Groundwater exploration using integrated geophysics method in hard rock terrains in Mount Betung Western Bandar Lampung, Indonesia
-
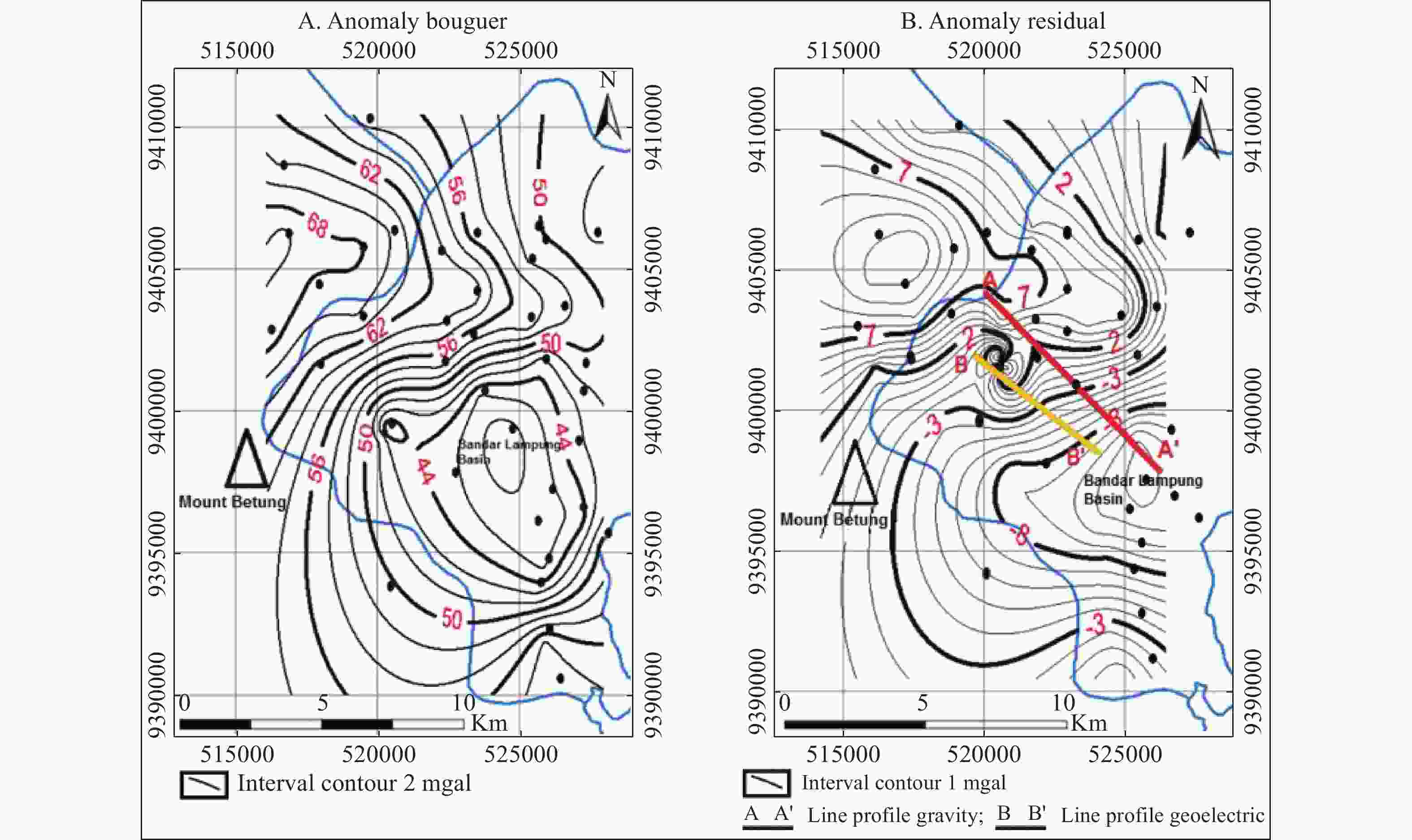
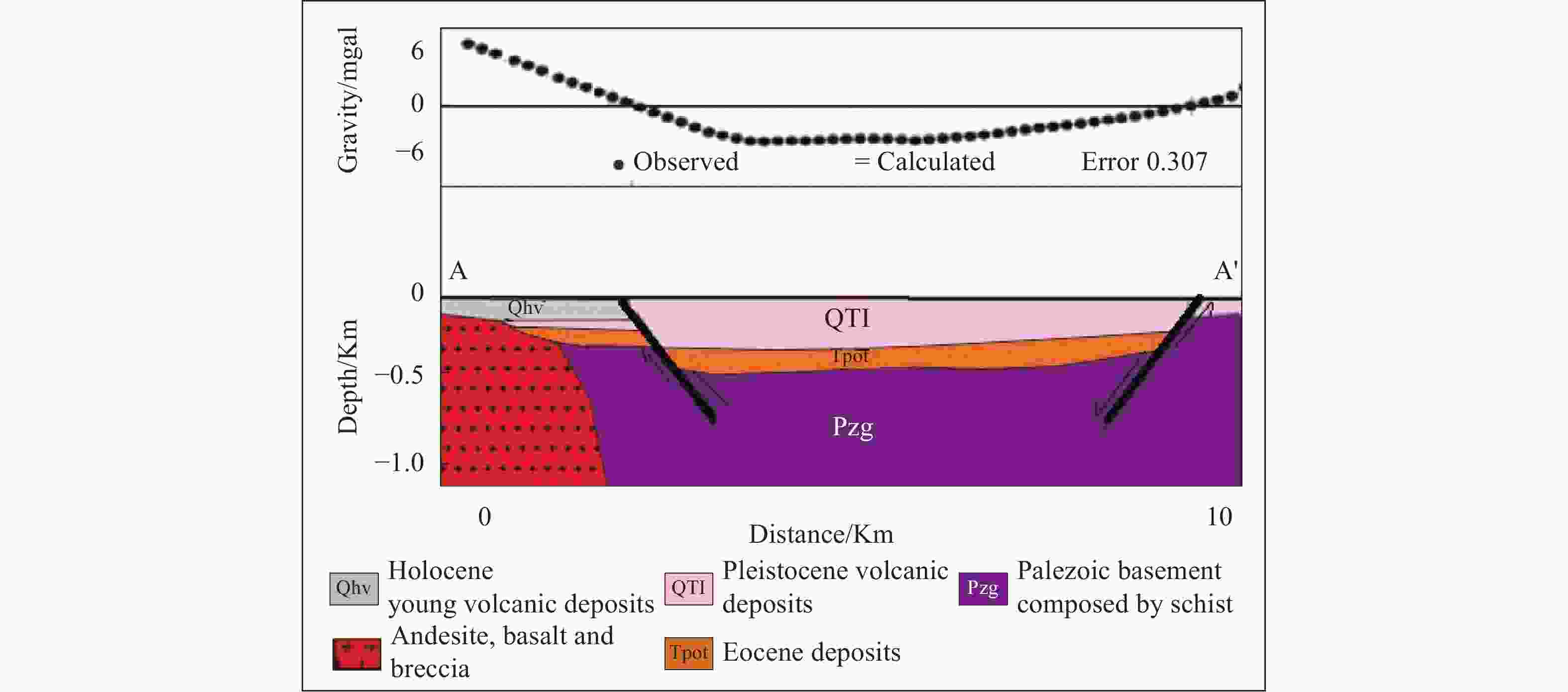
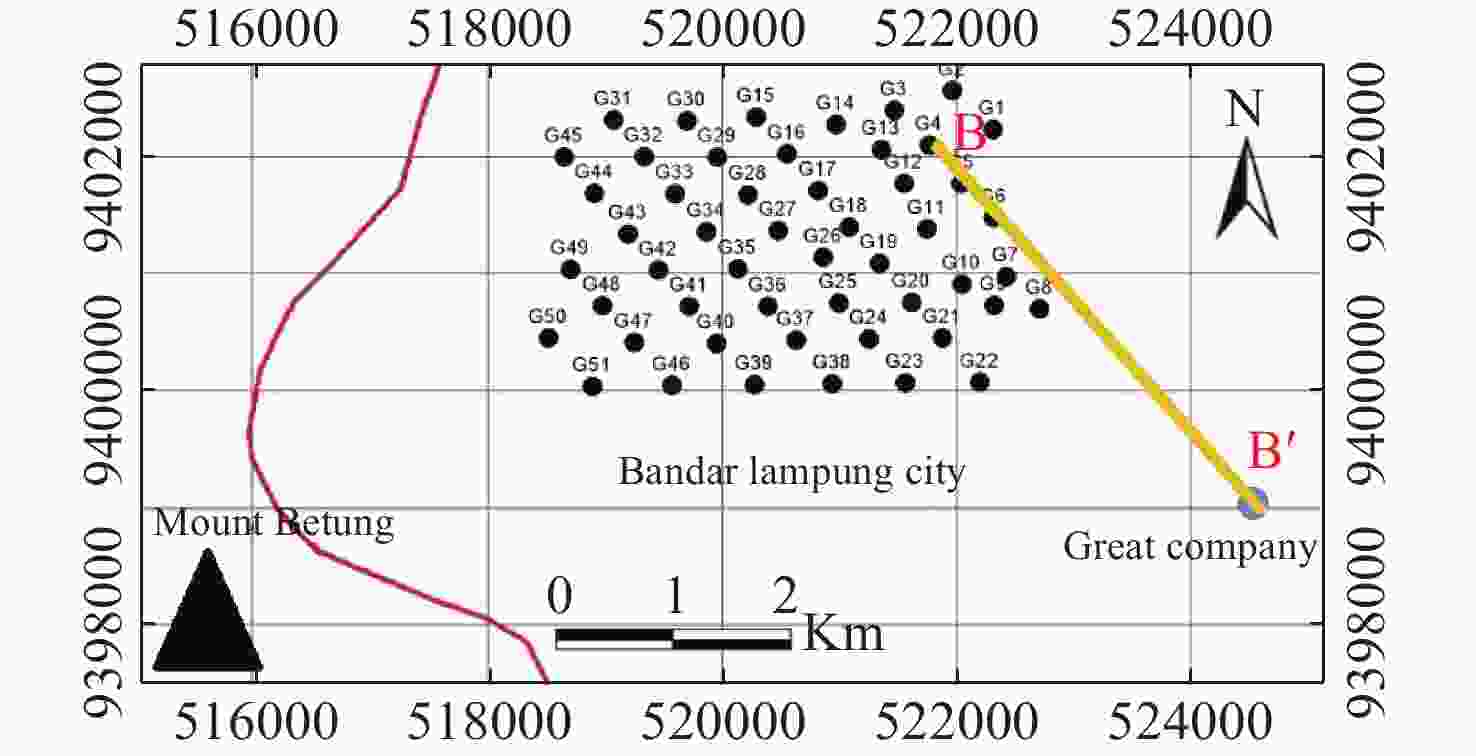
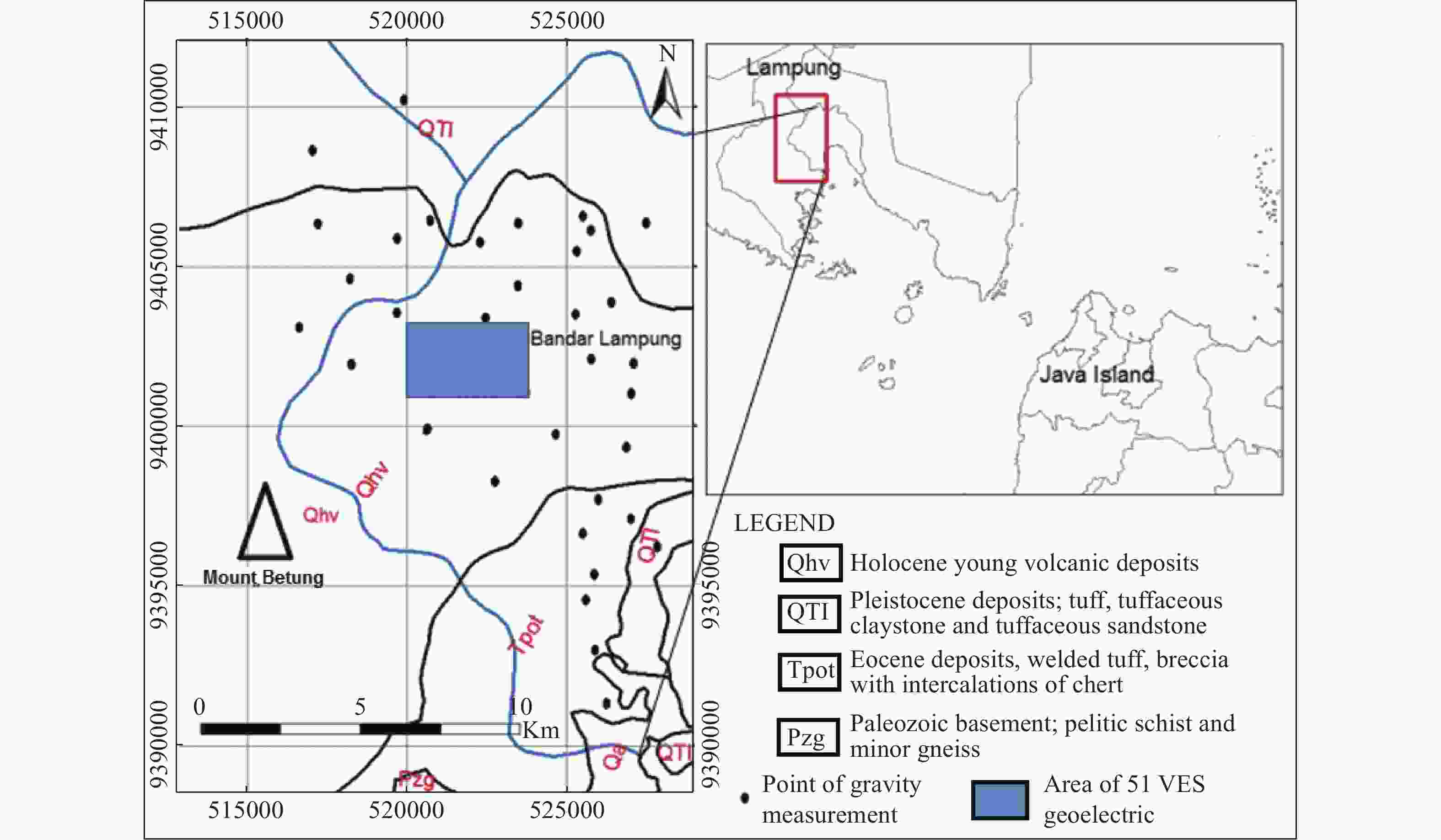
Abstract: The presence of hard rock in Mount Betung has caused the misalignment of the groundwater aquifers, and resulted in many drilling failures for groundwater. An integrated geophysics method using gravity survey and Geoelectric Vertical Electrical Soundings (VES) were conducted to study the effect of basement and hard rock on groundwater prospects. From the gravity method, 38 mapping points were carried out randomly, with a distance of 1-2 km in-between. Meanwhile, from the geoelectric method, 51 VES points were acquired at the foot of Mount Betung. The acquisition was conducted with a Schlumberger configuration with AB/2 = 1 m to 250 m. The results show the Bouguer Anomaly in the west is 50-68 mgal due to the presence of hard rock in Mount Betung. This anomaly responds to relatively shallow hard rocks near surface. Hard rocks composed of andesite and breccia normally present at the depth of 5-180 m during well construction. Resistivity isopach mapping from VES data (at AB/2 = 50 m, 100 m, and 150 m) shows the dominant constituents of hard rock. Fractures in hard rock contribute to secondary porosity, which could be a prospect zone that transmit groundwater. This finding shows that the fractures are randomly scattered, causing several well failures that have been worked. Furthermore, the fractures in the hard rock at the foot of Mount Betung acts as conduits between recharge at Mount Betung and the aquifer in the Bandar Lampung Basin.
-
Key words:
- Geoelectric /
- Gravity /
- Groundwater /
- Hard /
- Rocks /
- VES
-
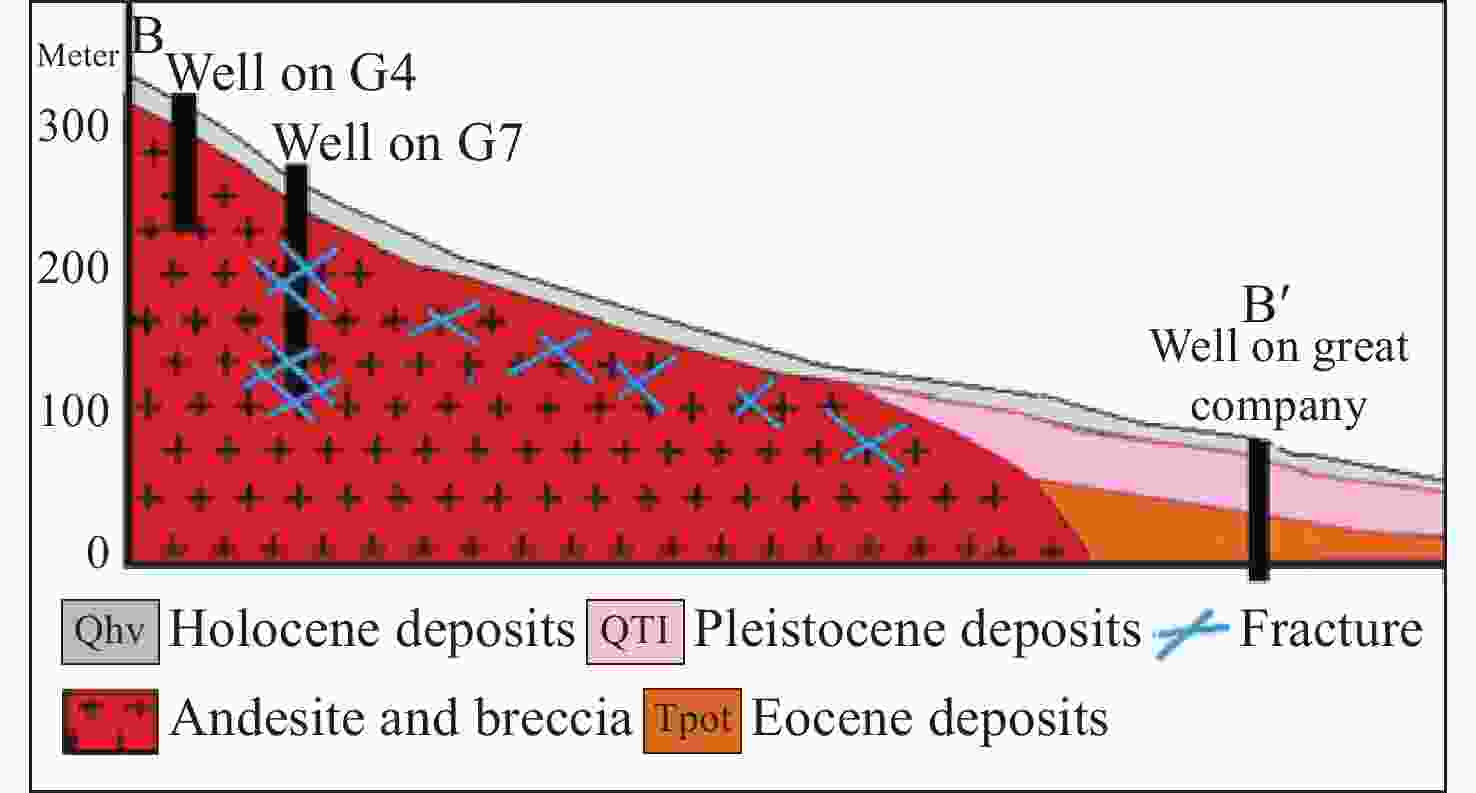
Table 1. Approximate depths, widths and the nature and geological conditions of aquifers of boreholes in the study area
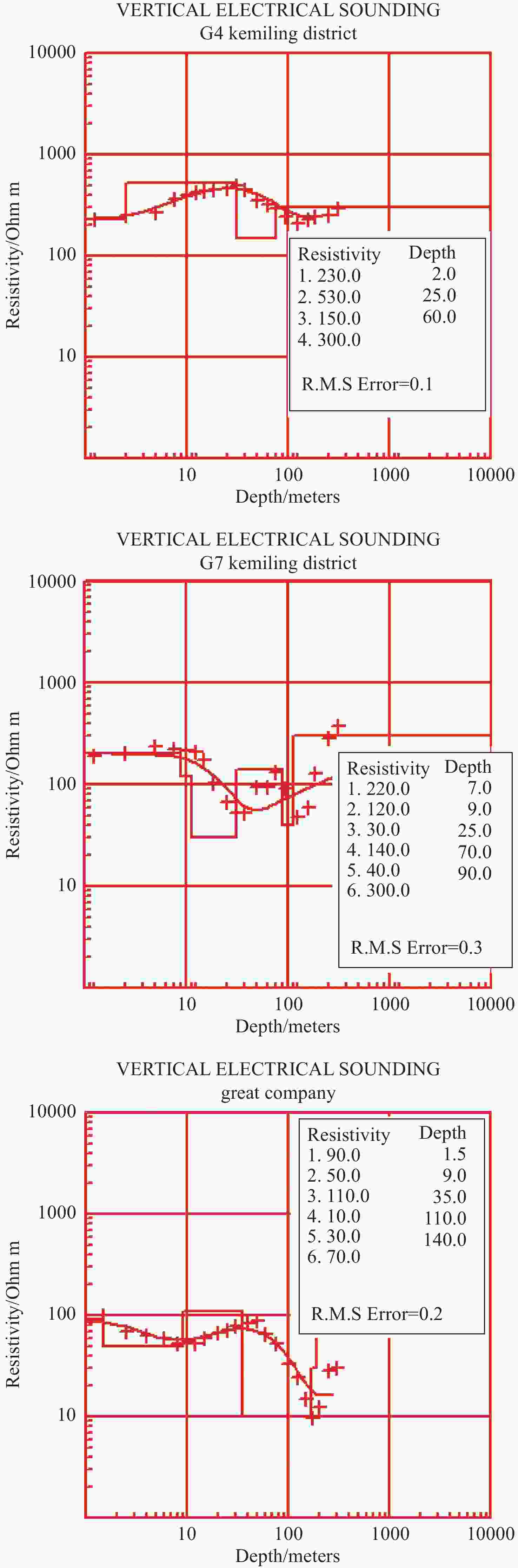
Well Depth/m Geological composition Groundwater presence G4 0-2 Clay and tuff 2-76 Dry andesite G7 0-4 Clay and tuff 4-30 Breccia 30-44 Dry andesite 44-59 Breccia Groundwater presence atdepth of 45-52 m 59-64 Dry andesite 64-77 Breccia Groundwater presence at depth of 69-73 m 77-106 Dry andesite 106-141 Breccia Groundwater presence at depth of 108-139 m 141-180 Dry andesite -
Abdulrazzaq ZT, Al-Ansari N, Aziz NA, et al. 2020. Estimation of main aquifer parameters using geoelectric measurements to select the suitable wells locations in Bahr Al-Najaf depression, Iraq. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 11: 100437. doi: 10.1016/j.gsd.2020.100437 Aizebeokhai AP, Ogungbade O, Oyeyemi KD. 2018. Geoelectrical resistivity data set for characterising crystalline basement aquifers in Basiri, Ado-Ekiti, southwestern Nigeria. Data in Brief, 19: 810-816. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2018.05.091 Ayala C, Bohoyo F, Maestro A, et al. 2016. Updated Bouguer anomalies of the Iberian Peninsula: A new perspective to interpret the regional geology. Journal of Maps, 12(5): 1089-1092. doi: 10.1080/17445647.2015.1126538 Barber AJ. 2000. The origin of the Woyla Terranes in Sumatra and the late Mesozoic evolution of the Sundaland margin. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 18(6): 713-738. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(00)00024-9 Barber AJ, Crow MJ. 2009. Structure of Sumatra and its implications for the tectonic assembly of Southeast Asia and the destruction of Paleotethys. Island Arc, 18(1): 3-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1738.2008.00631.x Bishop MG. 2001. South Sumatra Basin Province, Indonesia: The Lahat/Talang Akar-Cenozoic total petroleum system. USGS Open File Report: 99-50-S22. Bouderbala A, Remini B, Hamoudi AS. 2016. Geoelectrical investigation of saline water intrusion into freshwater aquifers: A case study of Nador coastal aquifer, Tipaza, Algeria. Geofisica Internacional, 55(4): 239-253. doi: 10.19155/geoint.2016.055.4.2 Chandra S, Ahmed S, Ram A, et al. 2008. Estimation of hard rock aquifers hydraulic conductivity from geoelectrical measurements: A theoretical development with field application. Journal of Hydrology, 357(3-4): 218-227. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.05.023 Gómez DD, Bevis M, Pan E, et al. 2017. The Influence of gravity on the displacement field produced by fault slip. Geophysical Research Letters, 44(18): 9321-9329. doi: 10.1002/2017GL074113 Karunianto AJ, Haryanto D, Hikmatullah F, et al. 2017. Penentuan anomali gayaberat regional dan residual menggunakan filter Gaussian Daerah Mamuju Sulawesi Barat. EKSPLORIUM, 38(2): 89. doi: 10.17146/eksplorium.2017.38.2.3921 Khan MR, Bilali SS, Hameed F, et al. 2018. Application of gravity and magnetic methods for the crustal study and delineating associated ores in the western limb of Hazara Kashmir Syntaxis, Northwest Himalayas, Pakistan. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 11: 131. doi: 10.1007/s12517-018-3483-9 Kusumastuty NAE, Manik TK, Timotiwu PB. 2021. Identification of temperature and rainfall pattern in Bandar Lampung and the 2020-2049 projection. IOP Conference Series:Earth and Environmental Science, 739: 012045. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/739/1/012045 Lachassagne P, Dewandel B, Wyns R. 2021. Review: Hydrogeology of weathered crystalline/hard-rock aquifers—guidelines for the operational survey and management of their groundwater resources. Hydrogeology Journal. Madu AJC, Mosto OK. 2016. Bouguer anomaly and free-air anomaly correlation signatures in parts of Benue and Kogi States of Nigeria. International Journal Geology and Mining, 2(1): 30-37. Mangga SA, Amirudin, Suwarti T, et al. 1993. Geological map of Tanjungkarang, Sumatra. Geological Research and Development Centre. Mohamaden MII, Ehab D. 2017. Application of electrical resistivity for groundwater exploration in Wadi Rahaba, Shalateen, Egypt. NRIAG Journal of Astronomy and Geophysics, 6(1): 201-209. doi: 10.1016/j.nrjag.2017.01.001 Montaña J, Candelo J, Duarte O. 2012. Sand’s electrical parameters vary with frequency| Variación de los parámetros eléctricos de la arena con la frecuencia. Ingenieria e Investigacion, 32(2): 34-39. Mulyasari R, Utama HW, Haerudin N. 2019. Geomorphology study on the Bandar Lampung Capital city for recommendation of development area. IOP Conference Series:Earth and Environmental Science, 279(1): 012026. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/279/1/012026 Pandey LMS, Shukla SK, Habibi D. 2015. Electrical resistivity of sandy soil. Géotechnique Letters, 5(3): 178-185. doi: 10.1680/jgele.15.00066 Panjaitan S, Astawa N. 2016. Studi potensi migas dengan metode gayaberat di Lepas Pantai Utara Jakarta. Jurnal Geologi Kelautan, 8(1): 23. doi: 10.32693/jgk.8.1.2010.183 Pubellier M, Morley CK. 2014. The basins of Sundaland (SE Asia): Evolution and boundary conditions. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 58(PB): 555-578. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.11.019 Purnomo J, Koesuma S, Yunianto M. 2016. Pemisahan anomali regional-residual pada metode gravitasi menggunakan metode moving average, polynomial dan inversion. Indonesian Journal of Applied Physics, 3(01): 10. doi: 10.13057/ijap.v3i01.1208 Raghavan B. 2002. The gravity method in groundwater exploration in crystalline rocks : A study in the peninsular granitic region of Hyderabad, India. Hydrogeology Journal, 10: 307-321. doi: 10.1007/s10040-001-0184-2 Rao PV, Subrahmanyam M, Anandagajapathi Raju B. 2021. Groundwater exploration in hard rock terrains of East Godavari district, Andhra Pradesh, India using AHP and WIO analyses together with geoelectrical surveys. AIMS Geosciences, 7(2): 244-267. doi: 10.3934/geosci.2021015 Salapare RC, Dimalanta CB, Ramos NT, et al. 2015. Upper crustal structure beneath the Zambales Ophiolite Complex, Luzon, Philippines inferred from integrated gravity, magnetic and geological data. Geophysical Journal International, 201(3): 1522-1533. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggv094 Subagio S, Patmawidjaya T. 2016. Pola anomali bouguer dan anomali magnet dan kaitannya dengan prospek sumber daya mineral dan energi di Pulau Laut, Pulau Sebuku dan Selat Sebuku, Kalimantan Selatan. Jurnal Geologi Kelautan, 11(3): 115. doi: 10.32693/jgk.11.3.2013.236 Teikeu WA, Njandjock PN, Bisso D, et al. 2012. Hydrogeophysical parameters estimation for aquifer characterisation in hard rock environment: A Case study from Yaounde, Cameroon. Journal of Water Resource and Protection, 04(11): 944-953. doi: 10.4236/jwarp.2012.411110 Varalakshmi V, Venkateswara Rao B, SuriNaidu L, et al. 2021. Groundwater flow modeling of a hard rock aquifer: Case study. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 19(5): 877-886. doi: 10.1061/(asce)he.1943-5584.0000627 Vélez-Nicolás M, García-López S, Ruiz-Ortiz V, et al. 2020. Towards a sustainable and adaptive groundwater management: Lessons from the Benalup Aquifer (Southern Spain). Sustainability (Switzerland), 12(12): 1-28. doi: 10.3390/su12125215 Waswa AK. 2019. Application of electrical resistivity method in mapping underground river channels: A case study of Kabatini area in the Kenyan rift valley. Universal Journal of Geoscience, 7(1): 1-14. doi: 10.13189/ujg.2019.070101 Wyns R, Baltassat JM, Lachassagne P, et al. 2004. Utilisation des sondages de résonance magnétique protonique pour la cartographie de la réserve en eau souterraine en contexte de socle altéré (Bretagne, France). Bulletin de La Societe Geologique de France, 175(1): 21-34. (in French) Xu C, Wang HH, Luo ZC, et al. 2015. Multilayer stress from gravity and its tectonic implications in urban active fault zone: A case study in Shenzhen, South China. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 114: 174-182. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2015.01.017 -

 E-mail alert
E-mail alert Rss
Rss


 下载:
下载: