Optimizing groundwater recharge plan in North China Plain to repair shallow groundwater depression zone, China
-
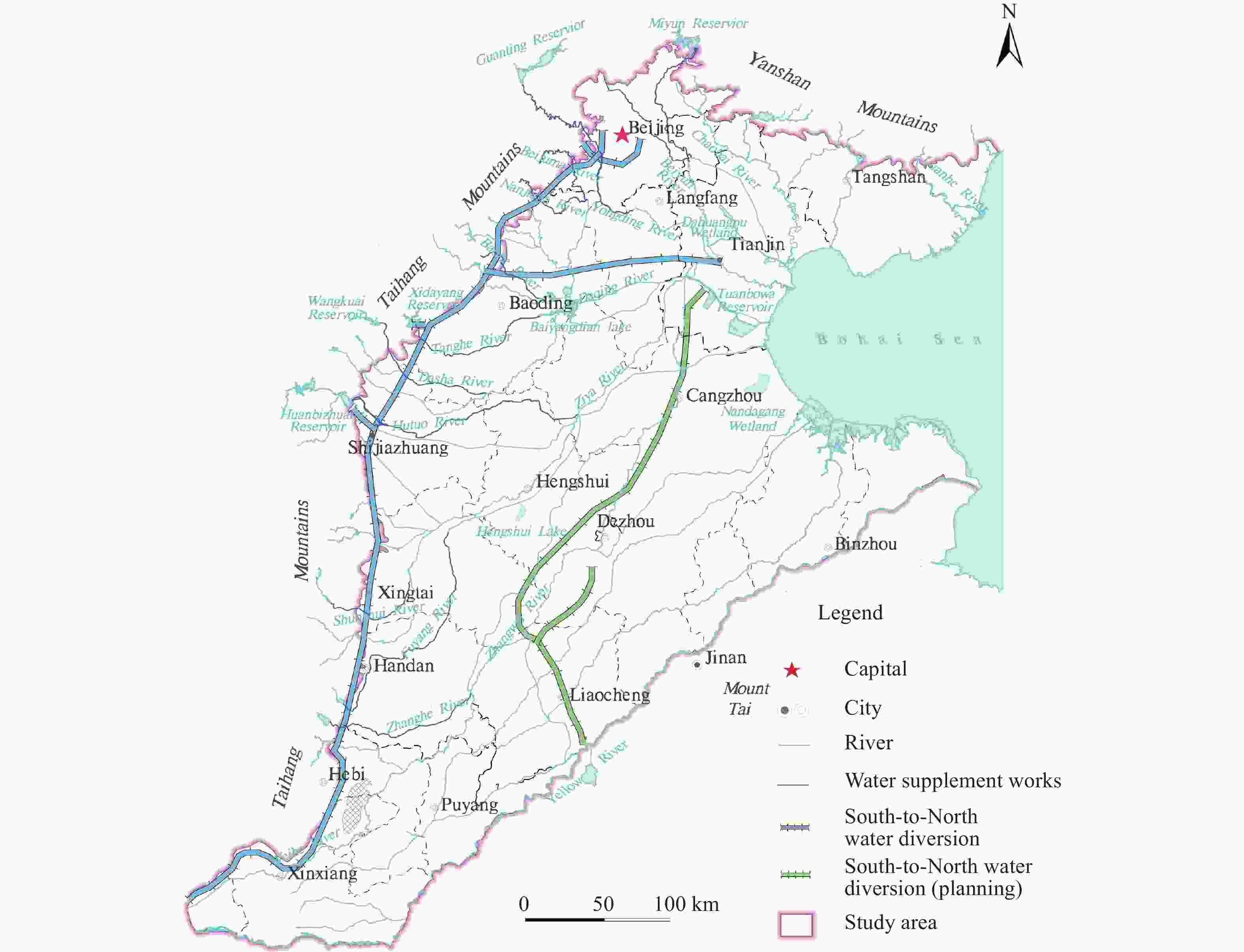
Abstract: The North China Plain is one of the main grain producing areas in China. However, over-exploitation has long been unsustainable since the water supply is mainly from groundwater. Since 2014, the South-to-North Water Diversion Project’s central route has been charted to the integrated management of water supply and over-exploitation, which has alleviated the problem to a certain extent. Although the Ministry of Water Resources has made many efforts on groundwater recharge since 2018 most of which have been successful, the recharge has not yet been sufficiently focused on the repair of shallow groundwater depression zones. It still needs further optimization. This paper discusses this particular issue, proposes optimized recharge plan and provides the following recommendations: (1) Seven priority target areas are selected for groundwater recharge in alluvial and proluvial fans in the piedmont plain, and the storage capacity is estimated to be 181.00×108 m3; (2) A recharge of 31.18×108 m3/a is required by 2035 to achieve the repair target; (3) It is proposed to increase the recharge of Hutuo River, Dasha River and Tanghe River to 19.00×108 m3/a and to rehabilitate Gaoliqing-Ningbailong Depression Zone; increase the recharge of Fuyang River, Zhanghe River and Anyang River to 7.05×108 m3/a and rehabilitate Handan Feixiang-Guangping Depression Zone; increase the recharge of Luanhe River by 0.56×108 m3/a and restore Tanghai Depression Zone and Luanan-Leting Depression Zone; moderately reduce the amount of water recharged to North Canal and Yongding River to prevent excessive rebound of groundwater; (4) Recharge through well is implemented on a pilot basis in areas of severe urban ground subsidence and coastal saltwater intrusion; (5) An early warning mechanism for groundwater quality risks in recharge areas is established to ensure the safety. The numerical groundwater flow model also proves reasonable groundwater level restoration in the depression zones by 2035.
-
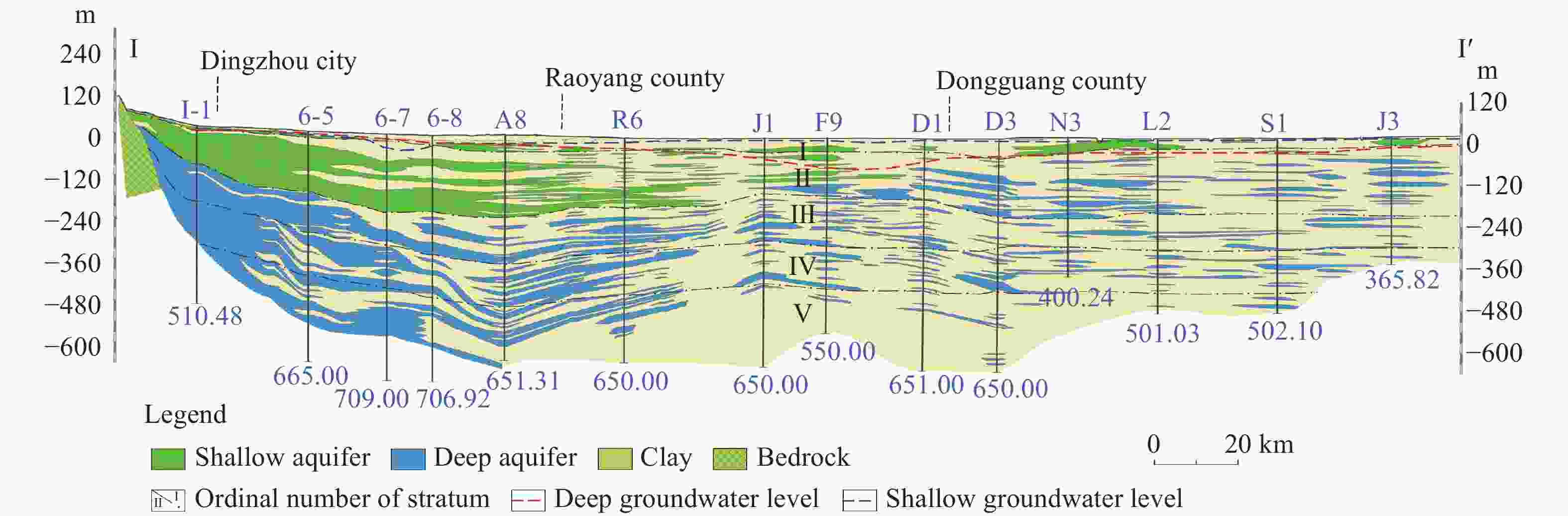
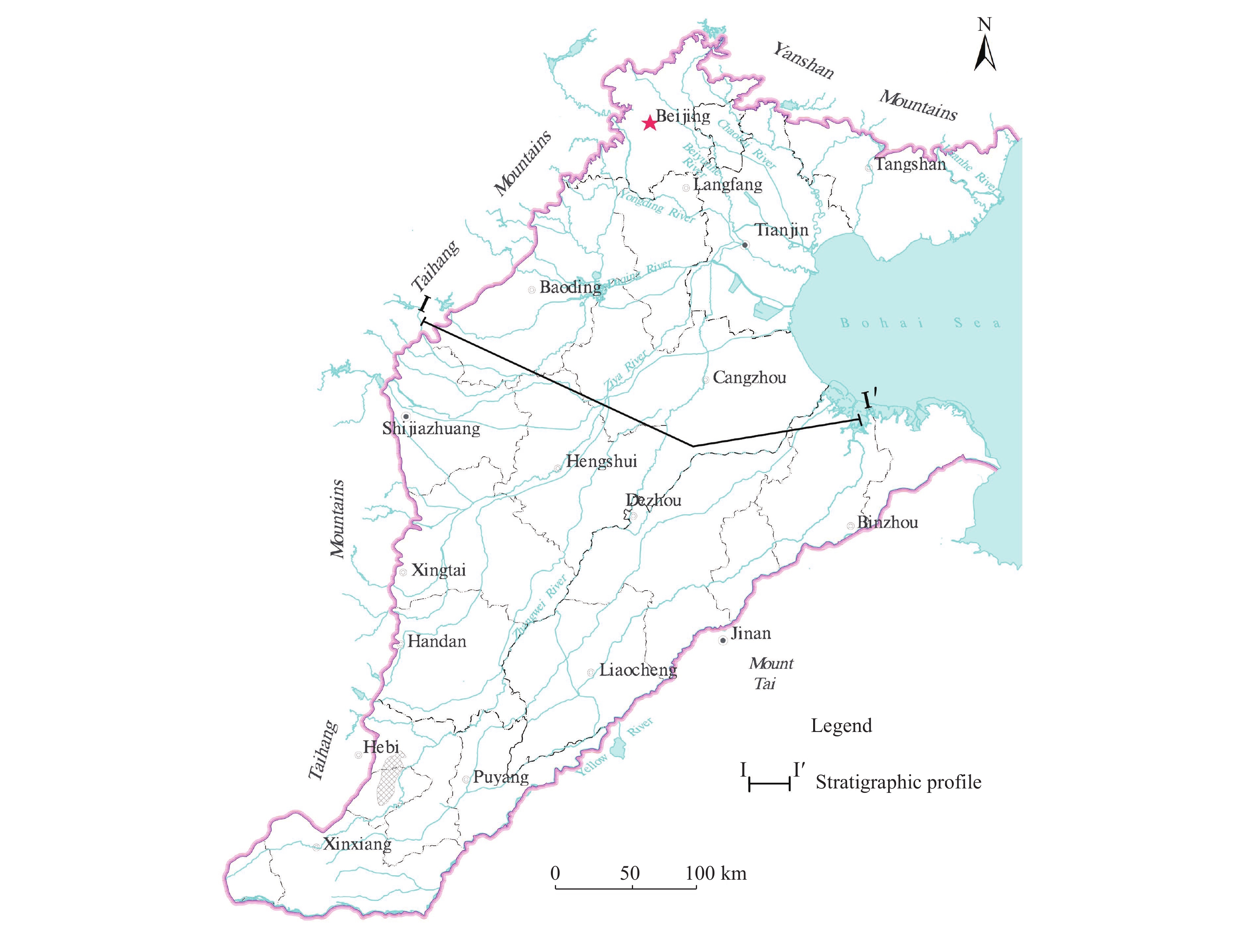
Figure 2. Hydrogeological profile of the North China Plain (Zhang et al. 2009)
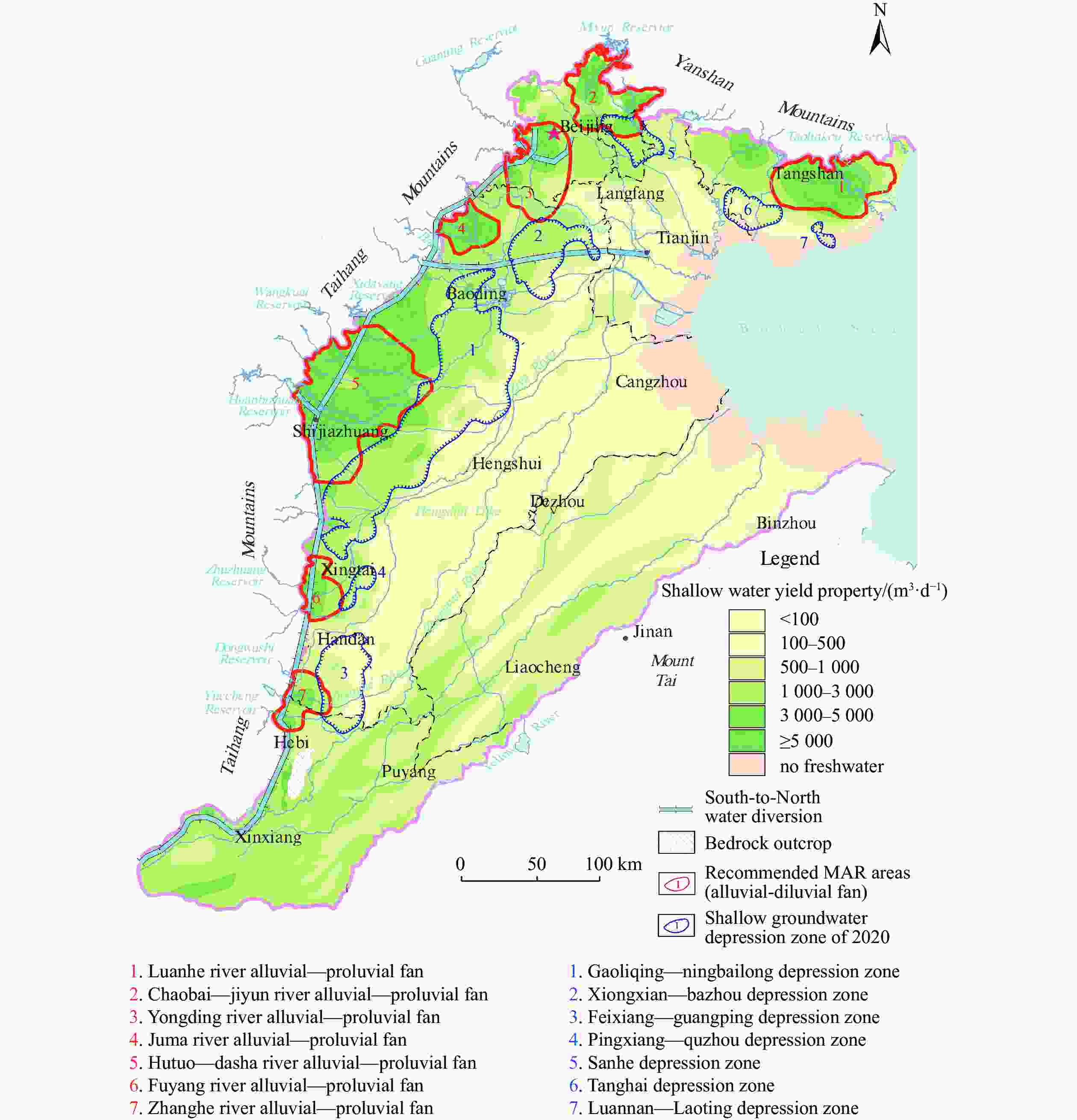
Table 1. Situation of shallow groundwater depression zones in the North China Plain in 2020
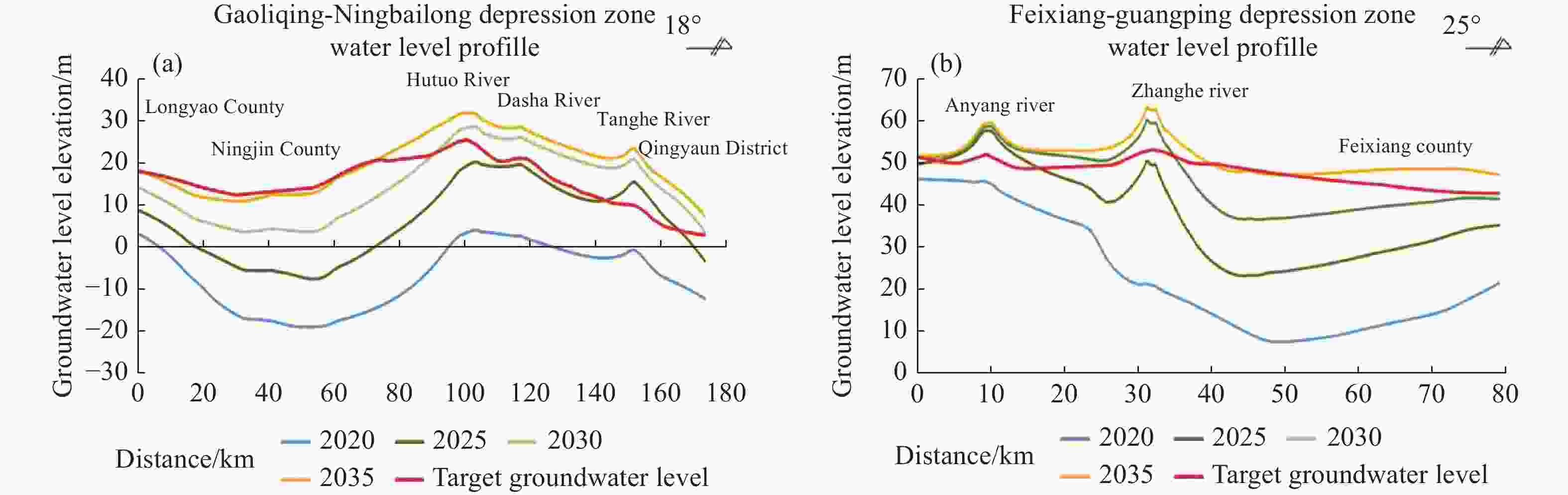
Depression zones Size/104 km2 Depth of the zone centre/m Gaoliqing-Ningbailong depression zone 9 636.60 103.19 Xiongxian-Bazhou depression zone 1 989.14 62.82 Handan Feixiang-Guangping depression zone 2 035.54 79.75 Pingxiang-Quzhou depression zone 356.82 53.52 Langfang Sanhe depression zone 873.63 38.51 Tanghai depression zone 823.12 30.49 Luannan-Leting depression zone 149.28 14.21 Table 2. Deficit in shallow groundwater depression zones
Depression zones Groundwater level in 2020/m Restoration targets/m Deficit/108 m3 Gaoliqing-Ningbailong depression zone −55–−10 5–30 227.99 Xiongxian-Bazhou depression zone −30–−5 1–10 19.52 Handan Feixiang-Guangping depression zone −30–20 42–60 46.55 Pingxiang-Quzhou depression zone −15–0 25–30 9.45 Langfang Sanhe depression zone −10–0 4–25 7.84 Tanghai depression zone −10–−25 0–4 4.93 Luannan-Leting depression zone −10–−5 0–2 0.97 Total 317.25 Table 3. Regulation space for recharge priority target areas in the North China Plain
Recharge priority target areas Size/km2 Buried depth/m Regulation space/108 m3 Luanhe River Alluvial-proluvial fan 2 728.78 6–30 8.30 Chaobai-Jiyun River Alluvial-proluvial fan 2 107.90 8–35 13.90 Yongding River Alluvial-proluvial fan 2 543.99 15–30 16.30 Juma River Alluvial-proluvial fan 927.36 12–28 7.90 Hutuo-Dasha River Alluvial-proluvial fan 6 456.71 18–57 118.90 Fuyang River Alluvial-proluvial fan 923.51 8–41 4.80 Zhanghe River Alluvial-proluvial fan 1 025.06 12–48 10.90 Total 16 713.31 181.00 Table 4. Optimized Plan for Groundwater Recharge in the North China Plain
Recharge
target areasDepression zone repair Recharge source Recharge river Deficit
/108 m3Recharge infiltration rate Repair water requirements
/108 m3Optimized plan
/108 m3/aTo be optimised plan—
recharge volume in 2020
/108 m3/aLuanhe River alluvial-proluvial fan Tanghai depression Zone, Luannan-Leting depression zone Luanhe River Source, Panjikou Reservoir, Daheiting Reservoir, Taolinkou Reservoir Luanhe River 5.90 0.70 7.38 0.56 / Chaobai-Jiyun River alluvial-proluvial fan Langfang Sanhe depression zone Source of South-to-North Water Diversion Project’s Central Route, Miyun Reservoir, Huairou Reservoir Chaobai River, North Canal 7.84 0.85 9.22 0.61 7.56 Yongding River alluvial-proluvial fan Xiongxian-Bazhou depression zone Source of South-to-North Water Diversion Project’s Central Route, Guanting Reservoir Yongding River, North Juma River-Baigou River 19.52 0.495 26.56 1.77 3.46 Juma River alluvial-proluvial fan Source of South-to-North Water Diversion Project’s Central Route, Angezhuang Reservoir South Juma River 0.57 11.18 0.75 0.88 Hutuo-Dasha River alluvial-proluvial fan Gaoliqing-Ningbailong depression zone Source of South-to-North Water Diversion Project’s Central Route, Huangbizhuang Reservoir, Wangkuai Reservoir, Xidayang Reservoir Hutuo River, Dasha River, Tanghe River 227.99 0.80 284.99 19.00 11.43 Fuyang River alluvial-proluvial fan Pingxiang-Quzhou depression zone Source of South-to-North Water Diversion Project’s Central Route, Zhuzhuang Reservoir Qili River-Shunshui River 9.45 0.44 21.48 1.43 2.06 Zhanghe River alluvial-proluvial fan Handan Feixiang-Guangping depression zone Source of South-to-North Water Diversion Project’s Central Route, Yuecheng Reservoir, Dongwushi Reservoir Fuyang River,Zhanghe River, Anyang River 46.55 0.44 105.80 7.05 3.19 Total 317.25 317.25 466.60 31.18 -
Auckenthaler A, Baenninger D, Zechner E, et al. 2010. Drinking water production close to contaminant sites: A case study from the region of Basel, Switzerland. IAHS Publication, 342: 167−170. Azizur RM, Rernd R, Gogu RC, et al. 2012. A new spatial multi-criteria decision support tool for site selection for implementation of managed aquifer recharge. Journal of Environmental Management, 99: 61−75. DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.01.003. Bouwer H. 2002. Artificial recharge of groundwater: Hydrogeology and engineering. Hydrogeology Journal, 10: 121−142. DOI: 10.1007/s10040-001-0182-4. Chen F, Ding YY, Tang SN, et al. 2021. Practice and effect analysis of river-lake ecological water supplement and groundwater recharge in the North China region. China Water Resources, 07: 36−39. (in Chinese) Cui X, Zhang B, He MX, et al. 2021. Impacts of ecological water replenishment on the hydrochemical characteristics of surface water and groundwater in Lake Baiyangdian Watershed. Journal of Lake Sciences, 33(06): 1675−1686. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.18307/2021.0606. Dillon PJ. 2004. Future management of aquifer recharge. Hydrogeology Journal, 13(1): 313−316. DOI: 10.1007/s10040-004-0413-6. Ghayoumian J, Ghermezcheshme B, Feizinia S, et al. 2005. Integrating GIS and DSS for identification of suitable for artificial recharge, case study Meimeh Basin, Isfahan, Iran. Environmental Geology, 47: 493−500. DOI: 10.1007/s00254-004-1169-y. He YP, Li SJ, Li Y, et al. 2019. Effect of South-to-North water transfer project on recharge and water level in Chaobai river area. Beijing Water, 03: 21−26. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.19671/j.1673-4637.2019.03.006. Hendricks FHJ, Kaiser HP, Kuhlmann U, et al. 2011. Operational real-time modeling with ensemble Kalman filter of variably saturated subsurface flow including stream-aquifer interaction and parameter updating. Water Resources Research, 47 (2): W02532. Hu LT, Guo JL, Zhang SQ, et al. 2020. Response of groundwater regime to ecological water replenishment of the Yongding River. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 47(05): 5−11. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202008027. Huo LT, Wang BX, Pan ZH, et al. 2020. Environmental impact by surface-water recharge of groundwater in Beijing Mihuaishun replenishment area-correspondence analysis. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science), 56(02): 195−203. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.12202/j.0476-0301.2020058. Jia WF, Yang Y, Zhao Y, et al. 2016. Simulation of the water-rock reaction in Chaobai River ground-water storage area. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 14(01): 143−148, 135. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.13476/j.cnki.nsbdqk.2016.01.024. Li HT, Shi P, Wu HX. 2008. Artificial recharge technology of groundwater. Natural Resource Economics of China, (03): 41−42, 45, 48. (in Chinese) Li WP, Wang LF, Yang HF, et al. 2020. The groundwater over-exploitation status and countermeasure suggestions of the North China Plain. China Water Resources, 13: 26−30. (in Chinese) Lin XY. 1984. On development and utilization of groundwater reservoir. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 02: 113−121. (in Chinese) Liu LC, Zheng FD, Li BH, et al. 2015. Experiment of groundwater quality change for simulating the South-to-North water into the Mihuaishun aquifer. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 42(04): 18−22, 55. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2015.04.04. Moeck C, Radny D, Borer P, et al. 2016. Multicomponent statistical analysis to identify flow and transport processes in a highly-complex environment. Journal of Hydrology, 542: 437−449. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.09.023. Sarfaraz A, Annesh B, Sujith R, et al. 2021. Managed aquifer recharge implementation criteria to achieve water sustainability. Science of the Total Environment, 768: 1−19. DOI: 10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2021.144992. Shi JS, Li GM, Liang X, et al. 2014. Evolution mechanism and control of groundwater in the North China Plain. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 35(5): 527−534. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3975/cagsb.2014.05.01. Sprenger C, Hartog N, Hernández M, et al. 2017. Inventory of managed aquifer recharge sites in Europe: Historical development, current situation and perspectives. Hydrogeology Journal, 25: 1909−1922. DOI: 10.1007/s10040-017-1554-8. Tian MZ, Zhao L, Cui WJ, et al. 2022. Control and influence of rising groundwater level on land under the background of South-to-North Water Diversion: A case study of Chaobai River groundwater system in Beijing. Geology in China. (in Chinese) Tian X, Meng SH, Cui XX, et al. 2021. Hydrochemical Effect of groundwater recharge in over-exploited area of Hutuo River Basin. Research of Environmental Sciences, 34(03): 629−636. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2020.07.19. Wang Z, Fu Y, Zhu JS, et al. 2021. Effect assessment on groundwater recharge for typical rivers in North China. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 51(03): 843−853. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.20200078. Xiao Y, Shan R, Li S, et al. 2017. Change in groundwater resource and environment of South-to-North water recharge area of Chaobai River. Beijing Water, (04): 5−8. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.19671/j.1673-4637.2017.04.002. Yang HF, Cao WG, Zhi CS, et al. 2021. Evolution of groundwater level in the North China Plain in the past 40 years and suggestions on its overexploitation treatment. Geology in China, 48(04): 1142−1155. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.12029/gc20210411. Yang HF, Meng RF, Bao XL, et al. 2022. Assessment of water level threshold for groundwater restoration and over-exploitation remediation the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Plain. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 10(02): 113−127. Yu Y, Qi TL. 2020. Analysis on the effect of comprehensive control pilot project of groundwater supplement for groundwater over-abstraction in Northern China. Haihe Water Resources, (03): 7−9,16. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7328.2020.03.003. Zhang GH, Fei YH, Liu KY, et al. 2007. Groundwater potential recovery and water level variation in the Shijiazhuang water-receiving area at the central line of the south-to-north water transfer project. Geological Bulletin of China, 144(05): 583−589. (in Chinese) Zhang GH, Lian YL, Liu CH, et al. 2011. Situation and origin of water resources in short supply in North China Plain. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 33(2): 172−176. (in Chinese) Zhang ZJ, Fei YH, Chen ZY, et al. 2009. Investigation and Evaluation of Sustainable Utilization of Groundwater in North China Plain. Beijing: Geological publishing house. (in Chinese) Zheng FD, Liu LC, Yang MQ, et al. 2012. Simulation of water-rock interaction in the injection of water from the South-to-North Diversion Project to the aquifer in the western suburb of Beijing. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 39(06): 22−28. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2012.06.005. Zhu JY, Guo HP, Li WP, et al. 2014. Relationship between land subsidence and deep groundwater yield in the North China Plain. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 12(3): 165−169. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.13476/j.cnki.nsbdqk.2014.03.036. -

 E-mail alert
E-mail alert Rss
Rss



 下载:
下载: