Assessing the potential of underground storage of flood water: A case study from Southern Punjab Region in Pakistan
-
Abstract: An intensively irrigated area in southern part of Punjab Province, Pakistan, has been selected by the Punjab Irrigation Department (PID) to implement a Managed Aquifer Recharge (MAR) project. This project involves diverting floodwater from the Islam Headwork on Sutlej River into the abandoned Mailsi Canal. Utilizing various structures such as depressions, abandoned canals, flood channels, open fields, and deserts for MAR can reduce the flood intensity while recharging aquifer and wetlands. The study area, known for its fertile lands and serving as a food basket for the Punjab Province, is experiencing groundwater depletion at the rate of 0.30 m to 0.70 m per year, significantly increasing pumping costs. This study aims to evaluate the suitability of the sites for the MAR project and assess the storage capacity of the aquifer for floodwater retention. Historical groundwater level data from 25 observation wells across an area of 1,522 km2 were analysed, with the study area divided in to 25 polygons using ArcMap10.6 software. Specific yield method was employed to assess the available storage capacity of the aquifer. Results indicate that the site is suitable for MAR and has the potential to store approximately 1.88 km3 of floodwater as of 2020, thereby reducing flood intensity and enhancing eco-hydrogeological conditions. MAR is identified as a Nature-Based Solution (NBS) for both flood mitigation and groundwater sustainability.
-
Key words:
- Groundwater /
- Managed Aquifer Recharge /
- Indus River Basin /
- Aquifer /
- Vehari /
- Punjab /
- Pakistan
-
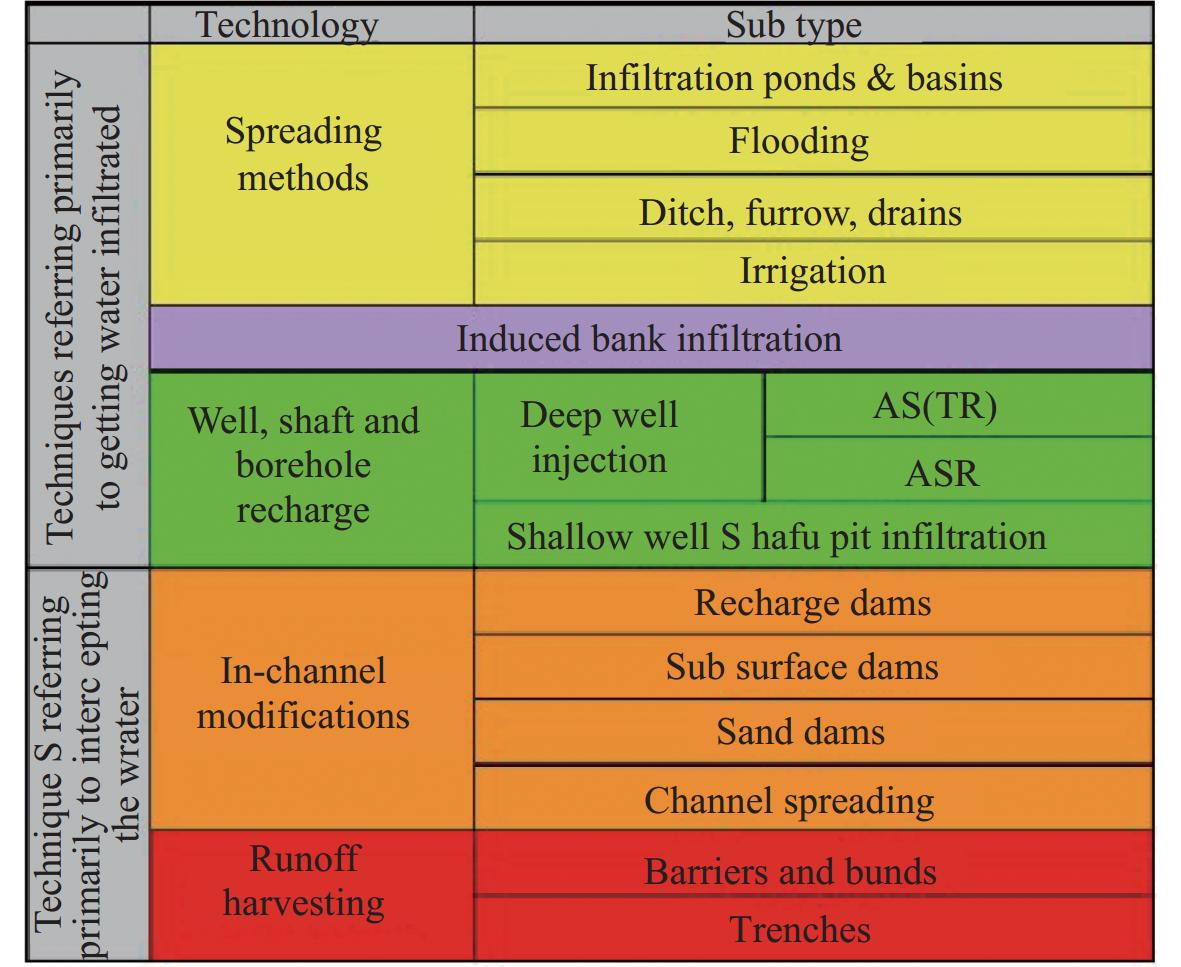
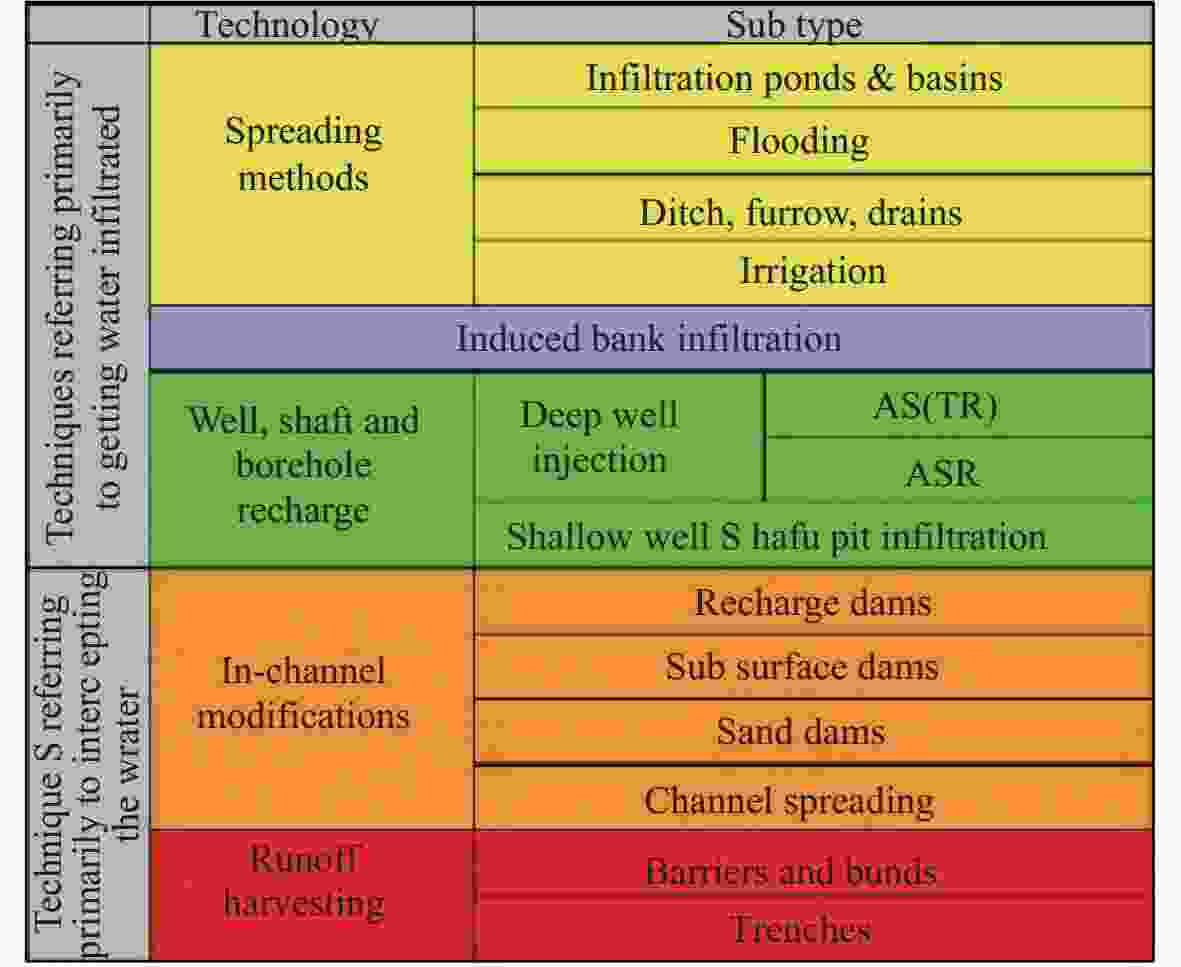
Figure 1. Applications and MAR technology classification (sub-type) (IGRAC, 2014)
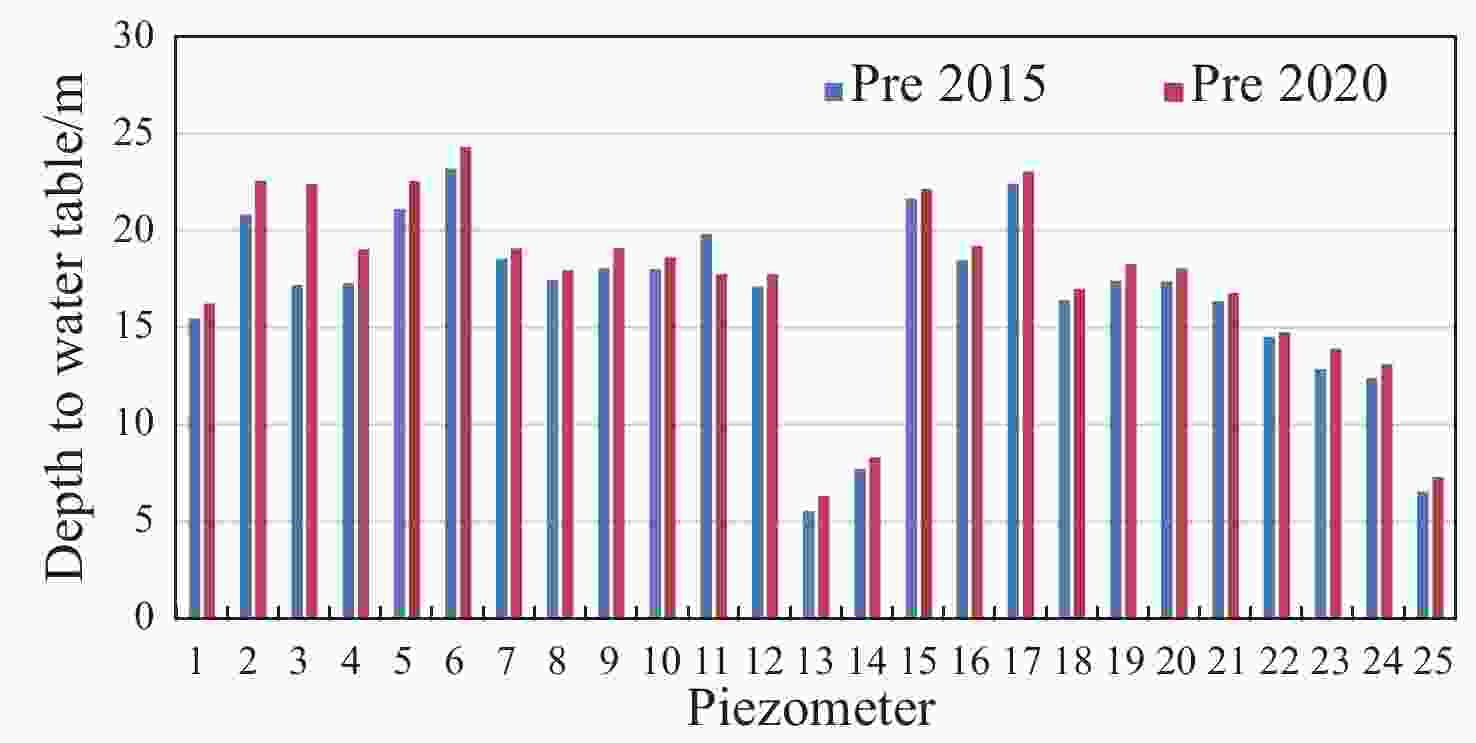
Table 1. Statistics of DTWT below natural land surface from 2015–2020
Parameter *Pre 2015 **Post 2015 Pre 2016 Post 2016 Pre 2017 Post 2017 Pre 2018 Post 2018 Pre 2019 Post 2019 Pre 2020 Post 2020 Max 23.2 22.6 23.8 22.6 23.8 22.7 24.0 22.7 24.1 22.8 24.3 22.8 Min 5.6 6.0 5.6 6.0 5.8 5.9 6.1 6.0 6.2 6.2 6.3 6.2 Avg 16.6 16.4 16.7 16.6 16.8 16.8 17.0 17.0 17.2 17.1 17.4 17.1 STDDEV 4.5 4.3 4.6 4.4 4.5 4.3 4.5 4.3 4.5 4.4 4.6 4.4 Notes: *Pre monsoon; **Post monsoon Table 2. Statistics of DTWL during Post-Monsoon periods from 2015 to 2020
Total Water level Rise/fall in Post monsoon in 5 years (m) Drop/Rise in water level in Post monsoon in per year (m) Max 3.49 0.70 Min −1.49 −0.30 Avg 0.75 0.15 STDDEV 0.97 0.19 Table 3. Statistics of DTWL in Pre-Monsoon periods from 2015 to 2020
Total Water level Rise/fall in Pre monsoon in 5 years (m) Drop/Rise in water level in Pre monsoon in per year (m) Max 2.08 0.42 Min −5.16 −1.03 Avg. −0.87 −0.17 STDDEV 1.13 0.23 Table 4. GWRP for the period of pre-2015 to pre-2020 at different locations in the study area
Parameter Area of polygon
(km2)Natural Surface Level
(NSL) (m-amsl)GWRP (BCM) Pre-2020 Pre-2019 Pre-2018 Pre-2017 Pre-2016 Pre-2015 Total 1522 1.88 1.85 1.82 1.79 1.78 1.76 Max 111.83 148 0.186 0.185 0.184 0.183 0.182 0.181 Min 18.69 134 0.003 0.002 0.001 0.000 −0.001 −0.002 Avg 55.88 139 0.075 0.074 0.073 0.072 0.071 0.070 STD 26.66 4 0.047 0.047 0.046 0.046 0.045 0.045 Table 5. GWRP for the period of post-2015 to post-2020
Parameter Area of polygon
(km2)Natural Surface Level
(NSL) (m-amsl)GWRP (BCM) Post-2020 Post-2019 Post-2018 Post-2017 Post-2016 Post-2015 Total 1522 1.87 1.85 1.83 1.80 1.77 1.74 Max 111.83 148 0.176 0.175 0.174 0.173 0.172 0.172 Min 18.69 134 0.000 −0.001 −0.001 −0.001 −0.002 −0.004 Avg 55.88 139 0.075 0.074 0.073 0.072 0.071 0.069 STD 26.66 4 0.047 0.047 0.046 0.046 0.045 0.044 -
Abid M, Scheffran J, Schneider UA, et al. 2019. Farmer perceptions of climate change, observed trends and adaptation of agriculture in Pakistan. Environmental Manage, 63(1): 110−123. DOI: 10.1007/s00267-018-1113-7. ADB. 2018. Pakistan: Punjab irrigated agriculture investment program: Completion Report, Project Number: 37231-013, Asian Development Bank. APHA. 2021. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water 23rd Ed: American Public Health Association (APHA). Bennett GD, Ata-Ur-Rehman Sheikh IA, Ali S. 1967. Analysis of aquifer tests in the Punjab Region of West Pakistan: Geological survey water-supply paper 1608-G, USGS, United States Government Printing Office, Washington DC. Chinnasamy P, Muthuwatta L, Eriyagama N, et al. 2017. Modeling the potential for floodwater recharge to offset groundwater depletion: A case study from the Ramganga basin, India. Sustainable Water Resources Management, 4(2): 331−344. DOI: 10.1007/s40899-017-0168-6. Dillon P. 2005. Future management of aquifer recharge. Hydrogeology Journal, 13(1): 313−316. DOI: 10.1007/s10040-004-0413-6. Dillon P. 2009. Water recycling via managed aquifer recharge in Australia. Boletín Geológico y Minero, 120(2): 121−130. Dillon PJ. (Ed.). 2020. Management of aquifer recharge for sustainability: Summary of the 4th International Symposium on Artificial Recharge of Groundwater, Adelaide, September 2002. CRC Press. Gale I, Macdonald D, Calow R, et al. 2006. Managed aquifer recharge: An assessment of its role and effectiveness in watershed management: Final report for DFID KAR project R8169, Augmenting groundwater resources by artificial recharge: AGRAR. Gale I, Neumann I, Calow R, et al. 2002. The effectiveness of artificial recharge of groundwater: A review. British Geological Survey Commercial Report CR/02/108N. GOP. 2018. Pakistan Bureau of Statistics, Government of Pakista. Greenman DW, Swarzenski WV, Bennett GD. 1967. Ground-water hydrology of Punjab-West Pakistan with emphasis on Problems caused by canal irrigation: Geological survey water-supply paper 1608-H, USGS, USAID, Washigton DC. Hasan MB, Driessen PP, Majumder S, et al. 2019. Factors affecting consumption of water from a newly introduced safe drinking water system: The case of managed aquifer recharge (MAR) systems in Bangladesh. Water, 11(12): 2459. DOI: 10.3390/w11122459. Hassan GZ, Bhutta MN. 1996. A water balance model to estimate groundwater recharge in Rechna doab, Pakistan. Irrigation and Drainage Systems, 10: 297−317. DOI: 10.1007/BF01104895. Hassan GZ, Hassan FR, Shabbir G. 2019. Impact of climate change on groundwater use for sustainable agriculture and food production in Indus Basin of Pakistan. Paper presented at the 1st International Conference on Sustainable Agriculture: Food Security under Changing Climate Scenarios: April, 3-5, 2019, Ghazi University, Dera Ghazi Khan, Punjab, Pakistan. IAH-MAR. 2018. International Association of Hydrogeologists Commission on Managing Aquifer Recharge. IGRAC. 2014. IGRAC MAR Portal International Groundwater Resources Assessment Centre. Imran M, Ali A, Ashfaq M, et al. 2018. Impact of Climate Smart Agriculture (CSA) practices on cotton production and livelihood of farmers in Punjab, Pakistan. Sustainability, 10(6): 2101. DOI: 10.3390/su10062101. IRI. 2019. Recharge of aquifer for groundwater management in Punjab (2016-2019): Report No IRR-GWMC/121, Groundwater Management Cell, Irrigation Reserach Institute (IRI), Irrigation Department, Lahore, Pakistan. IWASRI. 1995. Performance evaluation of different types of canal lining in FESS, Pakistan: Interim report of surface water section of the International Waterlogging and Salinity Research Institute (IWASRI), Lahore, Pakistan. Khalid S, Shahid M, Natasha Shah AH, et al. 2020. Heavy metal contamination and exposure risk assessment via drinking groundwater in Vehari, Pakistan. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(32): 39852−39864. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-020-10106-6. Konikow LF, Kendy E. 2005. Groundwater depletion: A global problem. Hydrogeology Journal, 13(1): 317–320. DOI: 10.1007/s10040-004-0411-8. Kuang X, Liu J, Scanlon BR, et al. 2024. The changing nature of groundwater in the global water cycle. Science, 383(6686): eadf0630. DOI: 10.1126/science.adf0630. Maréchal JC, Dewandel B, Ahmed S, et al. 2006. Combined estimation of specific yield and natural recharge in a semi-arid groundwater basin with irrigated agriculture. Journal of Hydrology, 329(1-2): 281−293. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.02.022. Missimer TM, Guo W, Maliva RG, et al. 2015. Enhancement of wadi recharge using dams coupled with aquifer storage and recovery wells. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73(12): 7723−7731. DOI: 10.1007/s12665-014-3410-7. Pakparvar M, Walraevens K, Cheraghi SA, et al. 2016. Assessment of groundwater recharge influenced by floodwater spreading: An integrated approach with limited accessible data. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 1–18. DOI: 10.1080/02626667.2016.1183164. Papa F, Frappart F. 2021. Surface water storage in rivers and wetlands derived from satellite observations: A review of current advances and future opportunities for hydrological sciences. Remote Sensing, 13(20): 4162. DOI: 10.3390/rs13204162. Pérez-Uresti SI, Ponce-Ortega JM, Jiménez-Gutiérrez A. 2019. A multi-objective optimization approach for sustainable water management for places with over-exploited water resources. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 121: 158−173. DOI: 10.1016/j.compchemeng.2018.10.003. Qureshi AS, McCornick PG, Qadir M, et al. 2008. Managing salinity and waterlogging in the Indus Basin of Pakistan. Agricultural Water Management, 95(1): 1−10. DOI: 10.1016/j.agwat.2007.09.014. Qureshi RH, Ashraf M. 2019. Water security issues of agriculture in Pakistan. Pakistan Academy of Sciences (PAS), Islamabad, Pakistan, 1: 41. Ross A. 2018. Speeding the transition towards integrated groundwater and surface water management in Australia. Journal of Hydrology, 567: e1−e10. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.01.037. Ross A, Hasnain S. 2018. Factors affecting the cost of Managed Aquifer Recharge (MAR) schemes. Sustainable Water Resources Management, 4(2): 179−190. DOI: 10.1007/s40899-017-0210-8. Sherif M, Sefelnasr A, Al Rashed M, et al. 2023. A review of managed aquifer recharge potential in the Middle East and North Africa Region with examples from the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates. Water, 15(4): 742. DOI: 10.3390/w15040742. Shiklomanov IA. 2000. Appraisal and assessment of world water resources. Water International, 25(1): 11−32. DOI: 10.1080/02508060008686794. Siddiqi A, Wescoat JL. 2013. Energy use in large-scale irrigated agriculture in the Punjab province of Pakistan. Water International, 38(5): 571−586. DOI: 10.1080/02508060.2013.828671. Sindhu AS. 2010. District Vehari: Hazard, vulnerability and development profile: Rural Development Policy Institute (RDPI), Islamabad, Pakistan. Sloan S, Cook PG, Wallis I. 2023. Managed Aquifer Recharge in Mining: A Review. Groundwater, 61(3): 305−317. DOI: 10.1111/gwat.13311. USGS. 1967. Groundwater hydrology of the Punjab–West Pakistan with emphasis on problem caused by canal irrigation. US Government Printing Office Washington DC: 20402. WB. 2017. Climate-Smart Agriculture in Pakistan. CSA Country Profiles for Asia Series. International Center for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT), The World Bank. Washington DC: 28. Wisser D, Frolking S, Hagen S, et al. 2013. Beyond peak reservoir storage? A global estimate of declining water storage capacity in large reservoirs. Water Resources Research, 49(9): 5732−5739. DOI: 10.1002/wrcr.20452. Zakir-Hassan G. 2023. Improving sustainable groundwater management: A case study of managed aquifer recharge in Punjab Pakistan. PhD thesis, School of Agricultural, Environmental, and Veterinary Sciences, Charles Sturt University, Australia. Zakir-Hassan G, Akhtar S, Shabir G, et al. 2023. Water budget study for groundwater recharge in Indus River Basin, Punjab (Pakistan). H2Open Journal, 6(3): 449−462. DOI: 10.2166/h2oj.2023.027. Zakir-Hassan G, Hassan FR, Shabir G, et al. 2021. Impact of floods on groundwater—A case study of Chaj Doab in Indus Basin of Pakistan. International Journal of Food Science and Agriculture, 5(4): 639−653. DOI: 10.26855/ijfsa.2021.12.011. Zhongming Z, Linong L, Xiaona Y, et al. 2014. United Nations World Water Development Report 2014: Water and Energy, 1. -

 E-mail alert
E-mail alert Rss
Rss


 下载:
下载: