Evaluating machine learning methods for predicting groundwater fluctuations using GRACE satellite in arid and semi-arid regions
-
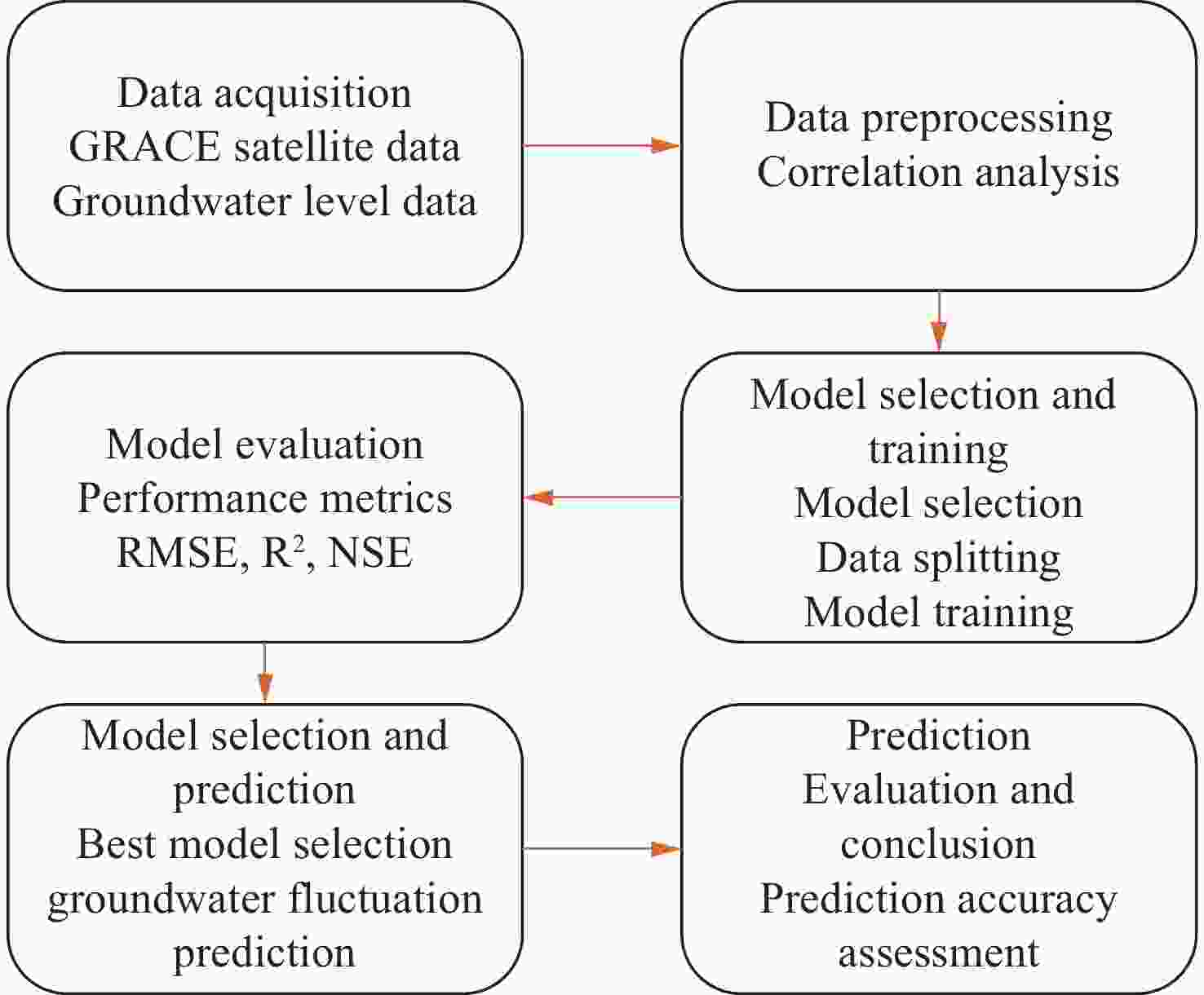
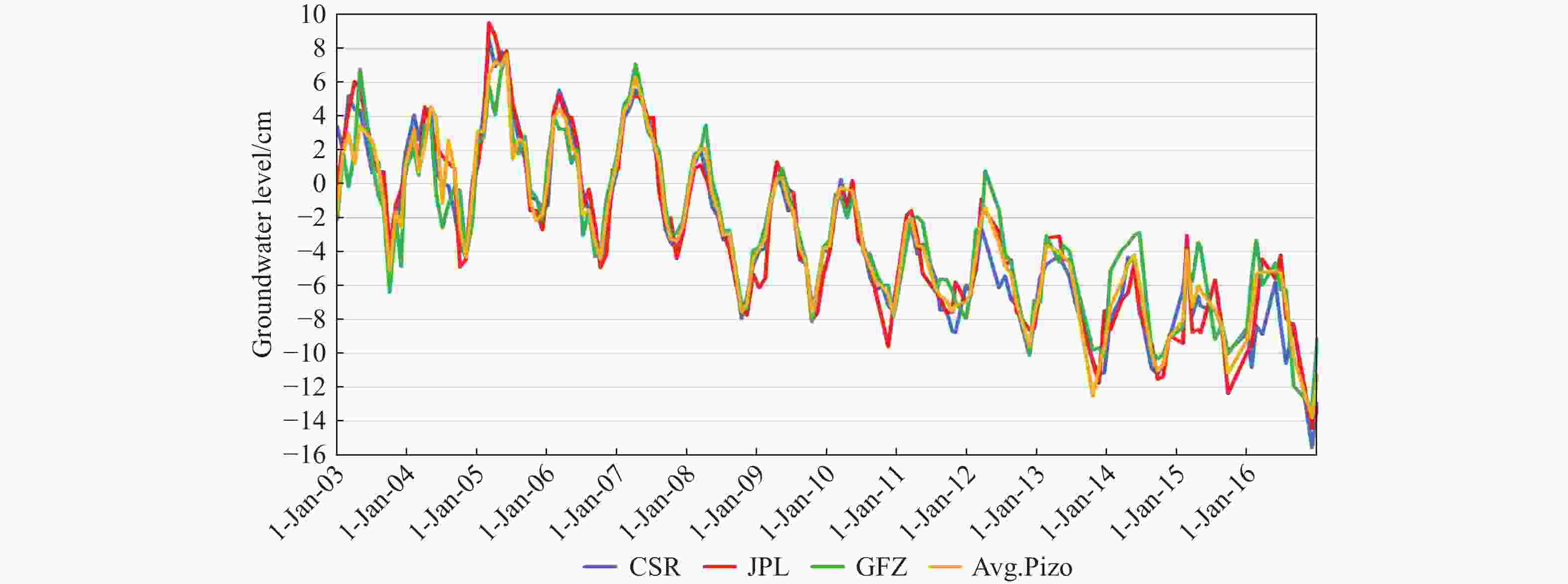
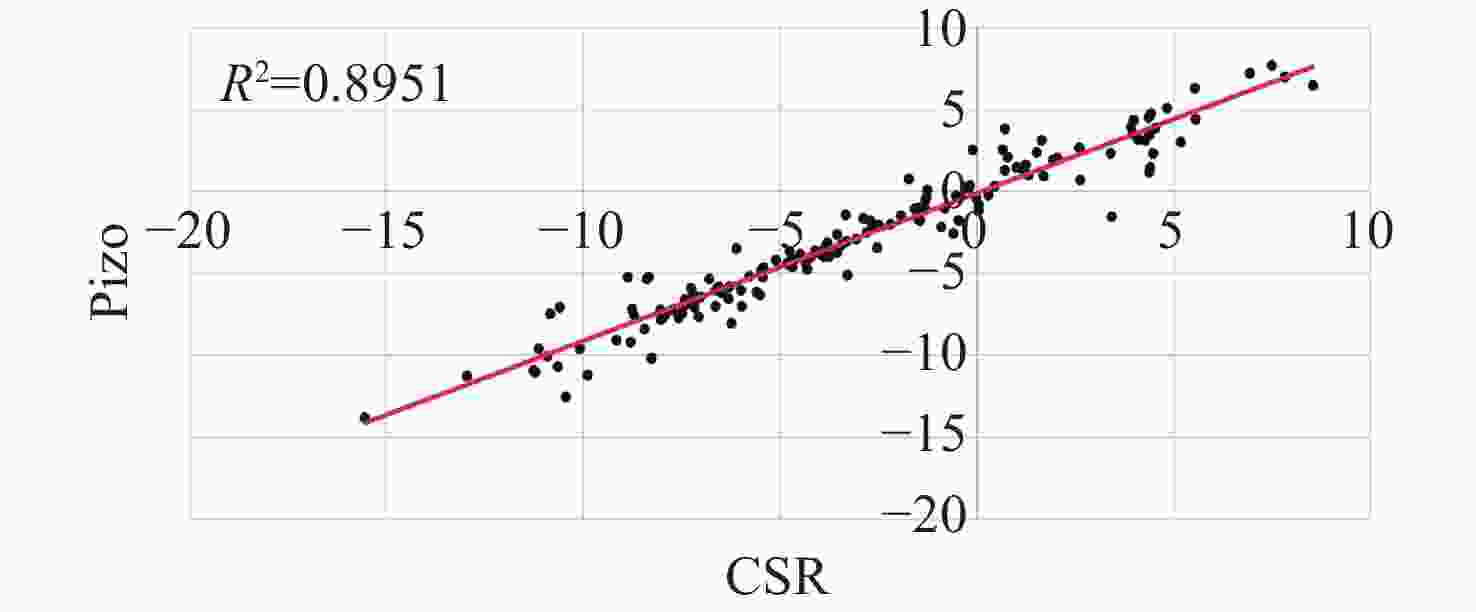
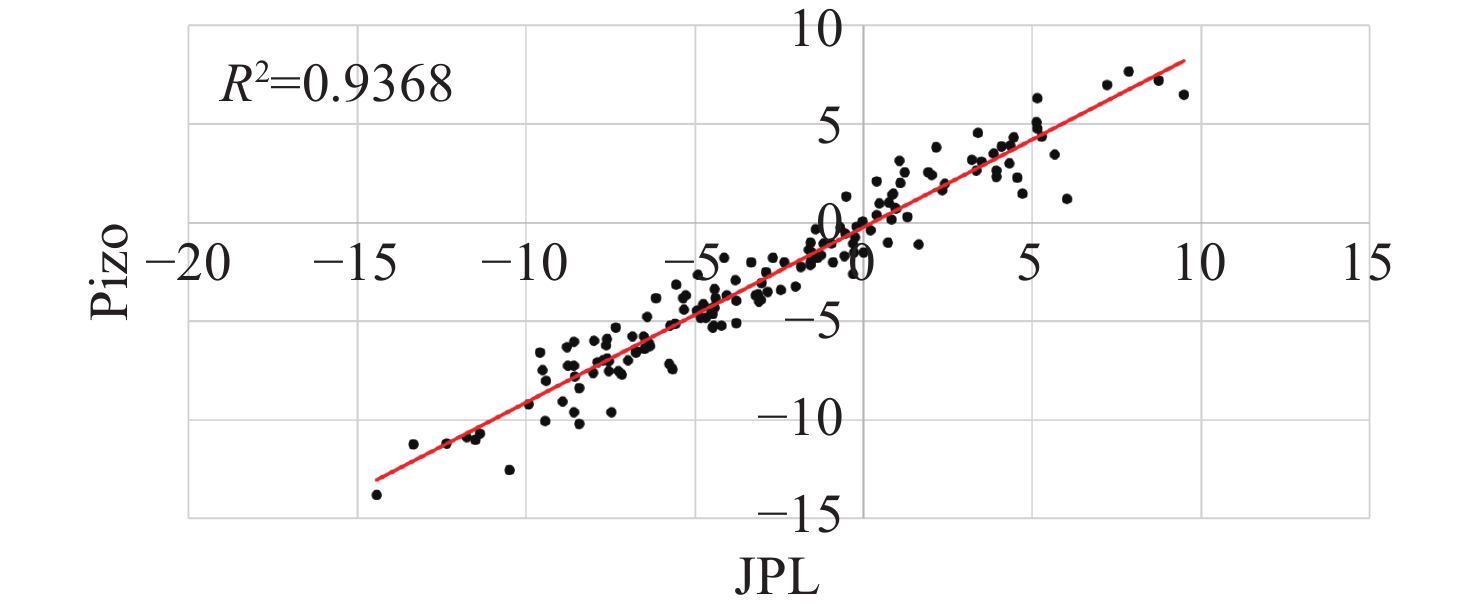
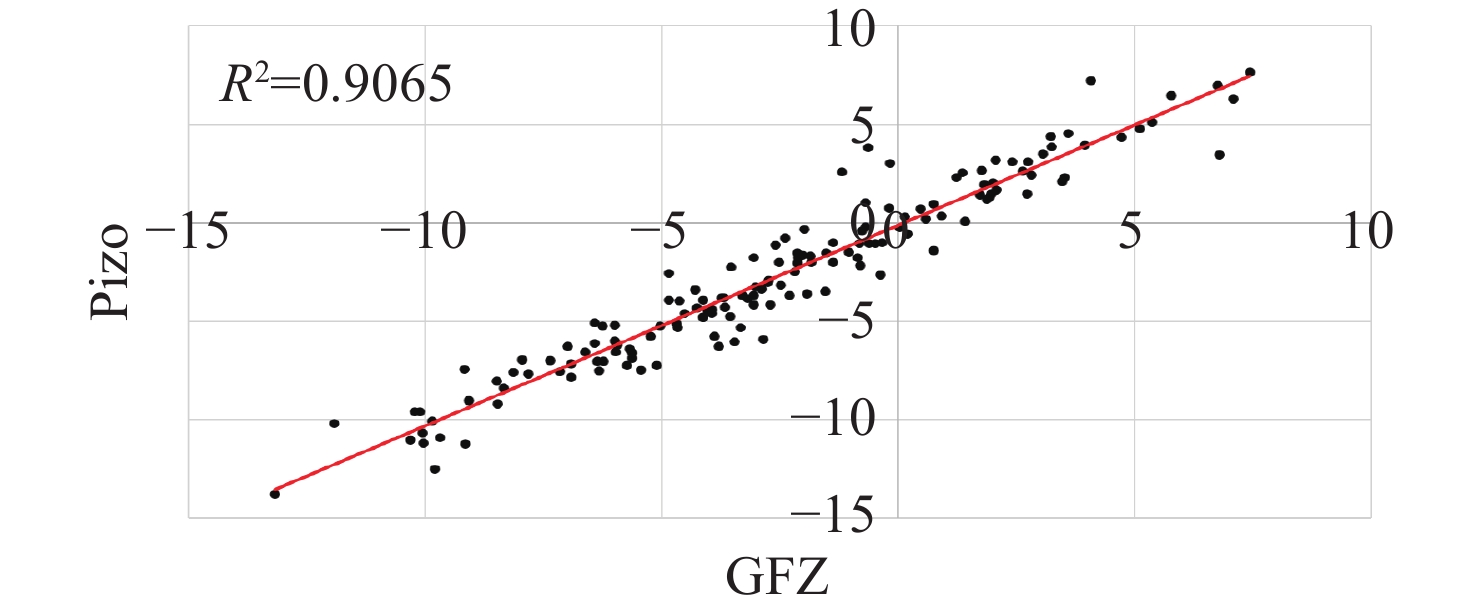
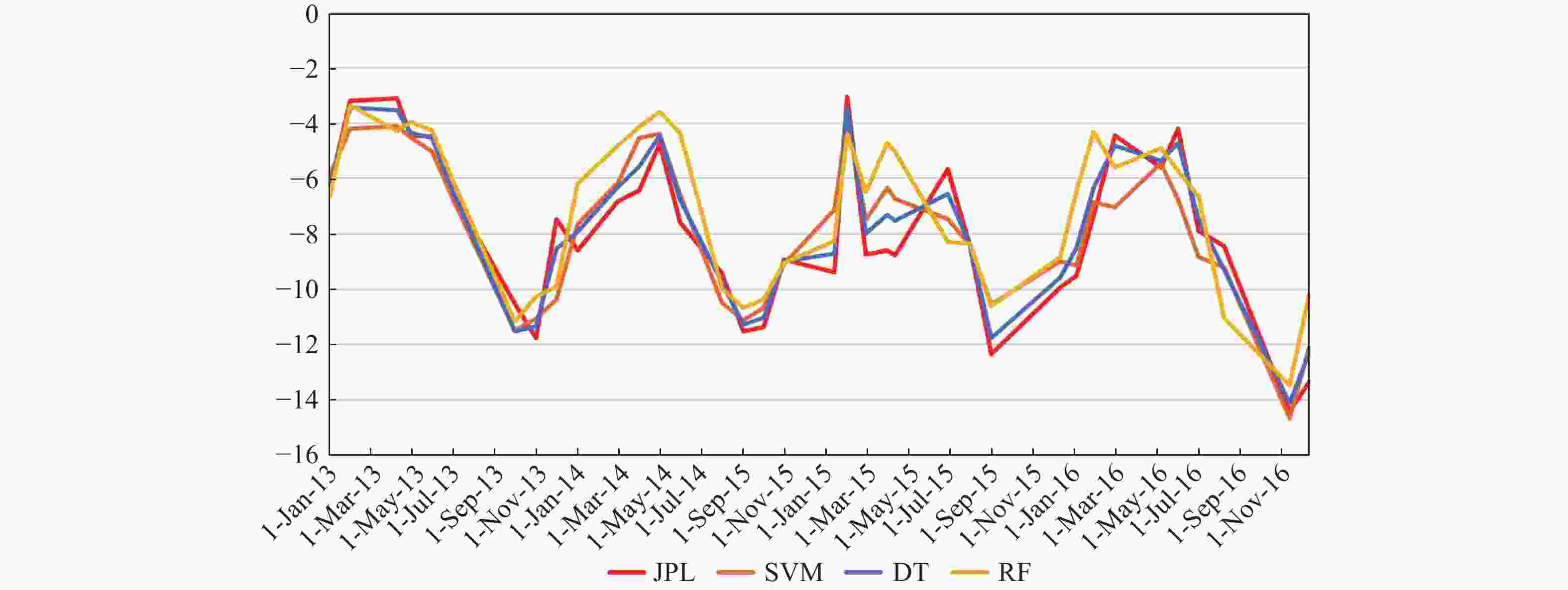
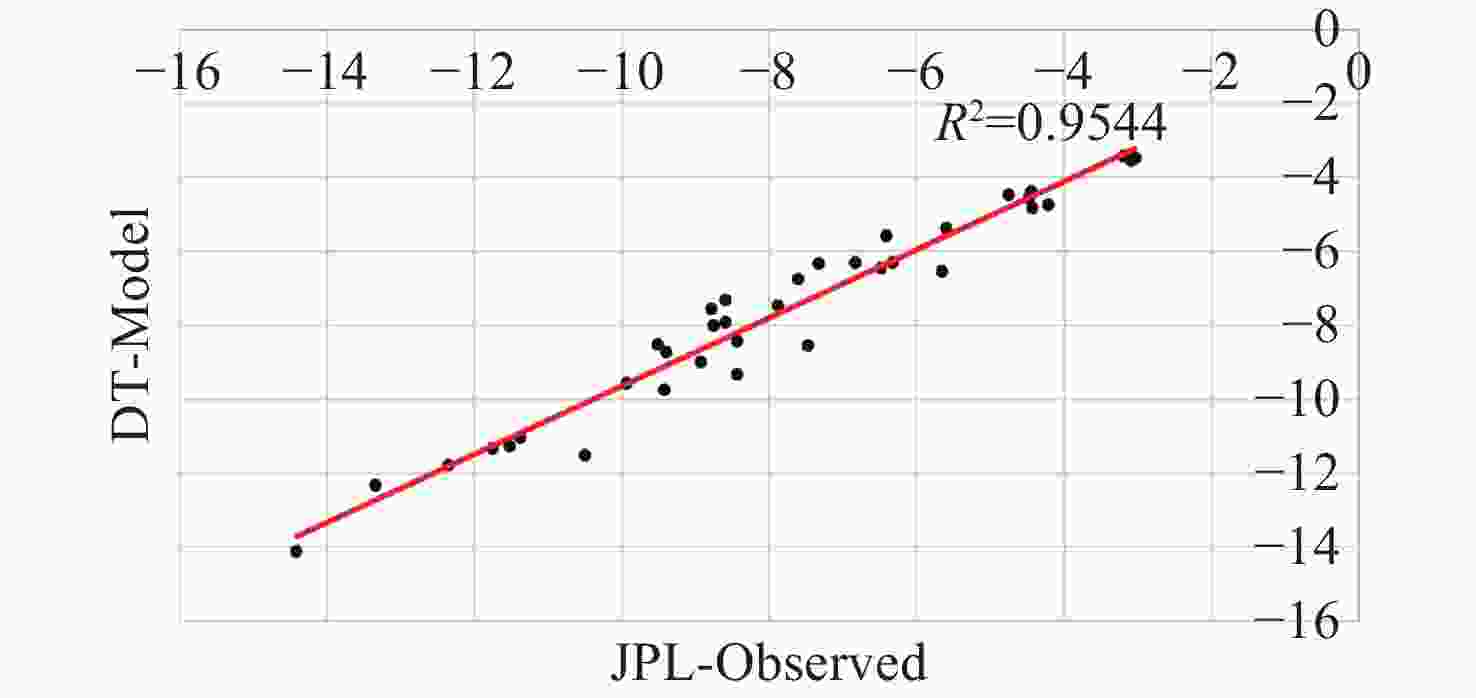
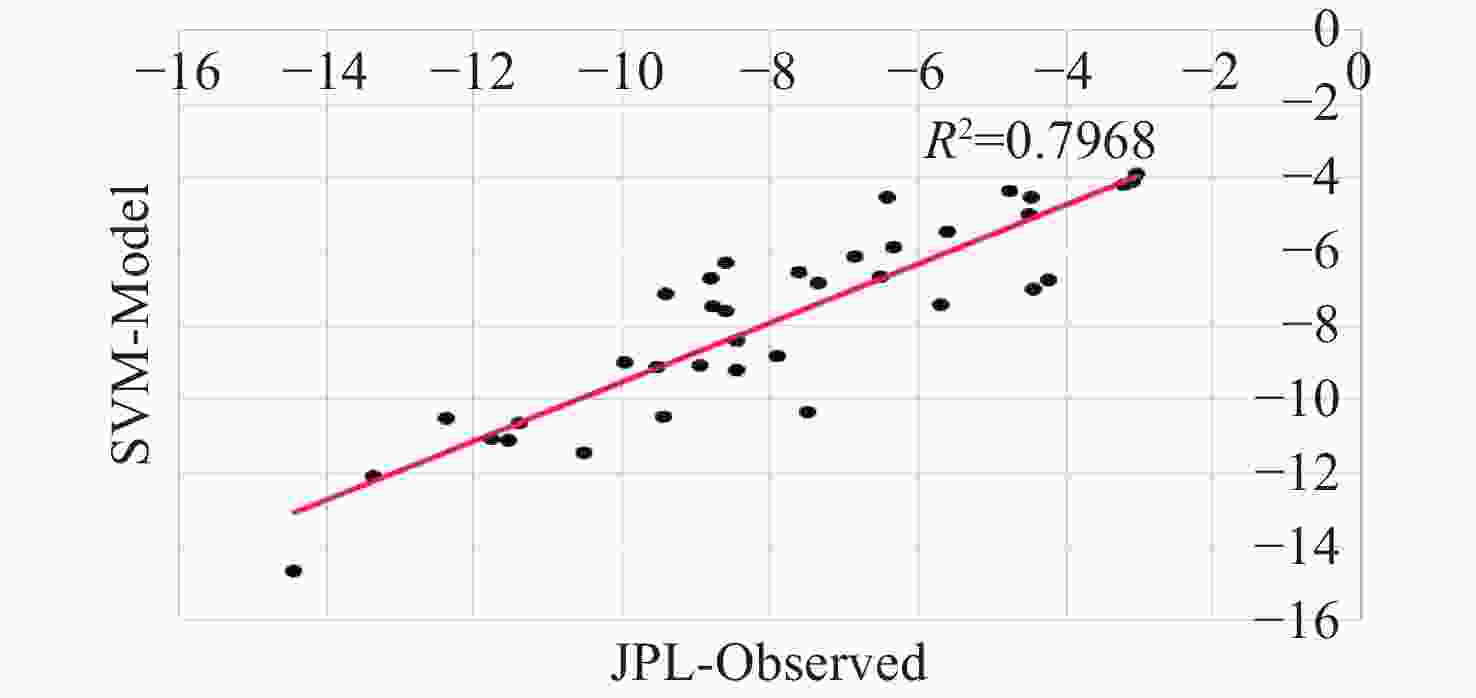
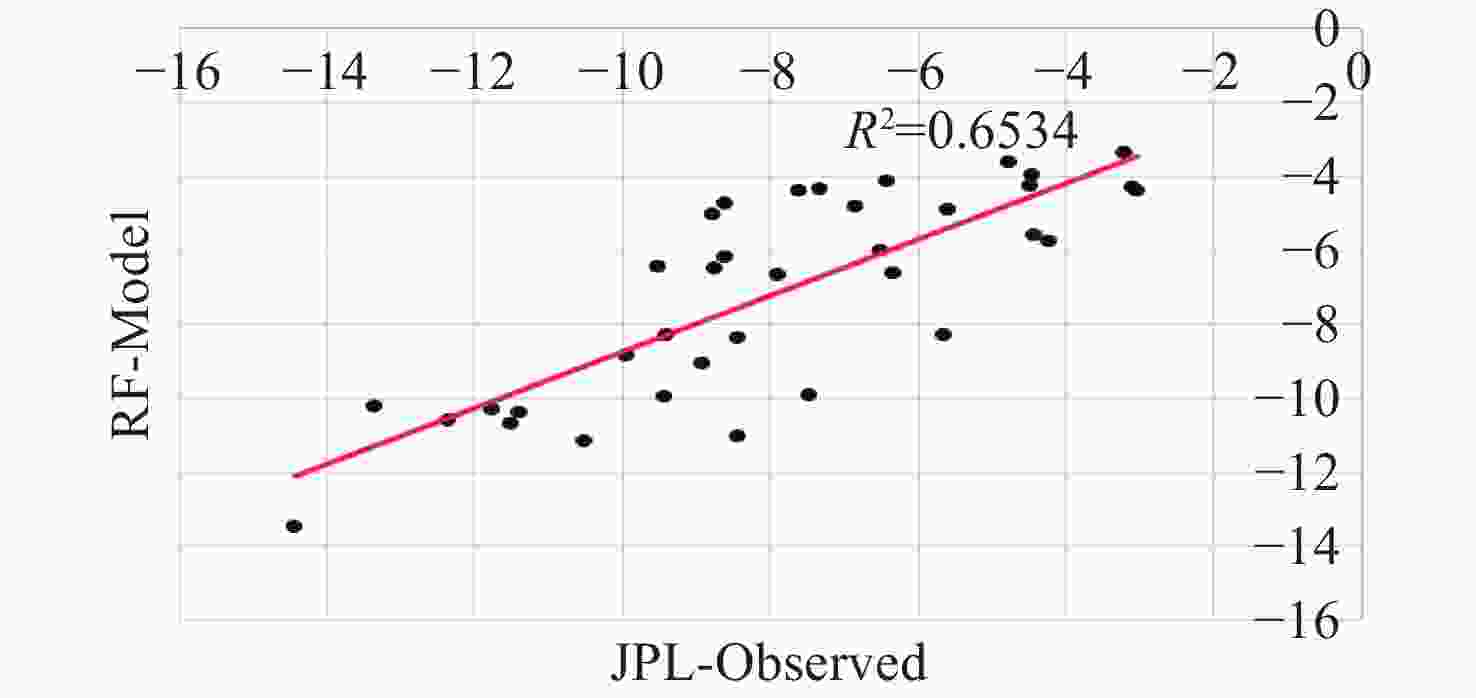
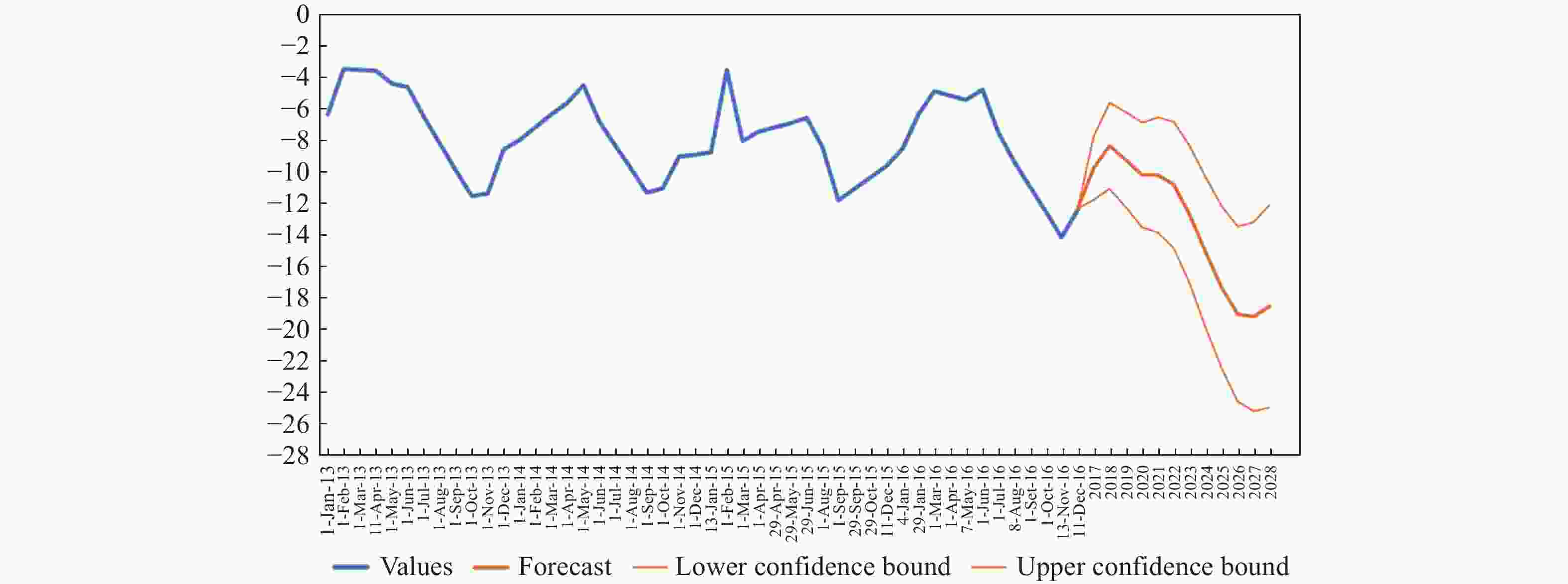
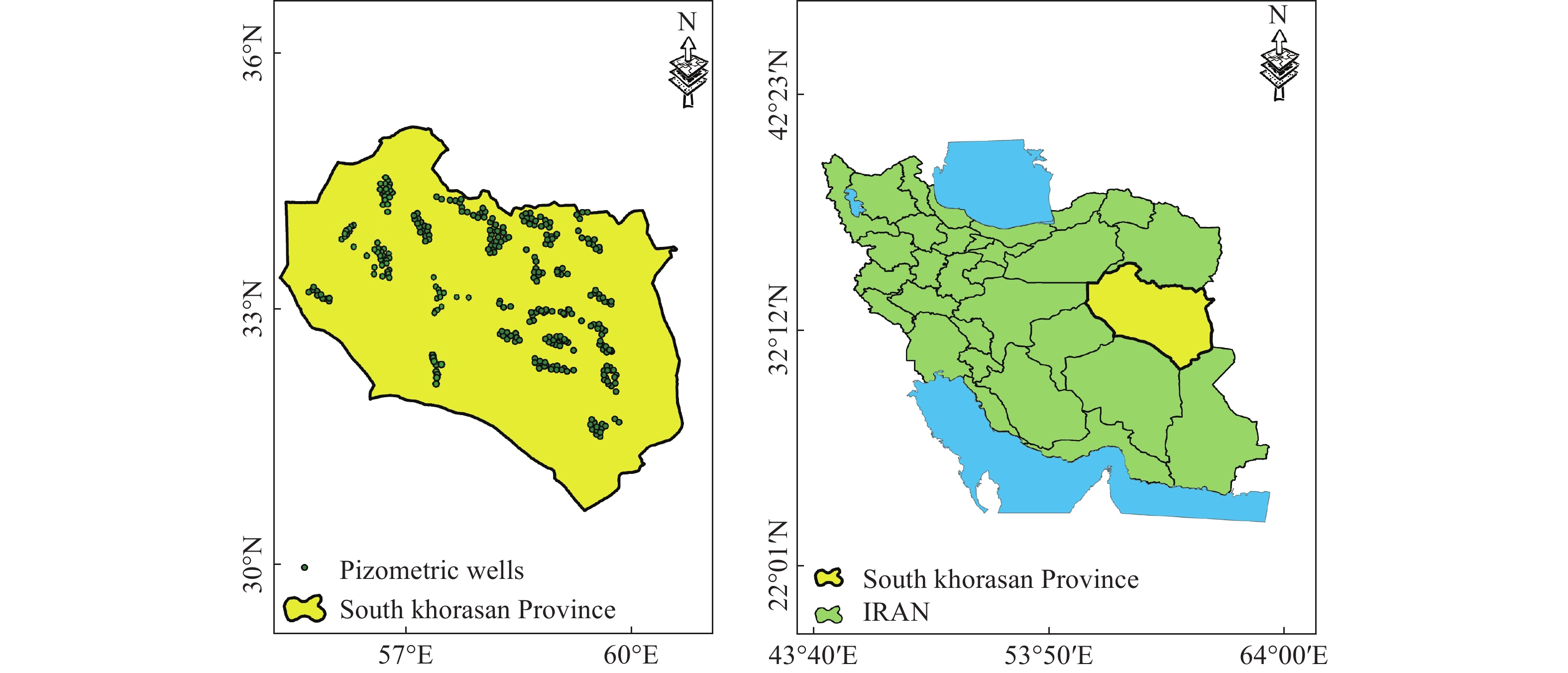
Abstract: This study aims to evaluate the effectiveness of machine learning techniques for predicting groundwater fluctuations in arid and semi-arid regions using data from the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment satellite mission. The primary objective is to develop accurate predictive models for groundwater level changes by leveraging the unique capabilities of GRACE satellite data in conjunction with advanced machine learning algorithms. Three widely-used machine learning models, namely DT, SVM and RF, were employed to analyze and model the relationship between GRACE satellite data and groundwater fluctuations in South Khorasan Province, Iran. The study utilized 151 months of GRACE data spanning from 2002 to 2017, which were correlated with piezometer well data available in the study area. The JPL model was selected based on its strong correlation (R2 = 0.9368) with the observed data. The machine learning models were trained and validated using a 70/30 split of the data, and their performance was evaluated using various statistical metrics, including RMSE, R2 and NSE. The results demonstrated the suitability of machine learning approaches for modeling groundwater fluctuations using GRACE satellite data. The DT model exhibited the best performance during the calibration stage, with an R2 value of 0.95, RMSE of 0.655, and NSE of 0.96. The SVM and RF models achieved R2 values of 0.79 and 0.65, and NSE values of 0.86 and 0.71, respectively. For the prediction stage, the DT model maintained its high efficiency, with an RMSE of 1.48, R2 of 0.87, and NSE of 0.90, indicating its robustness in predicting future groundwater fluctuations using GRACE data. The study highlights the potential of machine learning techniques, particularly Decision Trees, in conjunction with GRACE satellite data, for accurate prediction and monitoring of groundwater fluctuations in arid and semi-arid regions. The findings demonstrate the effectiveness of the DT model in capturing the complex relationships between GRACE data and groundwater dynamics, providing reliable predictions and insights for sustainable groundwater management strategies.
-
Key words:
- Decision Trees /
- Support Vector Machines /
- Random Forests /
- GRACE Satellite /
- Groundwater level
-
Table 1. Calibration evaluation of machine learning models
Models R2 RMSE NSE SVM 0.79 1.304 0.86 DT 0.95 0.655 0.96 RF 0.65 1.896 0.71 Table 2. Evaluation of the DT model in predicting groundwater fluctuations
RMSE R2 NSE 1.48 0.87 0.9 -
Afraz A, Eftekhari M, Akbari M, et al. 2021. Application assessment of GRACE and CHIRPS data in the Google Earth Engine to investigate their relation with groundwater resource changes (Northwestern region of Iran). Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 9(2): 102−113. DOI: 10.19637/j.cnki.2305-7068.2021.02.002. Ali S, Liu D, Fu Q, et al. 2021. Improving the resolution of GRACE data for spatio-temporal groundwater storage assessment. Remote Sensing, 13(17): 3513. DOI: 10.3390/rs13173513. Barros RC, Basgalupp MP, de Carvalho ACPLF, et al. 2012. A survey of evolutionary algorithms for decision-tree induction. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews), 42(3): 291−312. DOI: 10.1109/TSMCC.2011.2157494. Bhavsar H, Panchal MH. 2012. A review on support vector machine for data classification. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Engineering and Technology (IJARCET), 1(10): 185−189. Charbuty B, Abdulazeez A. 2021. Classification based on decision tree algorithm for machine learning. Journal of Applied Science and Technology Trends, 2(1): 20−28. DOI: 10.38094/jastt20165. Chen JL. 2019. Satellite gravimetry and mass transport in the earth system. Geodesy and Geodynamics, 10(5): 402−415. DOI: 10.1016/j.geog.2018.07.001. Chen JL, Cazenave A, Dahle C, et al. 2022. Applications and challenges of GRACE and GRACE follow-on satellite gravimetry. Surveys in Geophysics, 43(1): 305−345. DOI: 10.1007/s10712-021-09685-x. Chen JL, Famigliett JS, Scanlon BR, et al. 2016. Groundwater storage changes: Present status from GRACE observations. Surveys in Geophysics, 37(2): 397−417. DOI: 10.1007/s10712-015-9332-4. Coelho VHR, Bertrand GF, Montenegro SMGL, et al. 2018. Piezometric level and electrical conductivity spatiotemporal monitoring as an instrument to design further managed aquifer recharge strategies in a complex estuarial system under anthropogenic pressure. Journal of Environmental Management, 209: 426−439. DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.12.078. Dong HW, Yang LM, Wang X. 2021. Robust semi-supervised support vector machines with Laplace kernel-induced correntropy loss functions. Applied Intelligence, 51(2): 819−833. DOI: 10.1007/s10489-020-01865-3. Eftekhari M, Madadi K, Akbari M. 2019. Monitoring the fluctuations of the Birjand Plain aquifer using the GRACE satellite images and the GIS spatial analyses. Watershed Management Research Journal, 32(4): 51−65. (In Persian). DOI: 10.22092/wmej.2019.126204.1218. Fawagreh K, Gaber MM, Elyan E. 2014. Random forests: From early developments to recent advancements. Systems Science and Control Engineering, 2(1): 602−609. DOI: 10.1080/21642583.2014.956265. Feng W, Shum C, Zhong M, et al. 2018. Groundwater storage changes in China from satellite gravity: An overview. Remote Sensing, 10(5): 674. DOI: 10.3390/rs10050674. Font-Capo J, Pujades E, Vàzquez-Suñé E, et al. 2015. Assessment of the barrier effect caused by underground constructions on porous aquifers with low hydraulic gradient: A case study of the metro construction in Barcelona, Spain. Engineering Geology, 196: 238−250. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.07.006. Frappart F, Ramillien G. 2018. Monitoring groundwater storage changes using the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) satellite mission: A review. Remote Sensing, 10(6): 829. DOI: 10.3390/rs10060829. Genuer R, Poggi JM. 2020. Random forests. Cham: Springer International Publishing: 33−55. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-56485-8_3. Gilbert J, Boateng C, Aryee J, et al. 2023. A systematic review of machine learning algorithms in groundwater level simulations and forecasting. Preprint. Gleeson T, Cuthbert M, Ferguson G, et al. 2020. Global groundwater sustainability, resources, and systems in the anthropocene. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 48: 431−463. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-earth-071719-055251. Gong CC, Cook PG, Therrien R, et al. 2023. On groundwater recharge in variably saturated subsurface flow models. Water Resources Research, 59(9): e2023wr034920. DOI: 10.1029/2023wr034920. Gong CC, Zhang ZY, Wang WK, et al. 2021. An assessment of different methods to determine specific yield for estimating groundwater recharge using lysimeters. Science of the Total Environment, 788: 147799. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147799. Haileslassie T, Gebremedhin K. 2015. Hazards of heavy metal contamination in ground water. International Journal of Technology Enhancements and Emerging Engineering Research, 3(2), 1−6. Hilario M, Kalousis A, Pellegrini C, et al. 2006. Processing and classification of protein mass spectra. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 25(3): 409−449. DOI: 10.1002/mas.20072. Honarbakhsh A, Azma A, Nikseresht F, et al. 2019. Hydro-chemical assessment and GIS-mapping of groundwater quality parameters in semi-arid regions. Journal of Water Supply: Research and Technology-Aqua, 68(7): 509−522. DOI: 10.2166/aqua.2019.009. Humphrey V, Rodell M, Eicker A. 2023. Using satellite-based terrestrial water storage data: A review. Surveys in Geophysics, 44(5): 1489−1517. DOI: 10.1007/s10712-022-09754-9. Joachims T. 2012. Learning to classify text using support vector machines (Vol. 668). Springer Science and Business Media. DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0907-3. Kalbus E, Reinstorf F, Schirmer M. 2006. Measuring methods for groundwater–surface water interactions: Areview. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 10(6): 873−887. DOI: 10.5194/hess-10-873-2006. Khanlari G, Heidari M, Momeni AA, et al. 2012. The effect of groundwater overexploitation on land subsidence and sinkhole occurrences, western Iran. Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology and Hydrogeology, 45(4): 447−456. DOI: 10.1144/qjegh2010-069. King Z, Farrington J, Utley M, et al. 2022. Machine learning for real-time aggregated prediction of hospital admission for emergency patients. NPJ Digital Medicine, 5(1): 104. DOI: 10.1038/s41746-022-00649-y. Kumar D, Bhattacharjya RK. 2021. GRNN Model for prediction of groundwater fluctuation in the state of Uttarakhand of India using GRACE data under limited bore well data. Journal of Hydroinformatics, 23(3): 567−588. DOI: 10.2166/hydro.2021.108. Li FP, Wang ZT, Chao NF, et al. 2018. Assessing the influence of the Three Gorges Dam on hydrological drought using GRACE data. Water, 10(5): 669. DOI: 10.3390/w10050669. Li PY, Wu JH, Zhou WF, et al. 2023. Groundwater contamination and induced risk and hazard in a Karst aquifer. Environmental Earth Sciences. Cham: Springer International Publishing: 179−256. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-031-48427-8_7. Liu Q, Gui DW, Zhang L, et al. 2022. Simulation of regional groundwater levels in arid regions using interpretable machine learning models. Science of the Total Environment, 831: 154902. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154902. Liu W, Yu HJ, Yang LS, et al. 2021. Deep learning-based predictive framework for groundwater level forecast in arid irrigated areas. Water, 13(18): 2558. DOI: 10.3390/w13182558. Longuevergne L, Scanlon BR, Wilson CR. 2010. GRACE hydrological estimates for small basins: Evaluating processing approaches on the high Plains aquifer, USA. Water Resources Research, 46(11): e2009wr008564. DOI: 10.1029/2009wr008564. Louppe G. 2014. Understanding random forests: From theory to practice. Ph D. thesis. University of Liège: 1407. Maimon OZ, Rokach L. 2014. Data mining with decision trees: Theory and applications: 81. World scientific. Matin SS, Farahzadi L, Makaremi S, et al. 2018. Variable selection and prediction of uniaxial compressive strength and modulus of elasticity by random forest. Applied Soft Computing, 70: 980−987. DOI: 10.1016/j.asoc.2017.06.030. Meyer U, Sosnica K, Arnold D, et al. 2019. SLR, GRACE and swarm gravity field determination and combination. Remote Sensing, 11(8): 956. DOI: 10.3390/rs11080956. Moore S, Fisher JB. 2012. Challenges and opportunities in GRACE-based groundwater storage assessment and management: An example from Yemen. Water Resources Management, 26(6): 1425−1453. DOI: 10.1007/s11269-011-9966-z. Patel HH, Prajapati P. 2018. Study and analysis of decision tree based classification algorithms. International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering, 6(10): 74−78. DOI: 10.26438/ijcse/v6i10.7478. Rai K, Devi MS, Guleria A. 2016. Decision tree based algorithm for intrusion detection. International Journal of Advanced Networking and Applications, 7(4), 2828. Rajaee G, Hajizadeh F, Salman MA, et al. 2011. An analysis of physical-chemical properties and quality of underground agricultural and drinking water in Southern Khorasan Province. Environmental Researches, 3(5), 13−24. (In Persian) https://dorl.net/dor/20.1001.1.20089597.1391.3.5.3.4 Ram AP. 2022. Unsupervised representation learning of GRACE improves groundwater predictions. Water, 14(19): 2947. DOI: 10.3390/w14192947. Rivera-Lopez R, Canul-Reich J, Mezura-Montes E, et al. 2022. Induction of decision trees as classification models through metaheuristics. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 69: 101006. DOI: 10.1016/j.swevo.2021.101006. Roy DK, Munmun TH, Paul CR, et al. 2023. Improving forecasting accuracy of multi-scale groundwater level fluctuations using a heterogeneous ensemble of machine learning algorithms. Water, 15(20): 3624. DOI: 10.3390/w15203624. Sahour H, Sultan M, Abdellatif B, et al. 2022. Identification of shallow groundwater in arid lands using multi-sensor remote sensing data and machine learning algorithms. Journal of Hydrology, 614: 128509. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.128509. Sansone M, Fusco R, Pepino A, et al. 2013. Electrocardiogram pattern recognition and analysis based on artificial neural networks and support vector machines: A review. Journal of Healthcare Engineering, 4(4): 465−504. DOI: 10.1260/2040-2295.4.4.465. Saputra DCE, Ma'arif A, Sunat K. 2024. Optimizing predictive performance: Hyperparameter tuning in stacked multi-kernel support vector machine random forest models for diabetes identification. Journal of Robotics and Control (JRC), 4(6): 896−904. DOI: 10.18196/jrc.v4i6.20898. Schelter LN. 2021. On groundwater monitoring using machine learning and satellite remote sensing (Doctoral dissertation). Ph.D thesis. Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule Aachen. Seidu J, Ewusi A, Kuma JSY, et al. 2023. Impact of data partitioning in groundwater level prediction using artificial neural network for multiple wells. International Journal of River Basin Management, 21(4): 639−650. DOI: 10.1080/15715124.2022.2079653. Seni G, Elder JF. 2010. Ensemble Methods in Data Mining: Improving accuracy through combining predictions. ChamSpringer International Publishing, DOI: 10.1007/978-3-031-01899-2. Seo JY, Lee SI. 2021. Predicting changes in spatiotemporal groundwater storage through the integration of multi-satellite data and deep learning models. IEEE Access, 9: 157571−157583. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3130306. Shao Y, Lunetta RS. 2012. Comparison of support vector machine, neural network, and CART algorithms for the land-cover classification using limited training data points. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 70: 78−87. DOI: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2012.04.001. Shouval R, Bondi O, Mishan H, et al. 2014. Application of machine learning algorithms for clinical predictive modeling: A data-mining approach in SCT. Bone Marrow Transplantation, 49(3): 332−337. DOI: 10.1038/bmt.2013.146. Singha S, Pasupuleti S, Singha SS, et al. 2021. Prediction of groundwater quality using efficient machine learning technique. Chemosphere, 276: 130265. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130265. Springer A, Eicker A, Bettge A, et al. 2017. Evaluation of the water cycle in the European COSMO-REA6 reanalysis using GRACE. Water, 9(4): 289. DOI: 10.3390/w9040289. Sun AY. 2013. Predicting groundwater level changes using GRACE data. Water Resources Research, 49(9): 5900−5912. DOI: 10.1002/wrcr.20421. Swenson S, Wahr J. 2002. Methods for inferring regional surface-mass anomalies from Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) measurements of time-variable gravity. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 107(B9). DOI: 10.1029/2001jb000576. Wang J, Lu SY, Wang SH, et al. 2022. A review on extreme learning machine. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 81(29): 41611−41660. DOI: 10.1007/s11042-021-11007-7. Wang YH, Gupta HV. 2024. A mass-conserving-perceptron for machine-learning-based modeling of geoscientific systems. Water Resources Research, 60(4): e2023wr036461. DOI: 10.1029/2023wr036461. Werth S, Güntner A, Schmidt R, et al. 2009. Evaluation of GRACE filter tools from a hydrological perspective. Geophysical Journal International, 179(3): 1499−1515. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04355.x. Wilhite DA, Glantz MH. 1985. Understanding: The drought phenomenon: The role of definitions. Water International, 10(3): 111−120. DOI: 10.1080/02508068508686328. Wouters B, Bonin JA, Chambers DP, et al. 2014. GRACE, time-varying gravity, Earth system dynamics and climate change. Reports on Progress in Physics. Physical Society (Great Britain), 77(11): 116801. DOI: 10.1088/0034-4885/77/11/116801. Yaman A, Cengiz MA. 2021. The effects of kernel functions and optimal hyperparameter selection on support vector machines. Journal of New Theory, (34): 64−71. Yang YT, Long D, Guan HD, et al. 2014. GRACE satellite observed hydrological controls on interannual and seasonal variability in surface greenness over mainland Australia. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 119(12): 2245−2260. DOI: 10.1002/2014jg002670. Yao H, Qin RJ, Chen XY. 2019. Unmanned aerial vehicle for remote sensing applications—a review. Remote Sensing, 11(12): 1443. DOI: 10.3390/rs11121443. Zhang XM, Wang N, Cao LS, et al. 2024. Analysis of the contribution of rainfall to recharge in the Mu Us Desert (China) based on lysimeter data. Hydrogeology Journal, 32(1): 279−288. DOI: 10.1007/s10040-023-02750-2. Zhu FB. 2018. A classification algorithm of CART decision tree based on MapReduce attribute weights. International Journal of Performability Engineering, 14(1): 17. DOI: 10.23940/ijpe.18.01.p3.1725. Ziegler A, König IR. 2014. Mining data with random forests: Current options for real-world applications. WIREs Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 4(1): 55−63. DOI: 10.1002/widm.1114. -

 E-mail alert
E-mail alert Rss
Rss


 下载:
下载: