Experimental simulation and dynamic model analysis of Cadmium (Cd) release in soil affected by rainfall leaching in a coal-mining area
-
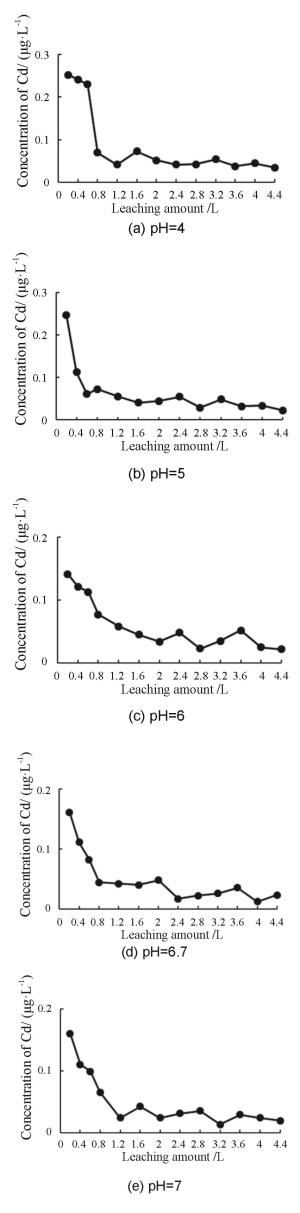
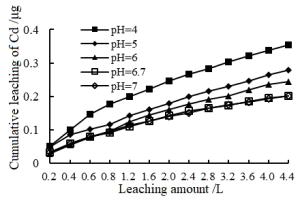
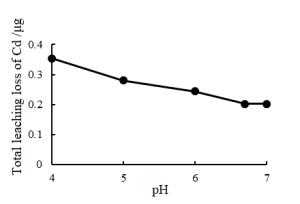
Abstract: In order to explore the influence of rainfall on the release of heavy metal Cadmium (Cd) in soil in a coal-mining area,soil column leaching experiments were carried out by simulating 3 types of rainfall (acid rain,normal rainfall,and actual rainfall) with 5 different pH values (4,5,6,6.7,7),and 65 groups of data about leachate pH value and Cd concentration were obtained respectively. The results indicate the general change rule of Cd concentration in leachate: (1) the easiness of Cd release is negatively correlated to the pH value of leaching solution and positively correlated the leaching amount; (2) leaching solution with lower pH values shows more obvious release stages. Leached by solution with different pH values,the release of Cd in soil ranks as follows: Acid rain group > normal rainfall group > actual rainfall group. In the first stage,the acidity of rainfall has a significant impact on the release of Cd in soil,but in the second stage,the release of Cd is alleviated due to the soil buffering. Among the four dynamic equations to simulate the release of Cd in soil,the modified Elovich equation can describe the process most accurately,with the highest coefficient of determination R2 of 0.997 5. These results can serve as a reference for further study on the migration,transformation and enrichment of Cd in soil.
-
Key words:
- Rainfall /
- pH value /
- Soil /
- Cd /
- Dynamic equation
-
Table 1. Kinetic fitted results of Cd release in soil under simulated rainfall conditions
Subject First-order kinetics equation y=ax+b Parabolic equation y=a+bx+cx2 Double constant rate equation y=axb Modified Elovich equation y=a-b*ln(x+c) pH a b R2 a b c R2 a b R2 a b c R2 4 0.062 9 0.099 5 0.925 1 0.061 4 0.118 6 -0.012 5 0.970 5 0.174 5 0.480 5 0.983 7 0.160 7 -0.118 4 0.210 2 0.992 0 5 0.050 2 0.069 7 0.974 8 0.052 0 0.076 0 -0.005 8 0.990 9 0.127 9 0.517 3 0.997 3 -0.040 1 -0.175 6 1.572 0 0.994 6 6 0.048 1 0.049 8 0.956 8 0.025 5 0.083 6 -0.008 0 0.989 5 0.105 2 0.579 0 0.993 6 0.042 1 -0.121 5 0.713 1 0.997 4 6.7 0.037 1 0.054 7 0.943 4 0.032 8 0.069 1 -0.007 2 0.987 4 0.098 5 0.498 4 0.993 4 0.070 1 -0.082 2 0.457 0 0.997 5 7 0.036 2 0.056 4 0.936 8 0.034 8 0.067 6 -0.007 1 0.981 1 0.099 4 0.485 1 0.990 9 0.081 2 -0.074 5 0.338 0 0.996 0 Note: X is the leaching amount, L; Y is the cumulative leaching loss of Cd, μg. Table 2. Mathematical statistics of pH value of leachate
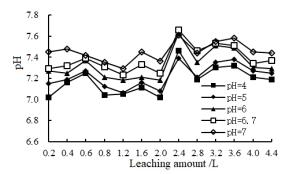
Soil column Number Maximum pH Minimum pH Average pH Standard deviation Mean square deviation Coefficient of variation (%) pH=4 13 7.46 7.02 7.18 0.128 0.133 1.78 pH=5 13 7.39 7.06 7.22 0.105 0.109 1.45 pH=6 13 7.63 7.18 7.33 0.135 0.140 1.84 pH=6.7 13 7.66 7.23 7.38 0.119 0.124 1.61 pH=7 13 7.61 7.29 7.45 0.087 0.090 1.17 Results 65 7.66 7.02 7.31 0.154 0.155 2.11 -
CAO Yan-ling, SONG Liang, LIU Lian, et al. 2020. Preliminary study on strontium-rich characteristics of shallow groundwater in Dingtao Area, China. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 8(03): 244-258. doi: 10.19637/j.cnki.2305-7068.2020.03.005 Doabi SA, Karami M, Afyuni M, et al. 2018. Pollution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soil, atmospheric dust and major food crops in Kermanshah province, Iran. Ecotoxicology and Environ-mental Safety, 163: 153-164. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.07.057 HUANG Yi. 2007. Study on cadmium release and solid-liquid equilibrium in soil under acid rain conditions in Chengdu City. Ph. D. thesis, Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology. (in Chinese) HUANG Yi, Ni Shi-jun, Zeng Ying, et al. 2007. Effects of acid rain leaching on release of cad-mium in surface soil in Chengdu City. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), (05): 596-598. (in Chinese). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG200705019.htm Joseph P, James R, Sarah M, et al. 2019. Arsenic variability and groundwater age in three water supply wells in southeast New Hampshire. Geoscience Frontiers, 10(05): 1669-1683. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2019.01.002 LEI Liang-qi. 2019. Study on release mechanism of heavy metals in carbonate tailings during buffer period-column leaching experiment. Journal of Petrology and Mineralogy, 38(01): 131-142. (in Chinese) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-YSKW201901014.htm LI Hong-ling. 2006. Effects of acid rain on activa-tion of Cd, Hg, Pb and their vegetation effects in purple soil. M. _S. thesis, Chongqing: South-west University. (in Chinese) LIU Chun-yang, ZHANG Yu-feng, TENG Jie. 2006. Research progress of heavy metal pollution in soil. Pollution Control Technology, 14(4): 42-45. (in Chinese) LIU Jia-li, WANG Zu-wei, ZHANG Hui. 2010. Effects of simulated rainfall on leaching and transformation of cadmium in alkaline salinized soil. Journal of Ecology and Environ-ment, 19(08): 1974-1978. (in Chinese) http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000039847774110_2fb0.html LIU Jian-gen. 2019. Current situation and control strategy of soil heavy metal pollution in China. Resources Conservation and Environ-mental Protection, (04): 145. (in Chinese) LUO Ying. 2016. Dynamic simulation of effects of acid rain on characteristics of Cr (Ⅵ), Cu and Cd release in soil. M. _S. thesis, Wuhan: Wuhan Textile University. (in Chinese). Papale M, Conte A, Del Core M, et al. 2018. Heavy-metal resistant microorganisms in sediments from submarine canyons and the adjacent continental slope in the northeastern Ligurian margin (Western Mediterranean Sea). Progress in Oceanography, 168: 155-168. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2018.09.015 RAN Jian-ping. 2013. Analysis on the current situation, hazards and treatments of soil pollution in China. China Agricultural Infor-mation, 15: 180. (in Chinese) Saleem M, Iqbal J, Akhter G, et al. 2018. Fractiona-tion, bioavailability, contamination and environ-mental risk of heavy metals in the sediments from a freshwater reservoir, Pakistan. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 184: 199-208. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.11.002 SU Guang-ming, HU Gong-ren, MAO Ping-ping, et al. 2013. Accumulative release character-istics of heavy metals from surface soil in Quanzhou traffic area under simulated acid rain conditions. Earth and Environment, 41(05): 512-517. (in Chinese) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201305007.htm WANG Xing-wen. 1993. Study on the factors affecting precipitation acidity in China. China Environmental Science, 13(6): 401-407. (in Chinese) YANG Ben-hong. 2000. Hazards and prevention measures of acid rain in China. Journal of Hefei Union University, 10(2): 102-106. (in Chinese). ZHANG Ji-zhou, WANG Hong-tao, NI Hong-wei, et al. 2012. Current situation, causes and diagnostic methods of heavy metal pollution in farmland soil in China. Soil and Crops, 1(04): 212-218. (in Chinese) ZHANG Li-hua, ZHU Zhi-liang, ZHENG Cheng-song, et al. 2008. Leaching process of simulated acid rain on heavy metal con-taminated soil in Sanming area. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, (01): 151-155. (in Chinese) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH200801028.htm ZHENG Tian. 2012. Analysis of influencing factors and control measures of acid rain in Leshan city. M. _S. thesis, Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University. (in Chinese) ZHOU Jian-jun, ZHOU Ju, FENG Ren-guo. 2014. Current situation and control strategy of soil heavy metal pollution in China. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 29(03): 315-320, 350, 272. (in Chinese) ZHOU Yong-zhang, Song Shu-qiao. 2005. Environ-mental geochemical response of soil along river to upstream mines and mining. Geological Bulletin of China, 24(10): 945-951. (in Chinese) -

 E-mail alert
E-mail alert Rss
Rss


 下载:
下载: