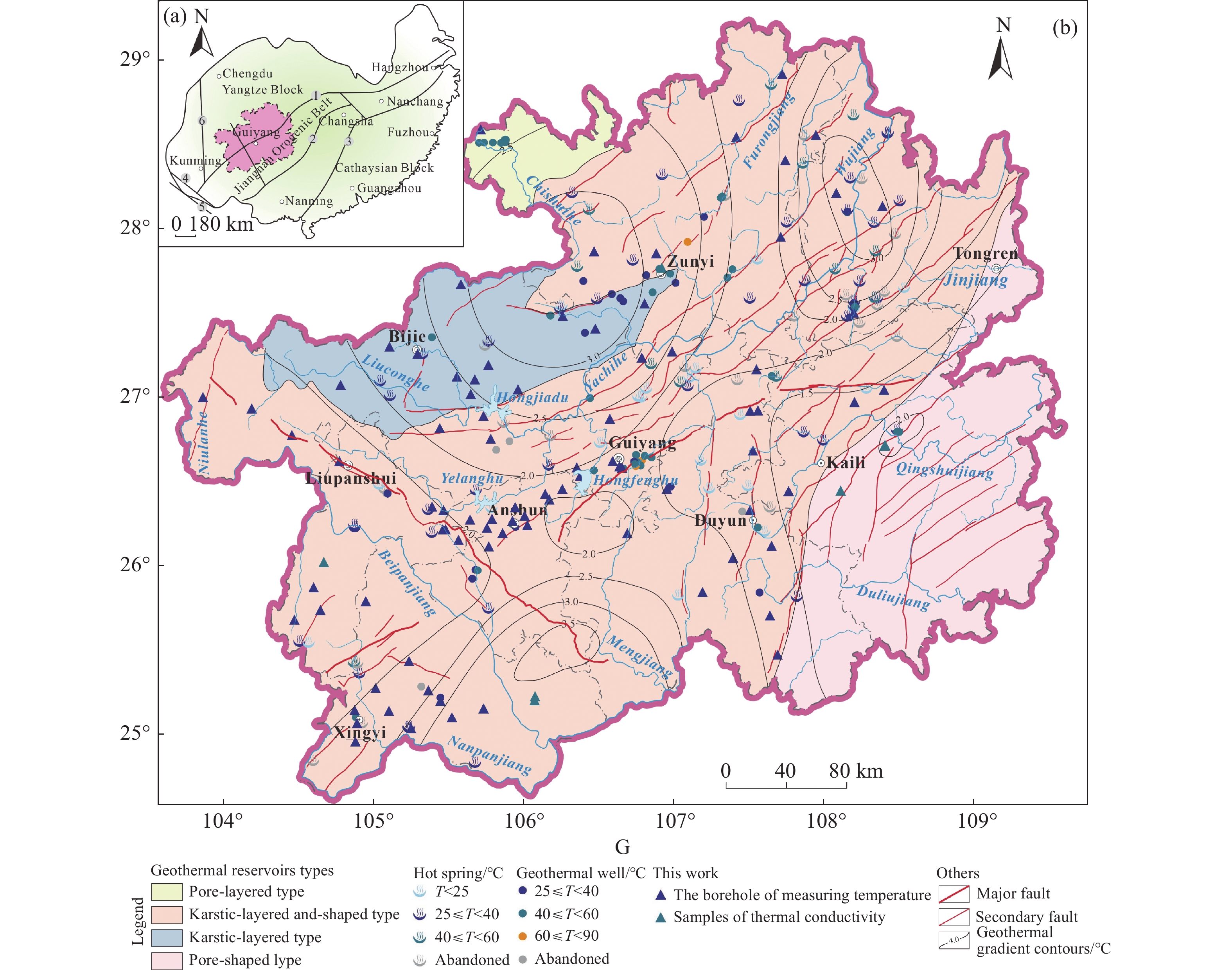
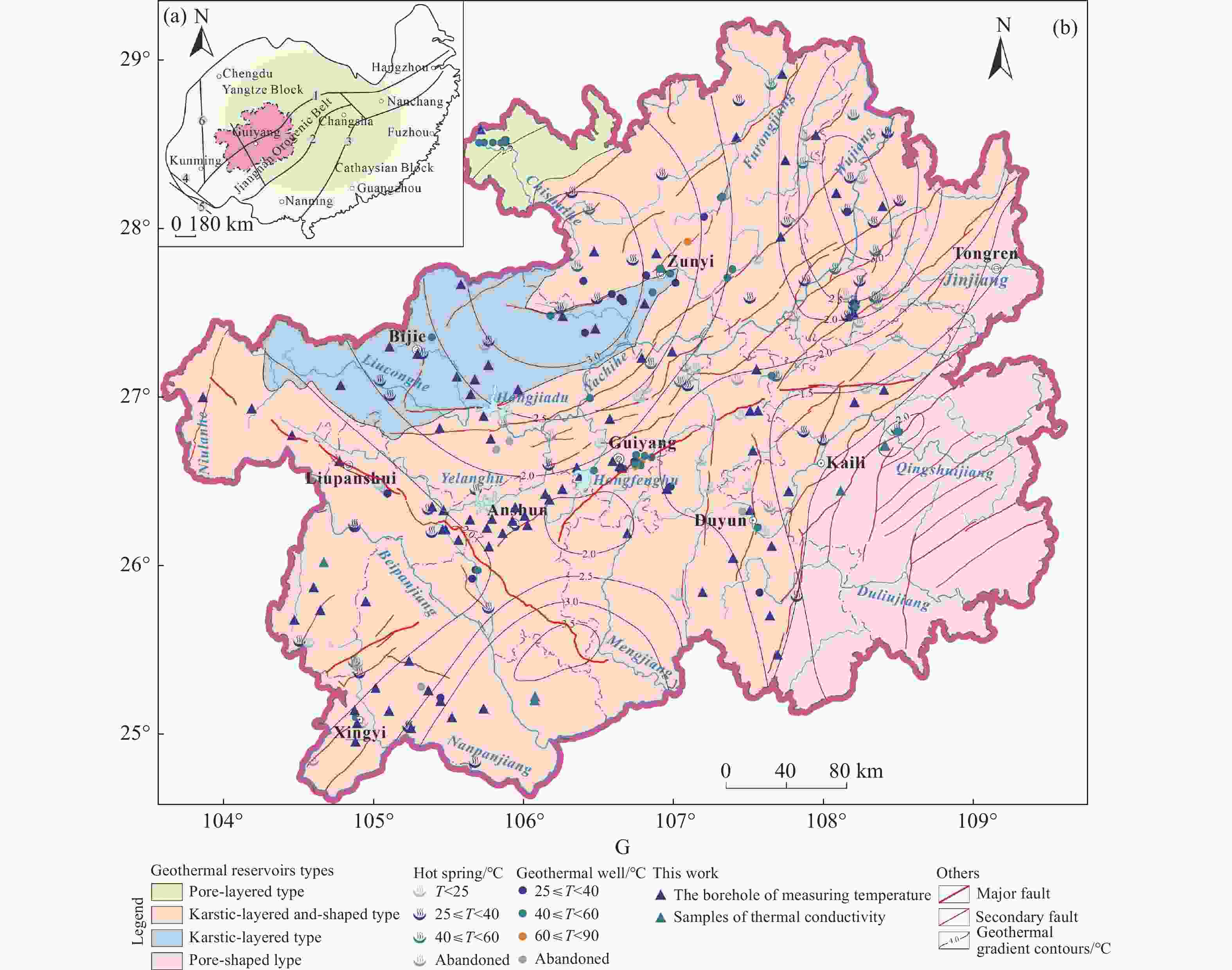
Figure 1. (a) Map showing the geotectonic location of Guizhou Province (modified from Dai et al. 2013); (b) Geological map showing geothermal resources in Guizhou Province (modified from Wang et al. 2018).
Notes: ① Shizong-Songtao-Cili-Jiujiang fault belt; ② Luocheng-Longsheng-Taojiang-Jingdezhen fault belt; ③ Beihai-Pingxiang-Shaoxing fault belt; ④ Honghe fault belt; ⑤ Ailaoshan fault belt; ⑥ Xiaojiang fault belt
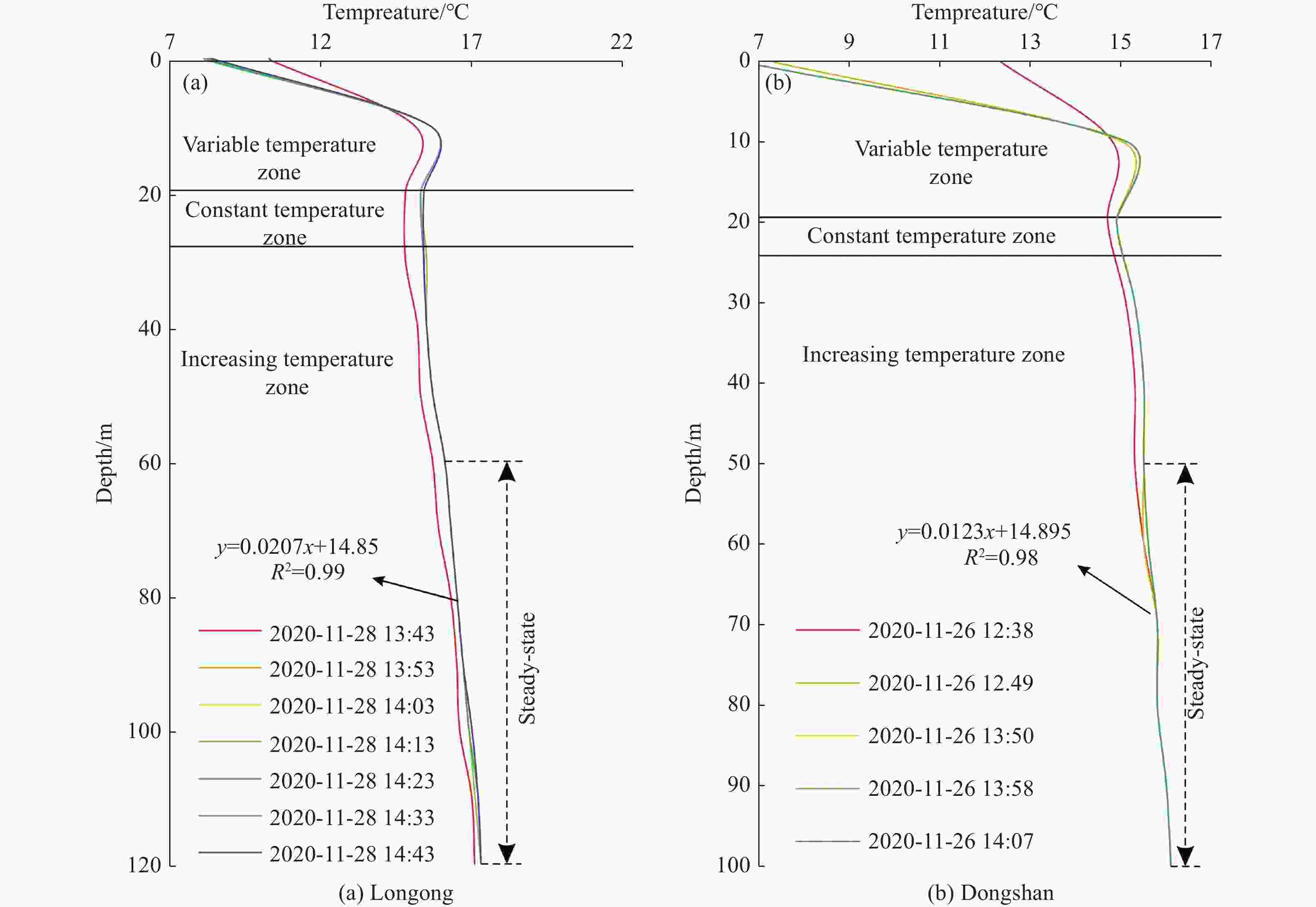
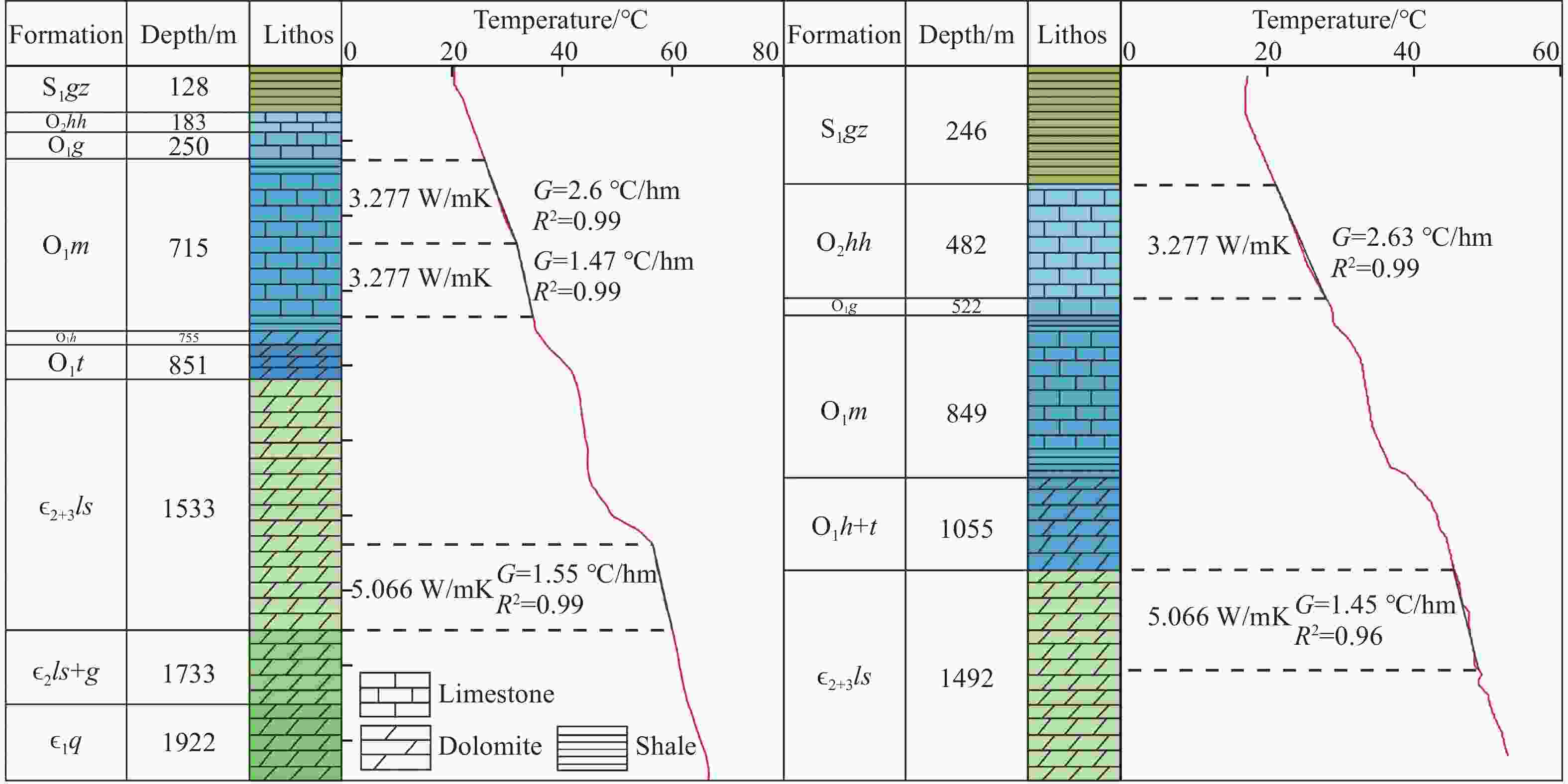
Figure 3. Stratigraphic column and temperature curve of ZK2 (left) and ZK3 (right) in Wudang geothermal field, Guizhou (modified from Wu et al. 2012)
Figure 6. Map of Moho depth in Guizhou Province (modified from Qu et al. 2019)
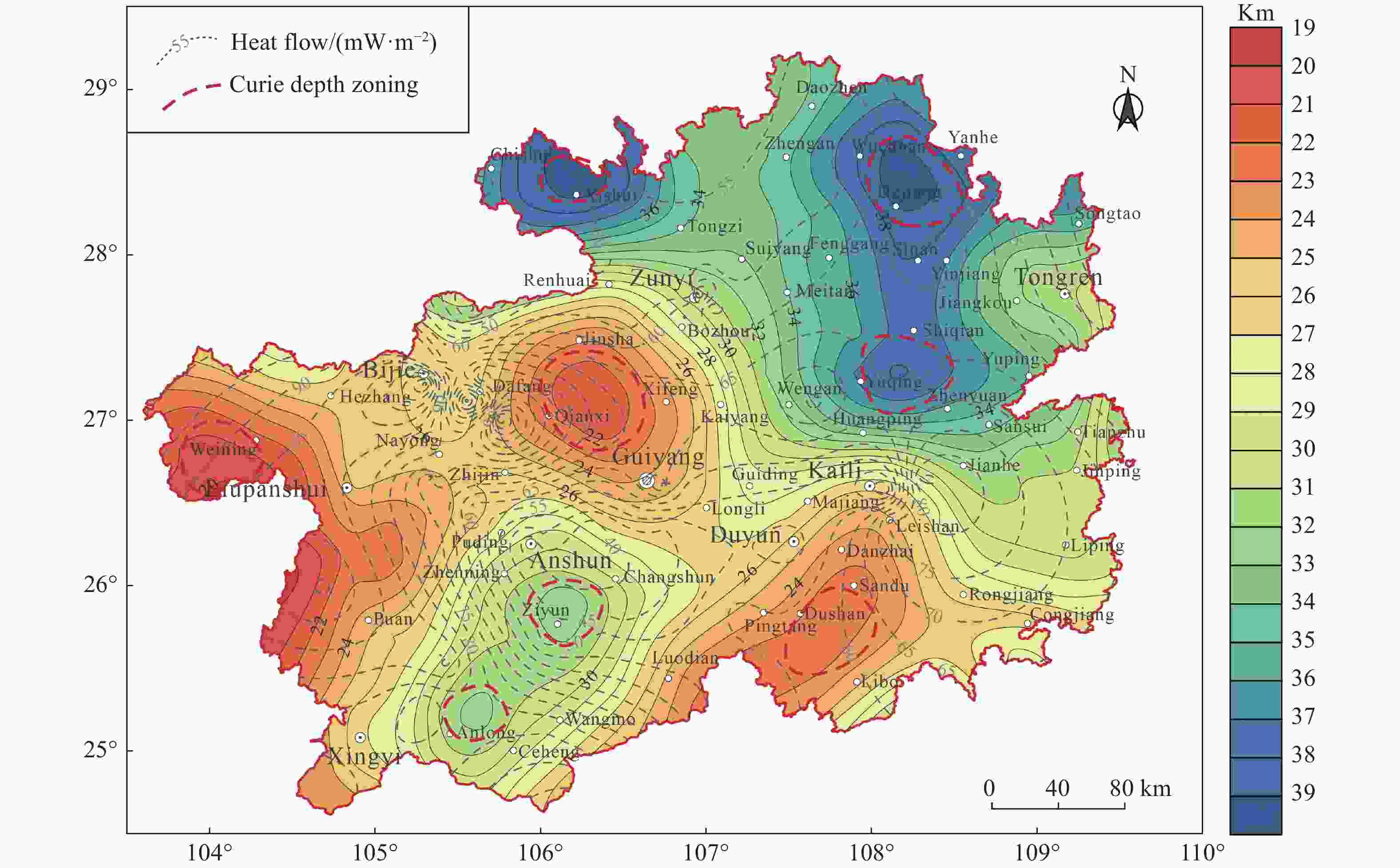
Figure 7. Map of depth of Curie in Guizhou Province (modified from Xiong et al. 2016)
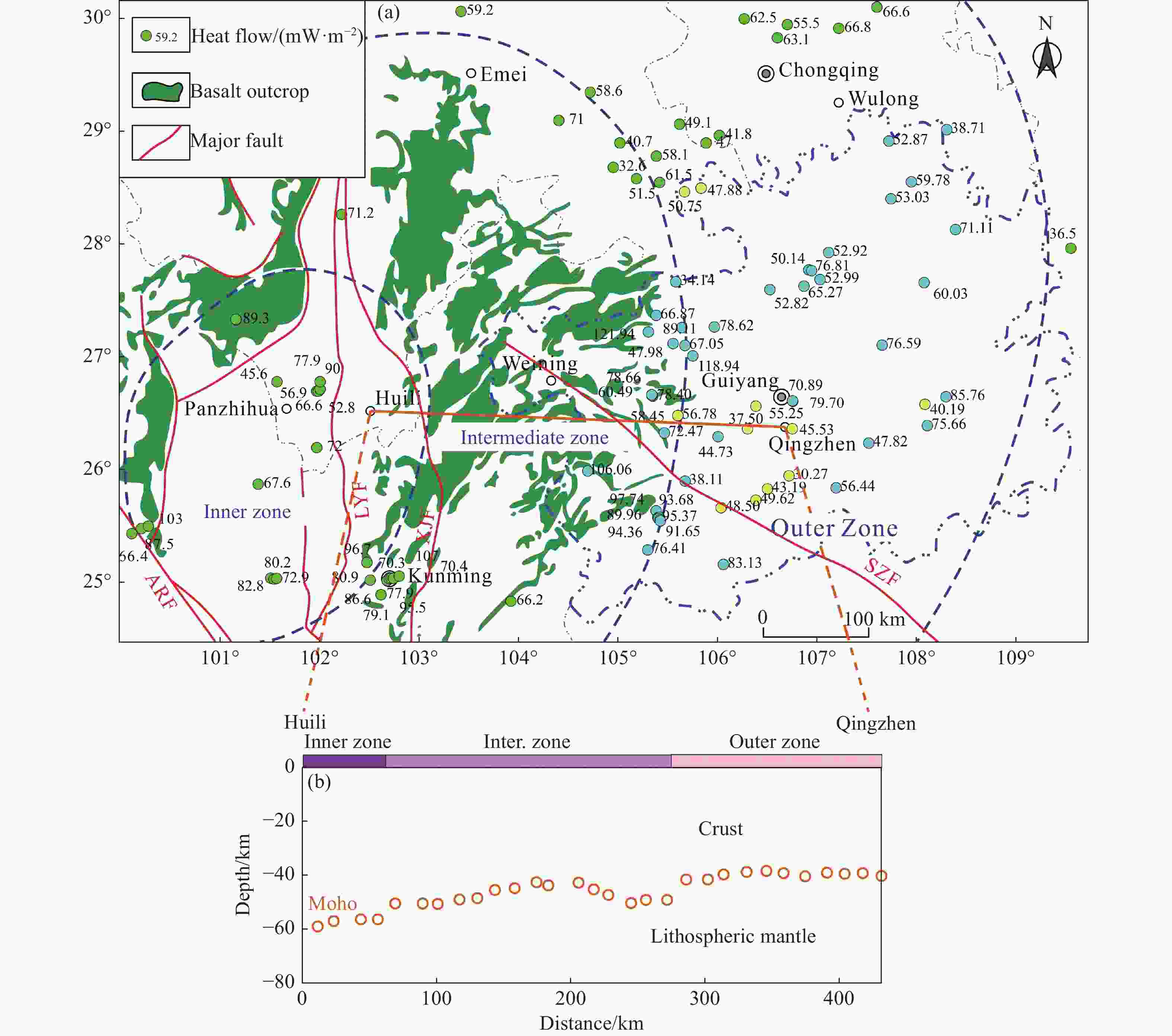
Figure 8. (a) Map of Emeishan large igneous province and regional thermal flow dispersion. (b)Thermal lithospheric thickness of the Huili-Qingzhen transect (modified from Jiang et al. 2018)
Notes: Blue heat flow value points are calculated in this paper. Yellow heat flow value points are quoted from Wang et al. (1990). Green heat flow value points are quoted from Wang and Huang (1990). The blue dash lines represent the boundaries of the inner, intermediate, and outer zones of the ELIP defined by He et al. (2003). ARF: Ailaoshan-Red River slip fault; LYF: Lvzhijiang-Yuanmou Fault; XJF: Xiaojiang Fault; SZF: Shuicheng–Ziyun Fault
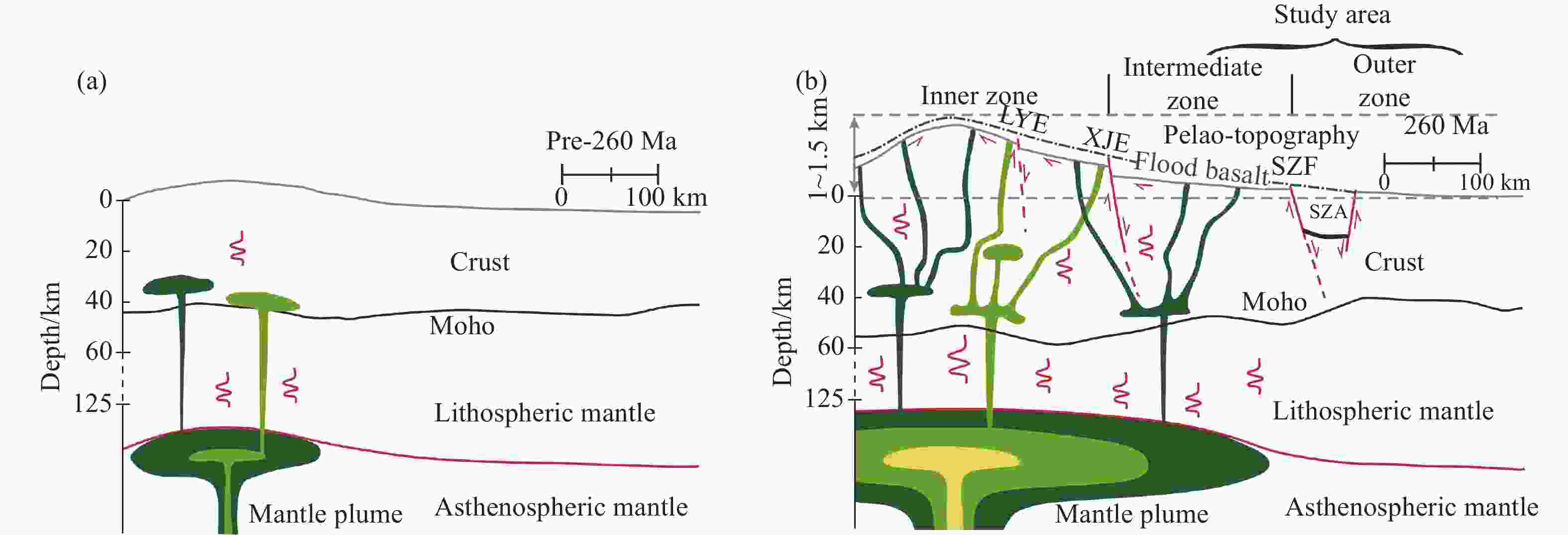
Figure 9. Conceptual model for (a) early magmatic underplating by a mantle plume (modified after Feng et al. 2021); (b) progressive magma emplacement at depth, topographic uplift in the Emeishan LIP (modified from Feng et al. 2021; Chen et al. 2015)
Notes: LYF: Lvzhijiang-Yuanmou Fault; XJF: Xiaojiang Fault; SZF: Shuicheng–Ziyun Fault; SZA: Shuicheng-Ziyun Aulacogen
Figure 10. Geological formations and heat flow distribution in Guizhou Province (hidden faults cited in Dai et al. 2013)
Notes: ①Hao-tan fault; ②Yangdeng-Zunyi-Weicheng fault; ③Muhuang-Guiyang-Pu'an fault; ④Yuping-Shidong-Sandu fault; ⑤Nayong-Kaiyang fault; ⑥Yadu-Ziyun fault; ⑦Shuicheng-Wangmu fault; ⑧Longgong-Zhenfeng fault; ⑨Mudai fault; ⑩Yanggong fault
Table 1. Test results of rock thermal conductivity in the study area
Sample Stratum Lithology Thermal conductivity(W/(m·K)) Error/% BLC-1 Middle Triassic Banna Fm. Fine sandstone 4.372 0.7 BLC-2 Sandy mudstone 1.523 0.2 DSC Middle Triassic Shizishan Fm. Muddy dolomite 2.776 0.6 GMC Middle Triassic Guanling Fm. Limestone 1.901 0.7 DWZ 2.379 0.7 NWC Dolomite 2.867 0.4 GJC Lower Triassic Yongningzhen Fm. Limestone 3.395 0.6 YZYC 3.369 0.4 BJ-1 Lower Triassic Maocaopu Fm. Muddy tuff 2.806 0.3 BJ-2 Limestone 1.847 0.3 LCQ-1 Lower Triassic Yelang Fm. Muddy tuff 3.294 0.4 LCQ-2 Limestone 1.965 0.2 LCQ-3 Sandy mudstone 3.122 0.5 LGC Limestone 3.239 0.5 LCB Lower Triassic Anshun Fm. Dolomite 1.986 0.4 QGQC Upper Permian Changxing Fm. Limestone 2.323 0.5 PMC Upper Permian Wujiaping Fm. Limestone 4.372 0.3 DJ-1 Middle Permian Longtan Fm. Fine sandstone 3.502 0.8 WD Siltstone 3.013 0.5 SC-1 Middle Permian Maokou Fm. Limestone 3.618 0.5 ZK01 Lower Carboniferous Shangsi Fm. Limestone 3.05 (10) — CY Upper Devonian Yaosuo Fm. Dolomite 3.305 0.5 PLC Siliceous tuff 1.591 0.3 KLC Siliceous tuff 5.533 0.6 LJXC Lower Ordovician Honghuanyuan Fm. Limestone 3.277 0.2 ZK02 Upper Cambodian shangsi Fm. Limestone 4.59 (9) — Dolomite 4.71 (6) — ZK03 Upper Cambrian Shilengshui Fm. Dolomite 4.84 (10) — MXC Upper Cambrian Houba Fm. Muddy dolomite 5.287 0.6 DCY Upper Cambodian Gaotai Fm. Dolomite 5.303 0.4 DBC Middle and Upper Cambrian Loushanguan Group Dolomite 3.640 0.1 CWTC 5.197 0.3 JH-2 Lower Cambrian Jindingshan Fm. Limestone 4.032 0.3 DSP Upper Proterozoic Qingshuijiang Fm. Tuff 3.330 0.7 JH-1 Upper Proterozoic Fanshao Fm. Slate 3.611 0.8 Notes: Number of samples is shown in brackets. Fm.- Formation. Table 2. Comparison of thermal conductivity statistics of different lithologies with other regions
Lithology This text W/(m·K) Guizhou
(Song et al. 2019)
W/(m·K)North China
(Chen et al.1988)
W/(m·K)Northwest China
(Wang et al.1995)
W/(m·K)Southeast China
(Xiong et al.1994)
W/(m·K)Siltstone 2.323(2) 1.806±0.326(46) 1.97±0.16(3) 2.506±0.688(26) 3.59±1.19(49) Fine sandstone 3.013(1) 3.362±0.536(30) 2.51±0.71(17) 1.811±0.578(21) 3.41±1.22(181) Dolomite 3.981(8) 4.540±0.823(60) 4.34±1.33(45) 3.501±0.922(4) 3.30±0.67(8) Limestone 3.096(14) 2.868±0.256(30) 2.86±1.13(21) 3.192±0.724(28) 3.33±0.56(56) Muddy tuff 3.050(2) 2.699±0.259(28) 1.79±0.10(1) — 1.85±0.49(7) Tuff 3.330(1) 3.355±0.378(30) — — 3.36±0.56(63) Slate 3.611(1) 3.040±0.488(30) — — — Notes: Number of samples is shown in brackets Table 3. List of terrestrial heat flow data in Guizhou Province (* is to update the heat flow value)
ID Longitude Latitude Depth (m) Measuring section (m) Geothermal gradient
(℃/km)Conductivity
W/(m·K)Staged Heat Flow
(mW/m2)Mean heat flow
(mW/m2)Grade Data source Dongshan 105.579 27.669 120.60 50–100 12.3 2.776 34.14 B Measured Longgong 105.671 27.105 120.10 60–120 20.7 3.239 67.05 B Measured Daping 108.390 28.133 107.48 30–80 21.7 3.277 71.11 B Measured Karo 107.190 25.843 151.20 60–140 10.2 5.533 56.44 A Measured Minxing 107.721 28.917 120.08 50–110 10.0 5.287 52.87 A Measured Dongkou 106.003 26.297 120.06 35–105 10.0 4.473 44.73 B Measured Duijiang 105.551 27.122 170.00 45–165 13.7 3.502 47.98 B Measured Longchang-qiao 105.464 26.330 120.00 40–80 22.0 3.294 72.47 B Measured WuchuanZK02 107.946 28.555 306.15 150–225 11.8 5.066 59.78 A Measured CK1 107.519 26.240 2521.56 794.29–1193.34 15.5 3.085 47.82 C GBBGMEDGP, 2015 ZK3 108.107 26.395 2300.00 1653.83–2196.21 26.0 2.910 75.66 C Ban et al. 2018、Tu et al. 2019 ZK2 108.295 26.650 1618.00 1017.88–1603.30 28.2 3.041 85.76 C ZK2 105.672 25.903 2301.00 1176.2–1994.8 1.60 2.382 38.11 C Chen et al. 2014 S-2 104.692 25.992 760.00 452.68–703.32 35.2 3.013 106.06 C Hou, 2016 ZK2 106.755 26.610 1922.44 157.65–728.96 21.4 3.277 70.13 73.59* C Wu et al. 2012 1279.72–1500 16.3 5.066 82.58 ZK3 106.751 26.614 2191.23 214.04–524.08 27.2 3.277 89.13 82.42* C 1082.62–1344.43 14.7 5.066 74.47 ZK5 108.224 27.511 567.00 200–300 31.1 5.066 157.55 C Tian, 2016 Dongjiu-chang 106.915 27.775 318.00 60–318 15.3 3.277 50.14 C Yuan,1997 SK08-2 107.653 27.108 1354.22 850–1103 23.0 3.330 76.59 C Duan et al. 2015; Song et al. 2012 CK1 105.303 27.225 2301.21 1327–2204 27.6 4.418 121.94 C Fang et al. 2020 CK2 105.966 27.270 1301.30 319–900 19.5 4.032 78.62 C ZK1 105.381 27.372 1934.62 1231–1936 13.2 5.066 66.87 C ZK4 105.640 27.263 2471.37 959–1632 22.1 4.032 89.11 C ZK5 105.750 27.012 2200.07 1701–2102 29.5 4.032 118.94 C ZK1 106.867 27.631 2696.00 0–279 23.6 2.320 54.75 65.27 C Zhang and Li, 2015; Zhang et al. 2014 279–1061 16.6 2.670 44.32 1061–1520 23.9 3.085 73.73 1756–2675.1 16.2 5.066 82.07 ZK2 106.944 27.768 3001.00 0–120 27.5 2.32 63.80 76.81 C 120–1823.5 22.6 4.032 91.12 1823.5–2362.9 15.2 2.271 34.52 ZK3 106.921 27.769 3002.00 0–375 10.4 2.271 23.62 38.05 C 375–1525 12.0 4.032 48.38 1525–2100 11.8 2.271 26.80 CK4 107.115 27.929 2500.00 0–745.16 11.8 5.066 59.78 52.92 C 745.16–1994.66 21.5 2.271 48.83 CK5 107.029 27.690 2641.00 0–1225 11.8 5.066 59.78 52.99 C 1225–1875 17.7 2.271 40.20 ZK4 106.524 27.601 1226.00 0–380 13.1 4.032 52.82 C 807 105.346 26.655 490.00 105–242 30.2 2.596 78.40 B Lu et al. 2013; Lu, 2014 10-6 105.339 26.660 893.00 327–527 23.3 2.596 60.49 B 8-1 105.374 26.655 650.00 200–324 14.7 2.596 38.16 B 1109 105.337 26.669 455.00 102–186 30.3 2.596 78.66 B Getang 105.297 25.292 — 1400–1900 30.0 2.547 76.41 C Zhu, 2020 ZK001 105.381 25.640 953.00 310–590 27.7 3.382 93.68 C Ding et al. 2019 ZK705 105.399 25.578 1364.00 470–990 28.2 3.382 95.37 C ZK302 105.413 25.582 1150.00 300–700 27.1 3.382 91.65 C ZK303 105.404 25.571 1250.00 300–700 26.6 3.382 89.96 C ZK402 105.420 25.560 950.00 250–700 27.9 3.382 94.36 C ZK1201 105.424 25.550 950.00 300–700 28.9 3.382 97.74 C ZK02 108.191 27.470 2060.37 600–1320 13.8 4.350 60.03 C Mu and Wu, 2021 -
Ban WT, Duan XQ, Yang Q, et al. 2018. A study of the occurrence law of zonal thermal reservoirs in the Gedong area of Guizhou. Geology and Exploration, 54(2): 0366-0375. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13712/j.cnki.dzykt.2018.02.015 Chen MX, Huang GS, Xiong LP, et al. 1988. Geothermics of North China. Beijing: Science Press: 61-70. (in Chinese) Chen P, Zhang BM, Jin B. 2014. Heat-reservoir structure study and its significance of Langgong scenic spot in Huangguoshu, Guizhou. Guizhou Geology, 31(4): 318-322. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2014.04.014 Chen XY, Jiang ZJ, Xu HY, et al. 2022. Heat control mechanism and productivity optimization of artificial fracture zone structure of dry hot rock in Gonghe Basin. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 49(1): 191-199. (in Chinese) Chen Y, Xu Y, Xu T, et al. 2015. Magmatic underplating and crustal growth in the Emeishan Large Igneous Province, SW China, revealed by a passive seismic experiment. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 432: 103-114. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2015.09.048 Chen ZS. 2021. The formation mechanism of physiotherapy thermomineral water (hot spring) in guizhou and its effect on human health. Ph. D thesis. Guizhou: Guizhou University: 53-166. (in Chinese) Dai CG, Qin SR, Chen JS, et al. 2013. Characteristics of deep concealed faults in Guizhou. Geological Science and Technology Information, 32(6): 1-13. (in Chinese) Ding J, Xiang T, You B, et al. 2019. Analysis on geothermal resources prospecting in Dashan-Xinzhuang area, Xingren County, Guizhou Province. West-China Exploration Engineering, 10: 142-146. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2019.10.053 Duan QB, Song XQ, Meng FT, et al. 2015. Study on occurrence law of geothermal water in metamorphic rock area of eastern Guizhou. Groundwater, 37(4): 37-39. (in Chinese) Fang SW, Li Q, Chen G, et al. 2020. Study on distribution characteristics of geothermal field in central and Eastern Bijie, Guizhou Province. West-China Exploration Engineering, 10: 130-134. (in Chinese) Feng K, Xu S, Chen A, et al. 2021. Middle permian dolomites of the SW Sichuan Basin and the role of the Emeishan large igneous province in their origin. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 128(3-4): 1-18. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.104981 Furlong KP, Chapman DS. 2013. Heat flow, heat generation, and the thermal state of the lithosphere. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 41: 385-410. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.031208.100051 GBBGMEDGP (Geological Brigade of Bure of Geology and Mineral Exploration and Development Guizhou Province). 2015. Report on well completion of CK1 geothermal exploration hole in Longjing geothermal water survey in Duyun City, Guizhou Province. 114 Geological Brigade of Bure of Geology and Mineral Exploration and Development Guizhou Province. (in Chinese) GSGP (Geological Survey of Guizhou Province). 2017. Regional geologic annuals of Guizhou. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-788. (in Chinese) Grall C, Henry P, Tezcan D, et al. 2012. Heat flow in the Sea of Marmara Central Basin: Possible implications for the tectonic evolution of the North Anatolian fault. Geology, 40(1): 3-6. Guo C, Qin Y, Lu L. 2018. Terrestrial heat flow and geothermal field characteristics in the Bide-Santang basin, western Guizhou, South China. Energy Exploration & Exploitation, 36(5): 1114-1135. doi: 10.1177/0144598717752364 He B, Xu Y, Chung S, et al. 2003. Sedimentary evidence for a rapid, kilometer-scale crustal doming prior to the eruption of the Emeishan flood basalts. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 213(3-4): 391-405. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00323-6 He C, Santosh M, Wu J, et al. 2014. Plume or no plume: Emeishan Large Igneous Province in Southwest China revisited from receiver function analysis. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 232: 72-78. He L. 2015. Thermal regime of the North China Craton: Implications for craton destruction. Earth-Science Reviews, 140: 14-26. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.10.011 Hou DG. 2016. Research on reservoir characteristics and recoverability of CBM resources in Songhe mine field, Guizhou province. M.S. thesis. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology: 21-51. (in Chinese) Hu S, He L, Wang J. 2000. Heat flow in the continental area of China: A new data set. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 179(2): 407-419. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(00)00126-6 Jiang G, Hu S, Shi Y, et al. 2019. Terrestrial heat flow of continental China: Updated dataset and tectonic implications. Tectonophysics, 753(20): 36-48. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2019.01.006 Jiang GZ, Gao P, Rao S, et al. 2016. Compilation of heat flow data in the continental area of China (4th edition). Chinese Journal of Geophysis, 59(8): 2892-2910. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6038/cjg20160815 Jiang Q, Qiu N, Zhu C. 2018. Heat flow study of the Emeishan large igneous province region: Implications for the geodynamics of the Emeishan mantle plume. Tectonophysics, 724-725: 11-27. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2017.12.027 Li YL, Yu CS, Jiang ZC, et al. 2021. An experimental study of heating tail water treatment of the Lindian geothermal fields in the Northern Songnen Basin. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 48(1): 188-194. (in Chinese) Liu F, Wang GL, Zhang W, et al. 2020a. Terrestrial heat flow and geothermal genesis mechanism of geothermal resources in northern Ningdu County, Jiangxi Province. Geological Bulletin of China, 39(12): 1883-1890. (in Chinese) Liu Y, Qiu N, Li H, et al. 2020b. Terrestrial heat flow and crustal thermal structure in the northern slope of Tazhong uplift in Tarim Basin. Geothermics, 83: 101709. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2019.101709 Lu JR. 1996. Dynamical characteristics of the Emei Mantle Plume. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 17(4): 424-438. (in Chinese) Lu LL. 2014. Differentiation and geological controls of modern geothermal field in Bide-Santang basin. M. S. thesis. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology: 29-41. (in Chinese). Lu LL, Qing Y, Guo C. 2013. Modern geothermal field and coal seam heating temperature in Buzuo exploration area, Western Guizhou. Coal Geology of China, 25(10): 12-17. (in Chinese) Mao JQ, Zhang QH, Gu SY. 1997. The geological characteristics and tectonic evolution of Shuicheng fault subsidence. Journal of Guizhou University of Technology, 26(2): 1-6. (in Chinese) Mao X, Li K, Wang X. 2019. Causes of geothermal fields and characteristics of ground temperature fields in China. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 7(1): 15-28. doi: 10.19637/j.cnki.2305-7068.2019.01.002 Mu ZM, Wu L. 2021. Genetic analysis of hot mineral water in ZK2 geothermal well, Zhongba, Shiqian, Guizhou. West-China Exploration Engineering, 8: 131-136. (in Chinese) Pollack HN, Hurter SJ, Johnson JR. 1993. Heat flow from the Earth’s interior: Analysis of the global data set. Reviews of Geophysics, 31(3): 367-280. doi: 10.1029/93RG01249 Qu NN, Li JB, Zhang XJ, et al. 2019. Study of deep structural feature in Guizhou based on gravity and magnetic data. Progress in Geophysics, 34(5): 1785-1793. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6038/pg2019CC0310 Rolandone F, Lucazeau F, Leroy S, et al. 2013. New heat flow measurements in Oman and the thermal state of the Arabian Shield and Platform. Tectonophysics, 589: 77-89. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2012.12.034 Shellnutt JG. 2014. The Emeishan large igneous province: A synthesis. Geoscience Frontiers, 5: 369-394. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2013.07.003 Song XQ, Jiang M, Peng Q, et al. 2019. Thermal property parameters and influencing factor analysis of main rock strata in Guizhou province. Acta Geologica Sinica, 93(8): 2092-2103. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19762/j.cnki.dizhixuebao.2019116 Song XQ, Peng Q, Xia YL. 2012. Estimation of reservoir temperature and circulation depth of geothermal water of SK08-2 well in Laofenzui metamorphic rock area of Wengan city. Water Saving Irrigation, 10: 24-26. (in Chinese) Sun Y, Lai X, Wignall PB, et al. 2010. Dating the onset and nature of the Middle Permian Emeishan large igneous province eruptions in SW China using conodont biostratigraphy and its bearing on mantle plume uplift models. Lithos, 119(1-2): 20-33. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2010.05.012 Tian XL. 2016. Occurrence and development of geothermal water in Shiqian fracture. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 36(4): 623-626. (in Chinese) Tu MJ, Li Q, Yi SY. 2019. Study on the occurrence condition of geothermal in Leishan, Guizhou. West-China Exploration Engineering, 7: 154-156. (in Chinese) Wang GL, Lin WJ, Zhang W, et al. 2018. Geothermal Records of China (Southwest Volume II). Beijing: Science Press: 499-525. (in Chinese) Wang GL, Wang WL, Zhang W, et al. 2020. The status quo and prospect of geothermal resources exploration and development in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in China. China Geology, 3: 173-181. doi: 10.31035/cg2020013 Wang JY. 2015. Geothermics and its applications. Beijing: Science Press: 56-122. (in Chinese) Wang JY. Huang SP. 1990. Compilation of heat flow data in the China continental area (2rd edition). Seismology and Geology, 12(4): 351-366. (in Chinese) Wang J, Huang SY, Huang GS, et al. 1990. Basic characteristics of the Earth’s temperature distribution in China. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-231. (in Chinese) Wang J, Wang JA, Shen JY, et al. 1995. Heat flow in tarim basin. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 20(4): 399-404. (in Chinese) Wang L, Zhang JW, Chen GY, et al. 2020. Delineation of concealed intermediate-acidic pluton and significance of mineral prospecting in Guizhou province. Geology and Exploration, 20(4): 399-404. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12134/j.dzykt.2020.02.013 Wang MZ, Wang SY. 2007. Concerns of developing geothermal resources in Guizhou province and counter measure proposals. Guizhou Geology, 24(1): 9-12. (in Chinese) Wang Z, Rao S, Xiao H, et al. 2021. Terrestrial heat flow of Jizhong depression, China, Western Bohai Bay basin and its influencing factors. Geothermics, 96: 102210. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2021.102210 Wu KB, Zeng GQ, Chen GX, et al. 2016. Deep structural features of Guizhou revealed by bouguer gravity anomaly. Geological Science and Technology Information, 35(1): 190-199. (in Chinese) Wu L, Zhao L, Luo XG. 2012. Characteristics of geothermal field and estimation of heat flow in Wudang district of Guiyang. Site Investigation Science and Technology, 3: 41-43. (in Chinese) Xing JS, Yang WR, Xing ZY, et al. 2007. Deep-seated structure characteristics of eastern China and its relation with metal mineralization-concentrated region. Earth Science Frontiers, 14(3): 114-130. (in Chinese) Xiong LP, Hu SB, Wang JA. 1994. Analysis on the thermal conductivity of rocks from SE China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 10(3): 323-329. (in Chinese) Xiong LP, Hu SB, Wang JY. 1993. Terrestrial heat flow values in southeastern China. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 36(6): 784-790. (in Chinese) Xiong SQ, Yang H, Ding YY. 2016. Characteristics of Chinese continent Curie point isotherm. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 59(10): 3604-3617. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6038/cjg20161008 Yang RK, Luo W, Pei RW, et al. 2018. Distribution and fluids hydrochemistry characteristics of hydrothermal geothermal resources in Guizhou Province. Geological Survey of China, 5(2): 38-44. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2018.02.06 Yang RK, Wang Q, Yang LJ, et al. 2015. Investigation, evaluation and zoning of geothermal resources in Guizhou Province. Guizhou Geological Environment Monitoring Institute: 1-157. (in Chinese) Yang YJ, Ding GL, Xu W, et al. 2020. Tracer test and geothermal resource quantity evaluation based on dynamic data in the Xiaotangshan area of Beijing. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 47(5): 196-200. (in Chinese) Yuan FG. 1997. Geotherm characteristic of the north suburb of Zunyi city. Guizhou Geology, 14(2): 175-178. (in Chinese) Yuan YS, Ma YS, Hu SB, et al. 2006. Present-day geothermal characteristics in South China. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 49(4): 1118-1126. (in Chinese) Zhang BJ, ZhaoT, Li YY,et al. 2019. The hydrochemical characteristics and its significance of geothermal water in both sides of large fault: Taking northern section of the Liaokao fault in north China as an example. China Geology, 2: 512-521. doi: 10.31035/cg2018132 Zhang CW, Li Q. 2015. Research of geotemperature field distribution characteristics and influence factors in Zunyi area. Guizhou Science, 33(2): 65-70. (in Chinese) Zhang J, Huang S, Zuo Y, et al. 2020. Terrestrial heat flow in the baiyinchagan sag, erlian Basin, northern China. Geothermics, 86: 101799. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2019.101799 Zhang L, Chen G, Li Q, et al. 2014. Formation condition and exploration prospecting of geothermal water in central Zunyi of Guizhou. Guizhou Geology, 31(1): 60-66. (in Chinese) Zhang YH, Li X, Xu ZX, et al. 2021. An analysis of the genesis and engineering influence of geothermal water in the Kangding tunnel site of the Sichuan-Tibet Railway. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 48(5): 46-53. (in Chinese) Zhu SY. 2020. Study on the characteristics of geothermal water occurrence and water and heat migration in Zhenfeng anticline. M. S. thesis. Guizhou: Guizhou University: 25-28. (in Chinese) -

 E-mail alert
E-mail alert Rss
Rss


 下载:
下载: