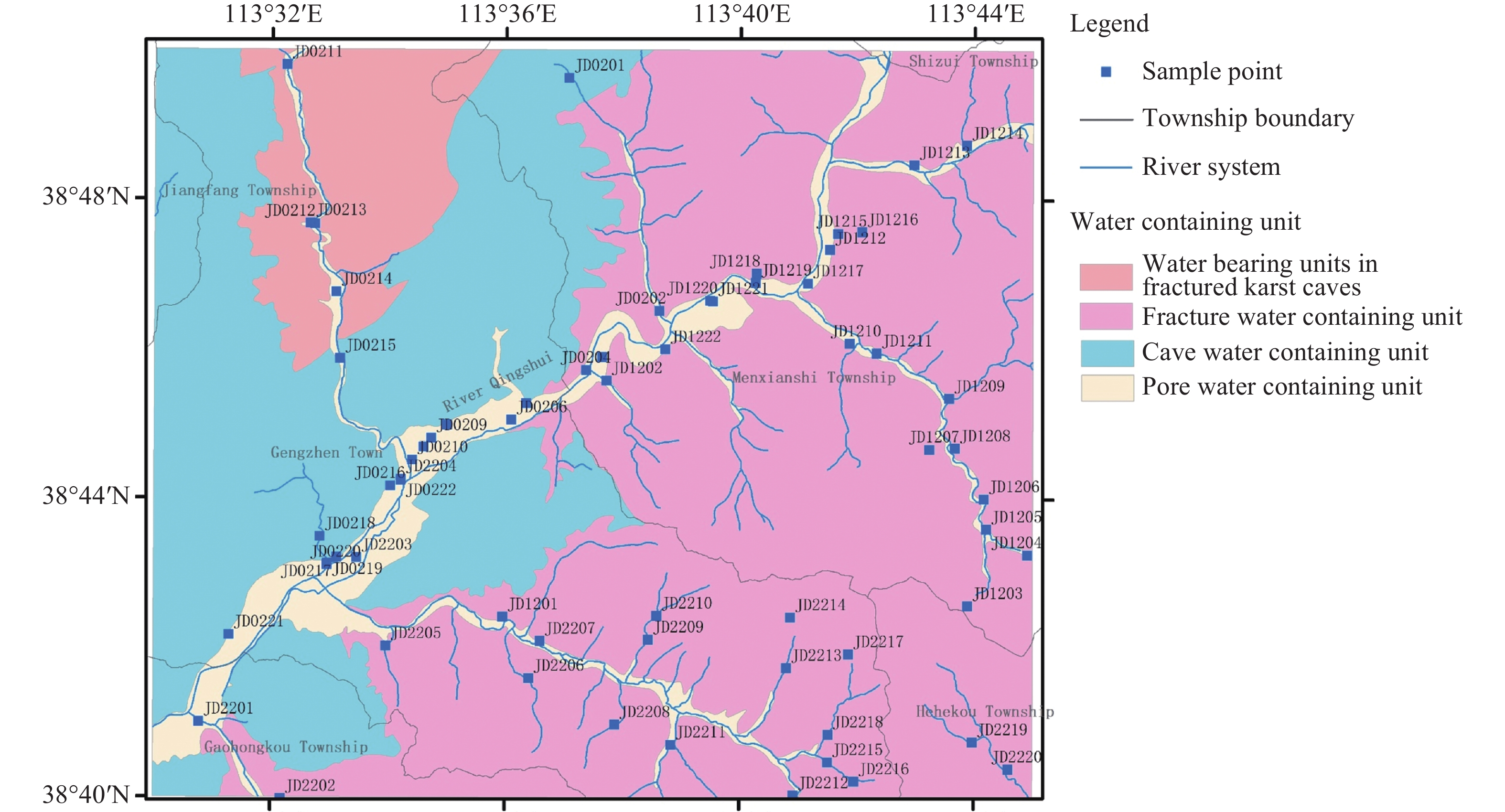
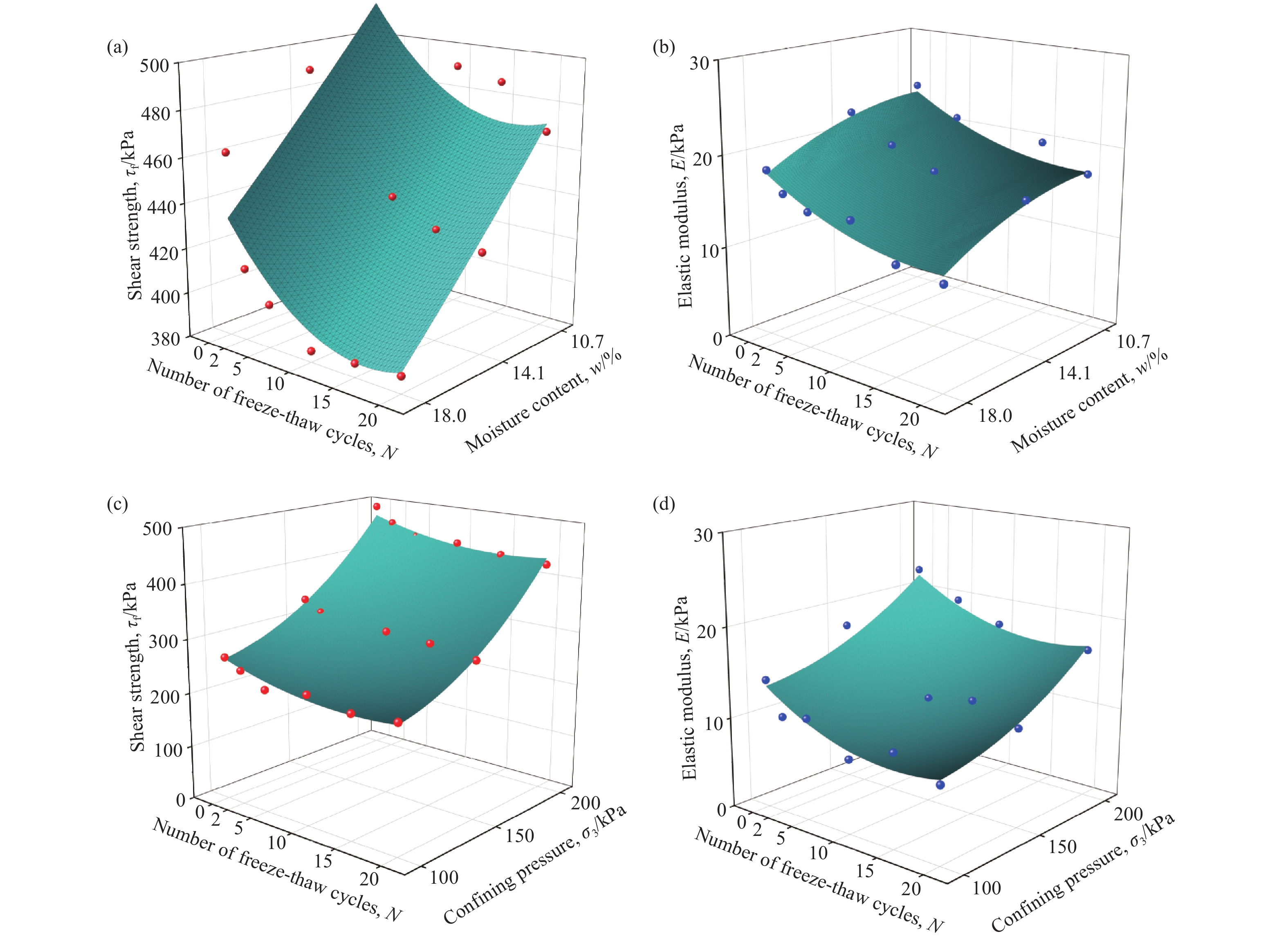
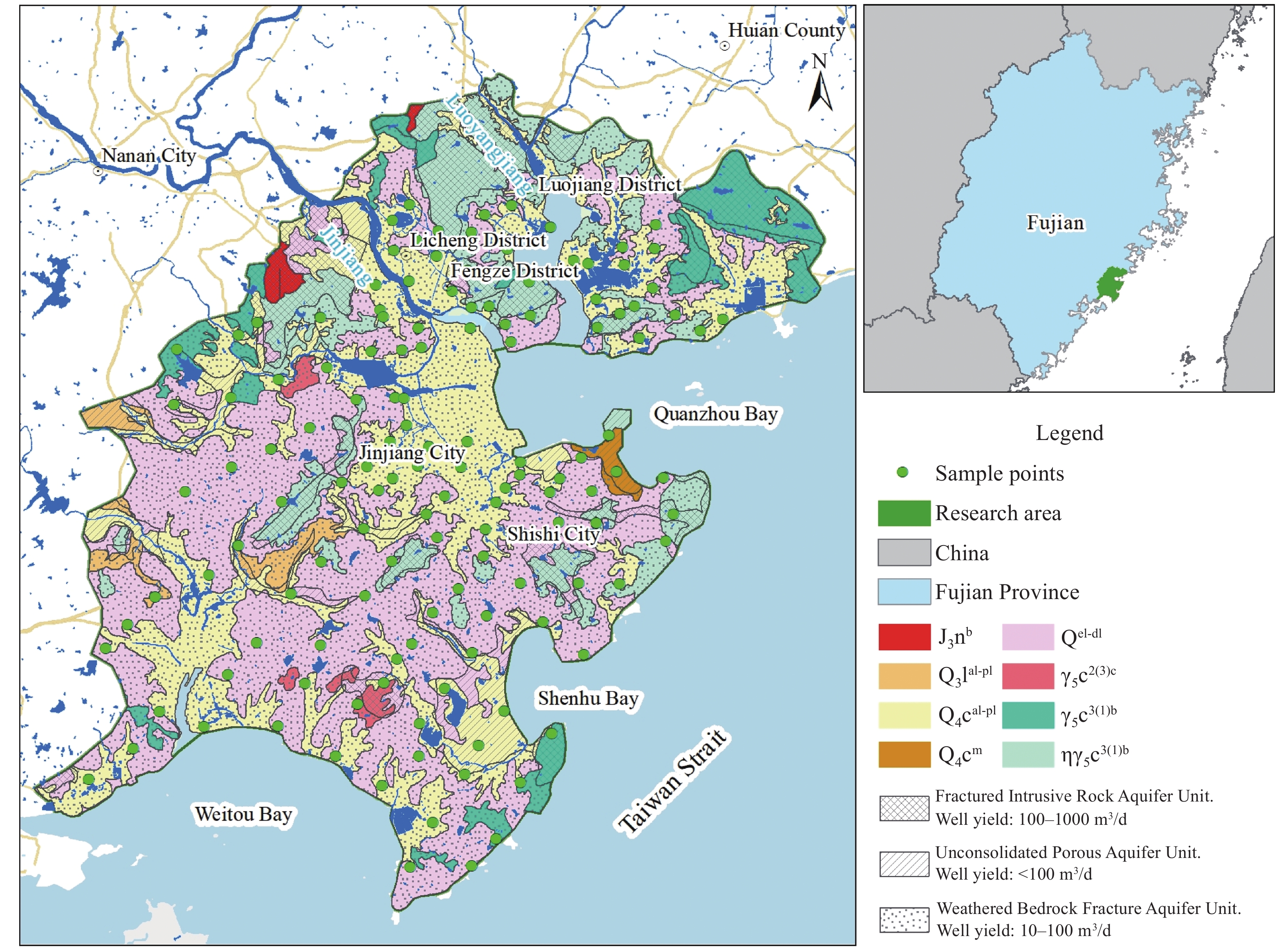
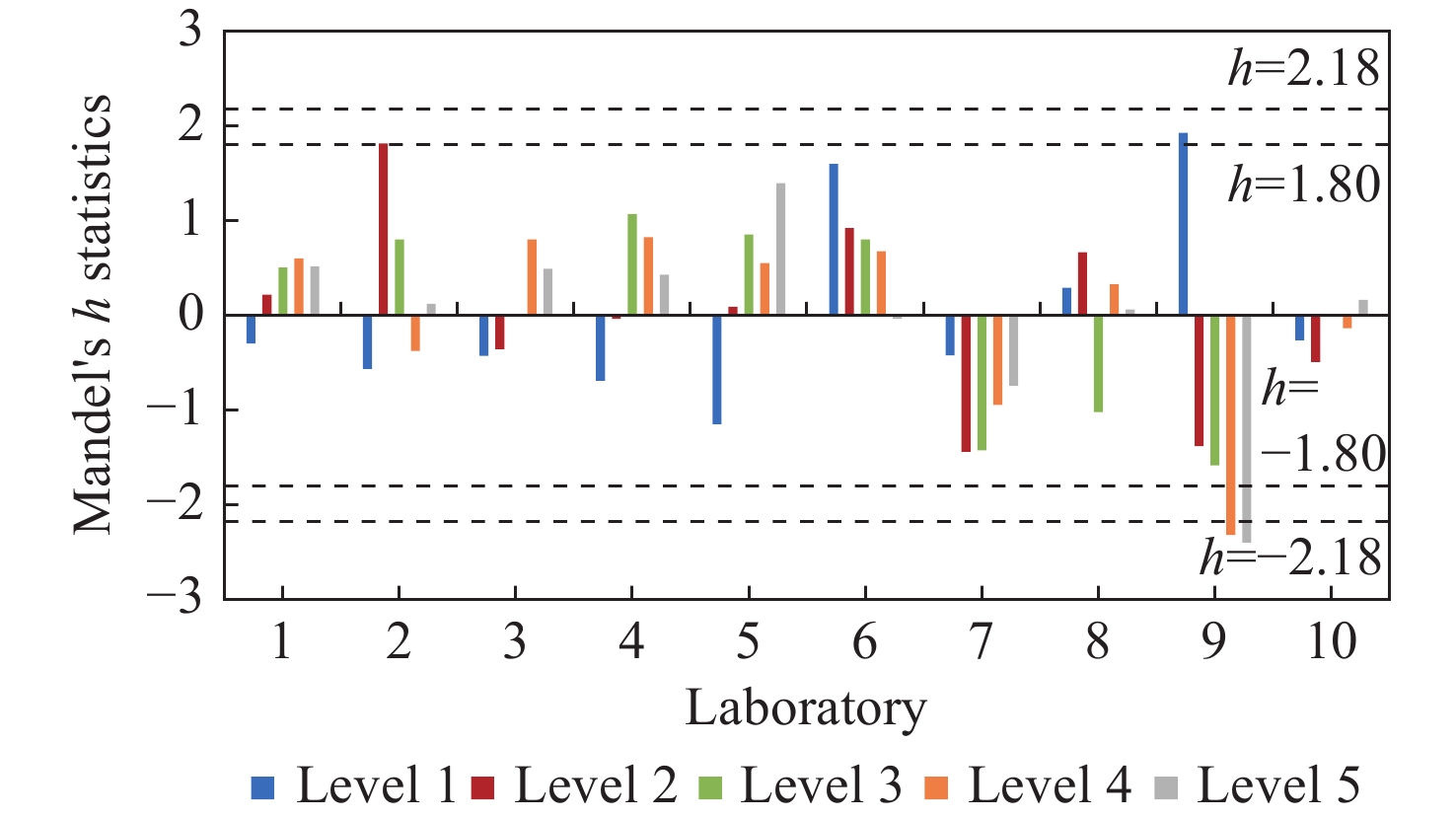
当期目录
2026年 第14卷 第1期
显示方式:
2026,
14(1):
1-14. doi: 10.26599/JGSE.2026.9280067
摘要:
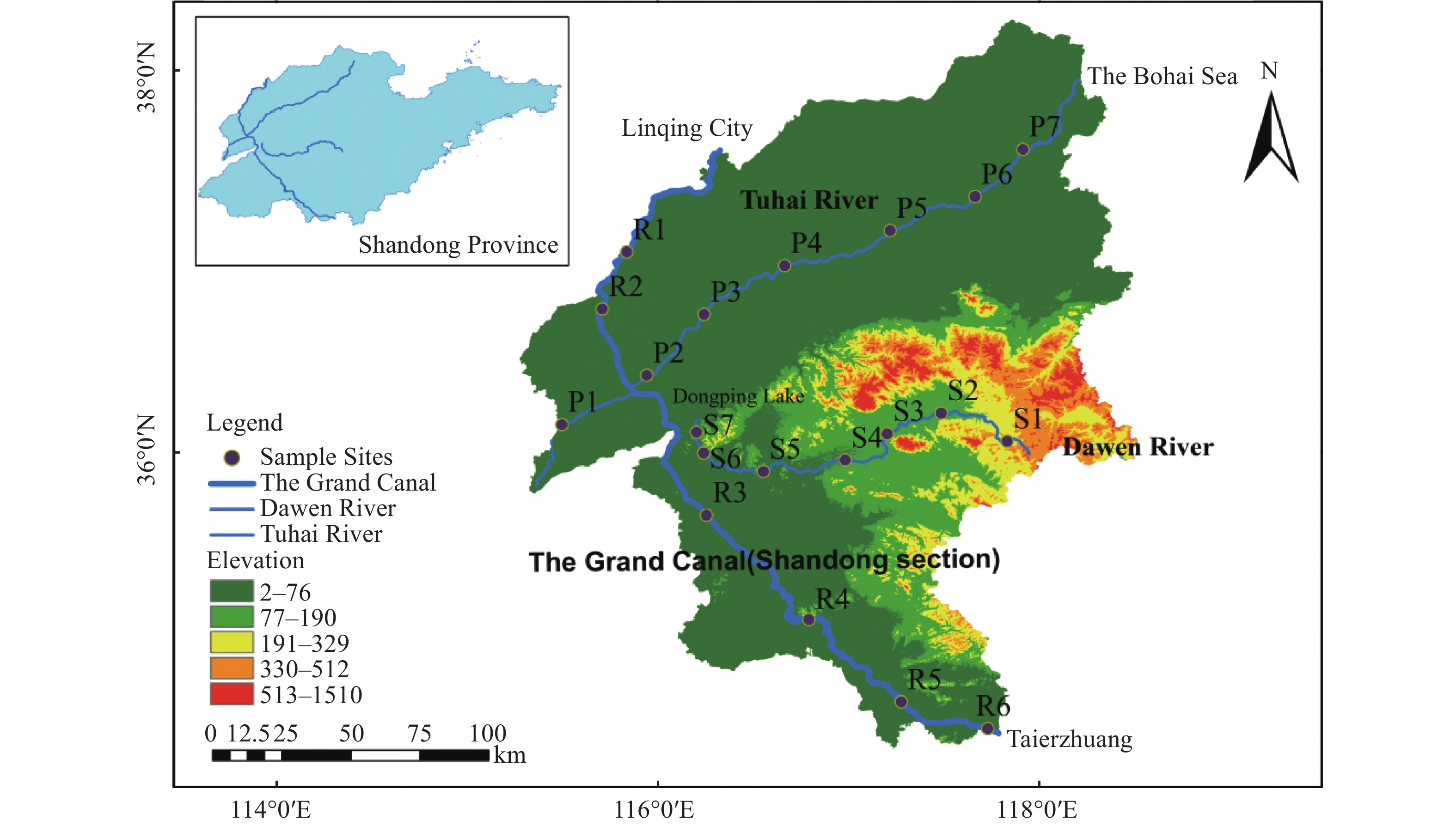
2026,
14(1):
15-31. doi: 10.26599/JGSE.2026.9280068
摘要:
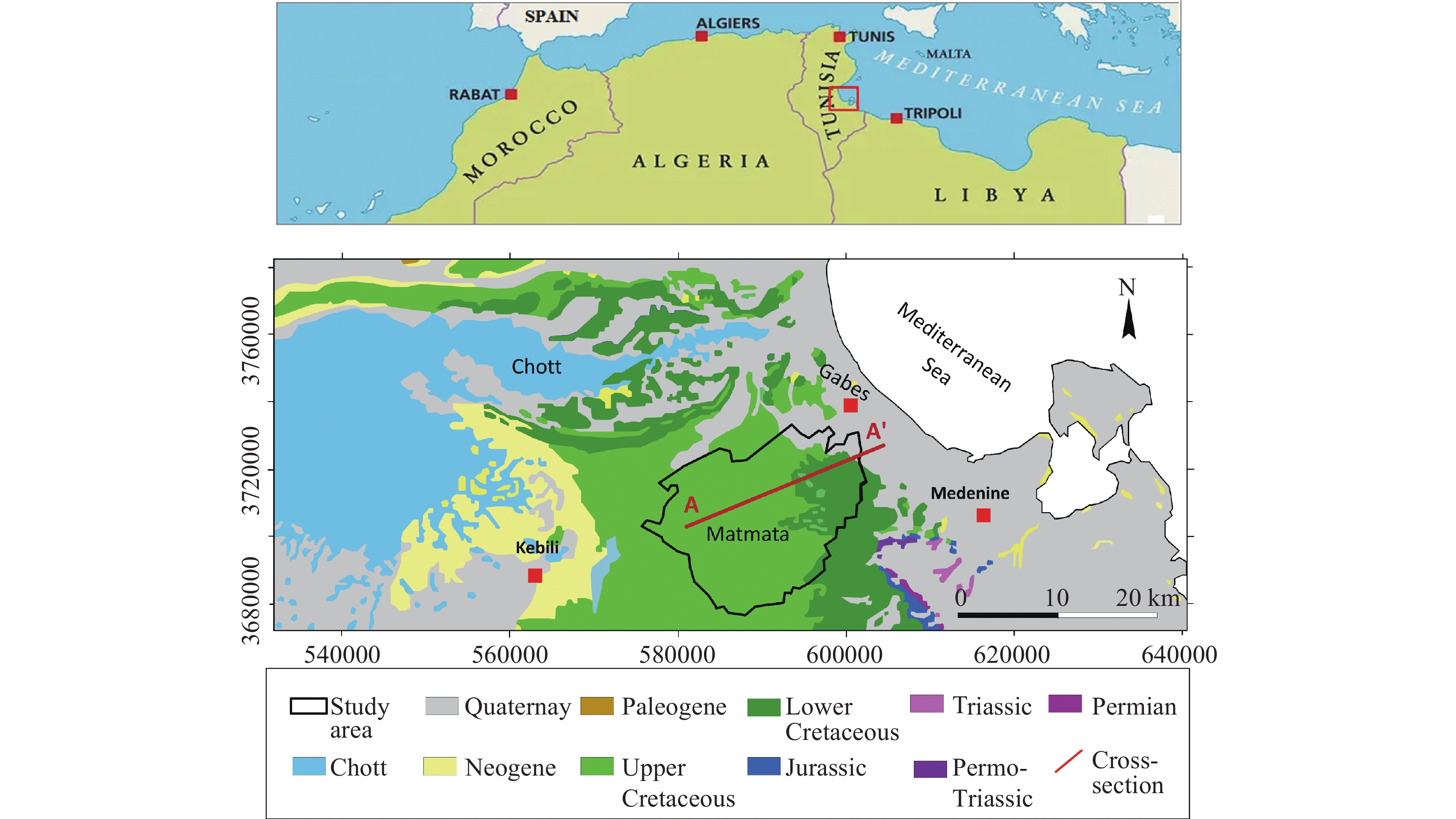
2026,
14(1):
32-48. doi: 10.26599/JGSE.2026.9280069
摘要:
2026,
14(1):
49-58. doi: 10.26599/JGSE.2026.9280071
摘要:
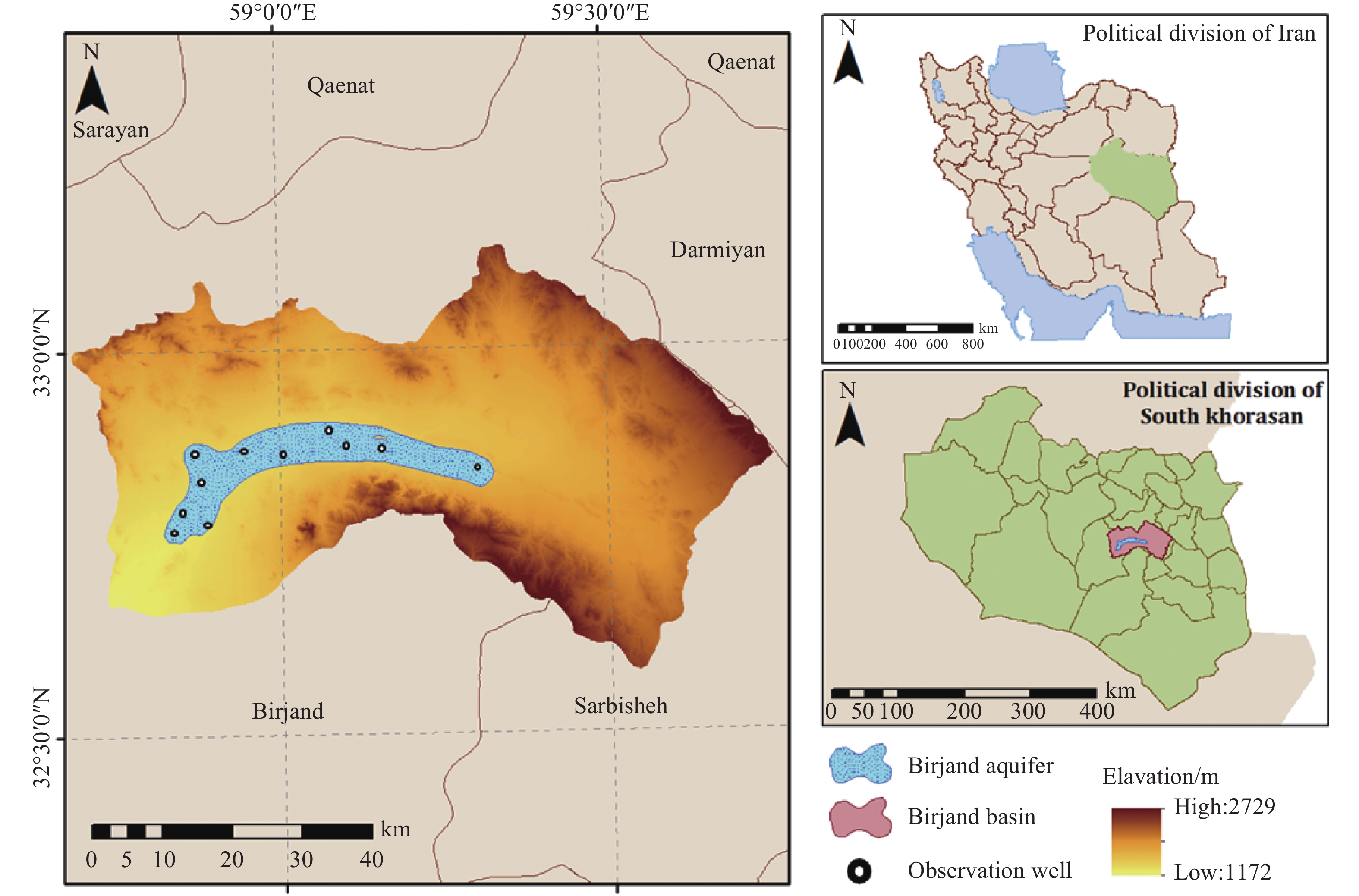
2026,
14(1):
69-82. doi: 10.26599/JGSE.2026.9280073
摘要:
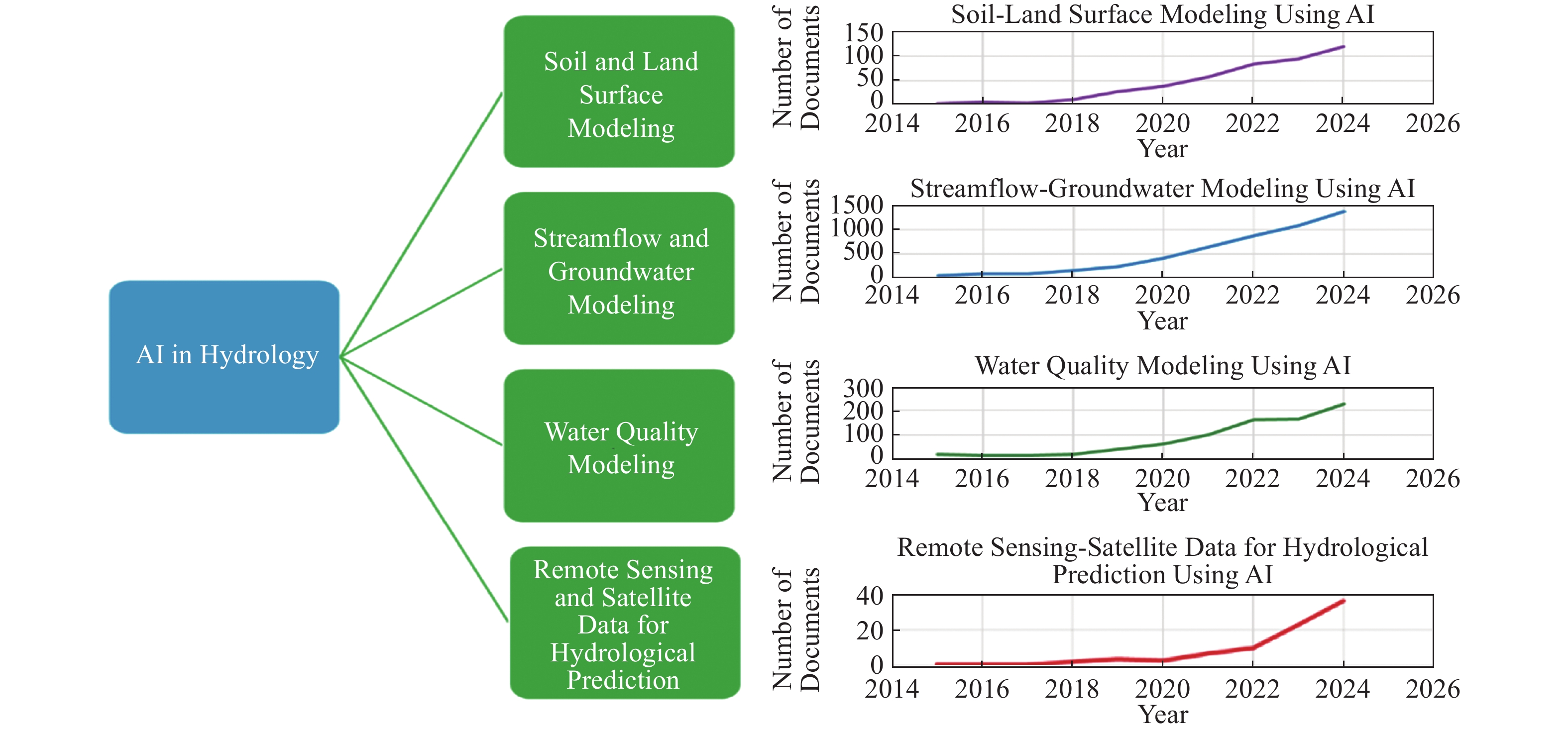
2026,
14(1):
100-122. doi: 10.26599/JGSE.2026.9280059
摘要:
 E-mail alert
E-mail alert Rss
Rss


 作者投稿
作者投稿 专家审稿
专家审稿 编辑办公
编辑办公 主编办公
主编办公 新闻动态
新闻动态 下载中心
下载中心 友情链接
友情链接





